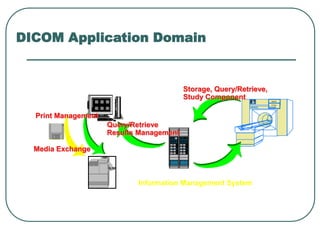
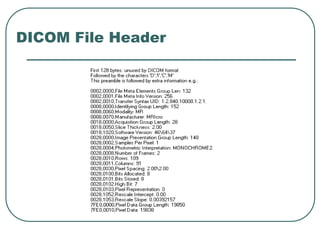
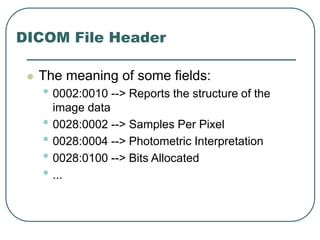
DICOM is a standard for handling, storing, printing, and transmitting information in medical imaging. It was developed by NEMA and ACR to enable sharing of digital medical images between devices. DICOM defines formats for medical images and communication protocols for transferring those images and associated reports between devices. It allows for images from different manufacturers and facilities to be shared through the use of unique identifiers and a standardized data format.