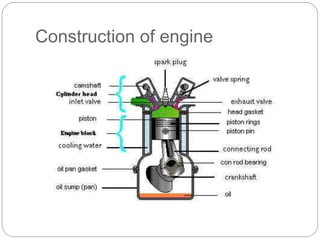
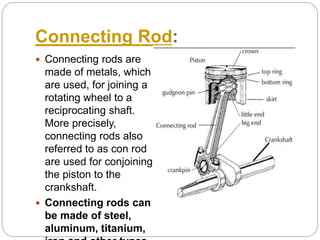
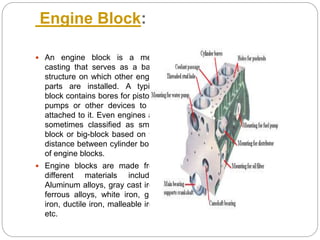
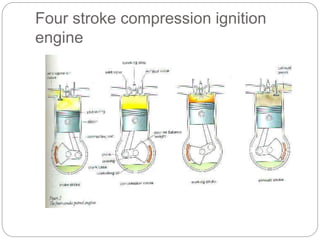
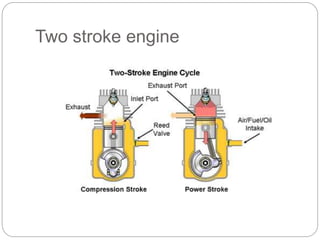
This document discusses the key components of internal combustion engines and their functions. It describes the purpose and typical materials used for major engine parts like the camshaft, crankshaft, connecting rods, crankcase, cylinder head, engine block, pistons, valves, and push rods. It also provides brief explanations of engine types (e.g. 4-stroke spark ignition, 4-stroke compression ignition), engine terminology, and comparisons of 4-stroke vs 2-stroke engines. The goal is to explain engine construction and operation at a high level.