Embed presentation
Download to read offline




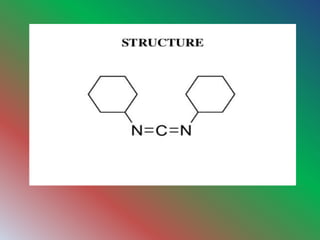





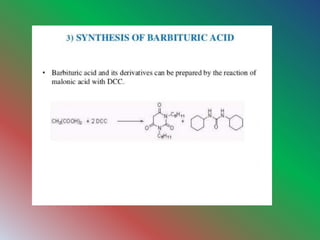


Dicyclohexylcarbodimide (DCC) is an organic compound used primarily for coupling amino acids in peptide synthesis, existing as white crystals with a sweet odor. It is soluble in various organic solvents but is moisture-sensitive and considered a potent allergen. DCC is involved in the Moffatt oxidation process to convert alcohols into aldehydes and ketones, via a specific reaction mechanism involving organosulfur intermediates.











