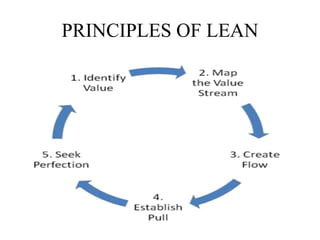
This document discusses Lean Manufacturing. It defines Lean Manufacturing as a systematic approach to identifying and eliminating waste through continuous improvement. The principles of Lean Manufacturing include specifying value from the customer perspective, identifying all value-creating steps, making those steps flow smoothly, and allowing customers to pull value. Lean focuses on eliminating waste and being responsive to customer needs. It allows for lower production costs and faster delivery compared to traditional manufacturing approaches. While Lean reduces costs, initial implementation can be expensive and requires expertise. Overall, Lean aims to maximize value for the customer.