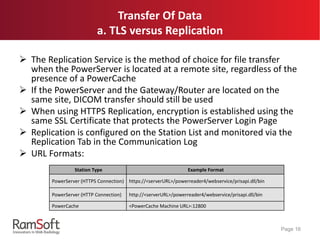
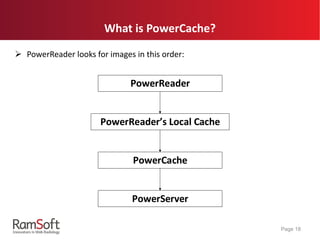
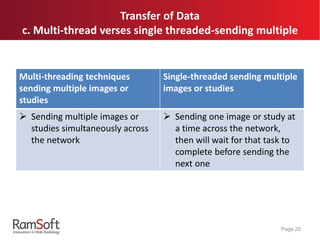
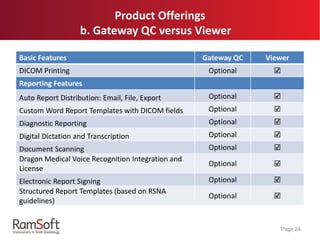
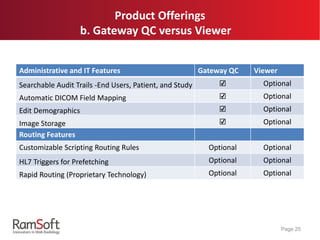
The document provides an extensive overview of the capabilities and features of RamSoft's PACS Gateway Router, including DICOM standards, connection setup, data cleansing options like tag mapping and scripting, and data transfer methods such as TLS and replication. It explains the advantages of using a DICOM vendor-neutral archive to ensure compatibility across various healthcare systems, as well as the benefits of using PowerCache for efficient image retrieval. Additionally, it covers product offerings and variations between different user interfaces and administrative features, highlighting the system's flexibility and customizability.