Embed presentation
Downloaded 194 times


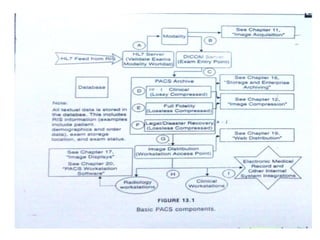
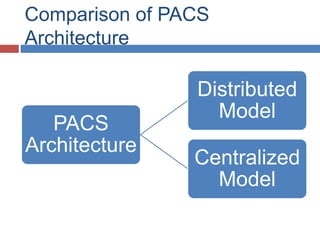
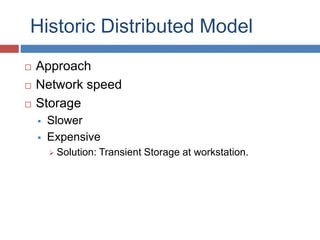
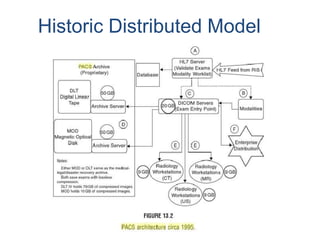
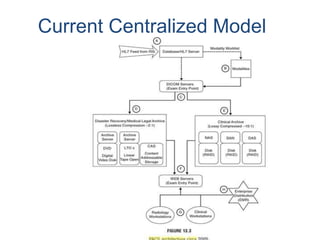



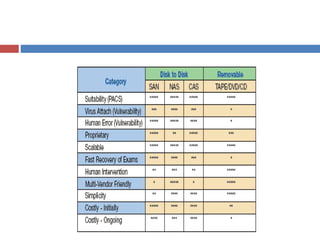


The document outlines the architecture of Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS), highlighting the need to consider both current and future challenges due to the dynamic nature of technology and organizations. It compares distributed and centralized models of PACS architecture, detailing aspects such as operational fit, scalability, and integration with other hospital systems. Additionally, it mentions various storage solutions like SAN, NAS, and CAS as part of the architecture's evolution.

















