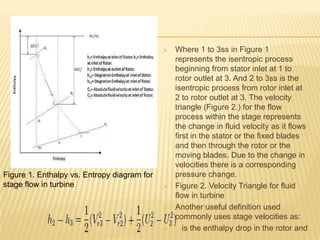
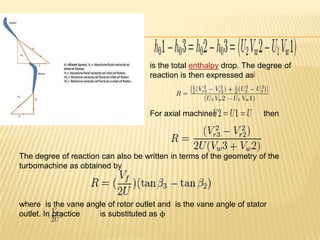
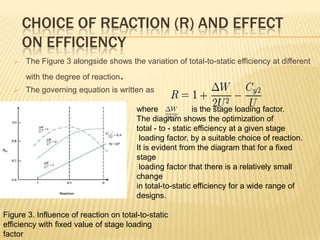
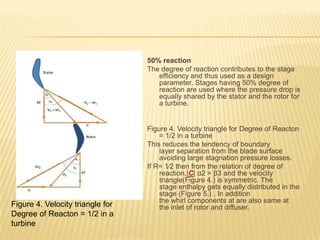
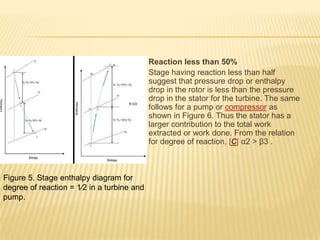
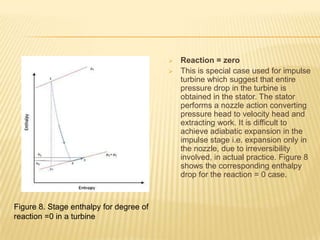
The document discusses degree of reaction, which is defined as the ratio of static pressure or enthalpy drop in the rotor to the total static pressure or enthalpy drop in a turbine stage. Degree of reaction is an important design parameter that affects efficiency. Reactions of 50%, less than 50%, and more than 50% are discussed. A reaction of 50% equally distributes the pressure drop between the rotor and stator, avoiding boundary layer separation. Reactions less than 50% mean more pressure drop occurs in the stator, while reactions over 50% mean more pressure drop occurs in the rotor. A reaction of 0% corresponds to an impulse turbine with all pressure drop in the stator. Charts show how reaction affects