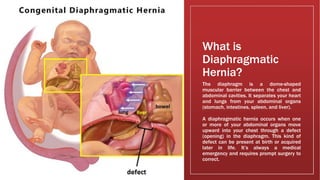
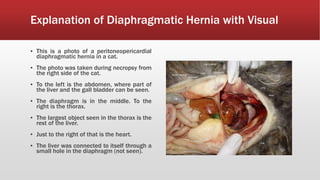
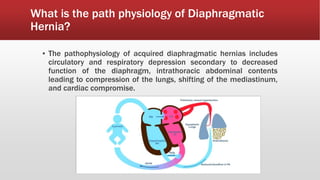
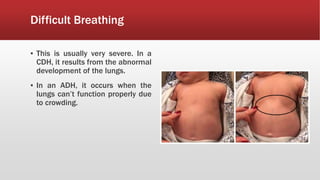
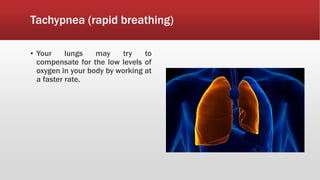
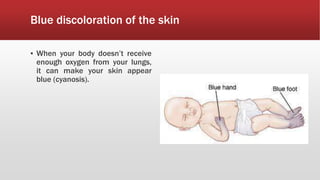
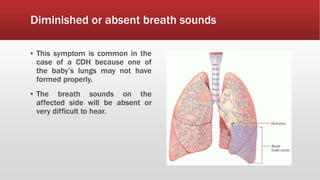
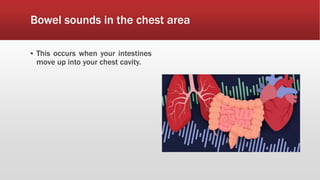
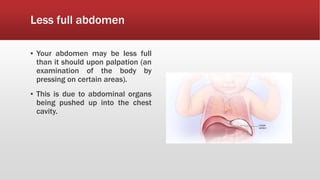
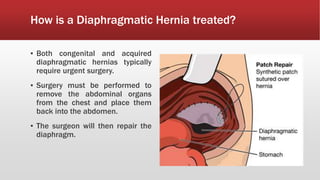
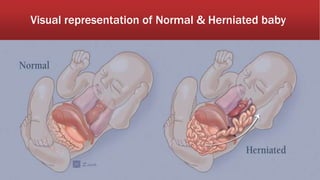
A diaphragmatic hernia is a defect where abdominal organs move into the chest through an opening in the diaphragm, necessitating urgent surgical intervention. It can be congenital or acquired, with symptoms ranging from difficulty breathing to blue skin discoloration, and is diagnosed through imaging techniques like X-rays and ultrasounds. The long-term outlook varies significantly based on lung damage and associated organ involvement, with survival rates for congenital hernias estimated at 70-90 percent.