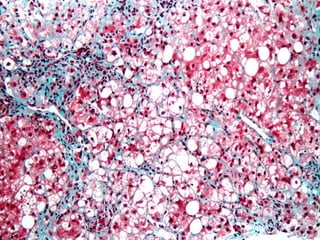
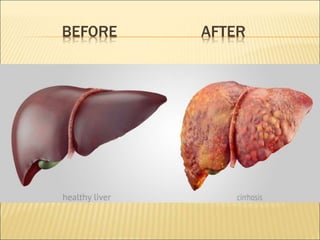
This document discusses steatohepatitis, which is a type of fatty liver disease characterized by fat accumulation in the liver combined with liver inflammation. It notes that steatosis is mere fat deposition, while steatohepatitis includes inflammation. The document outlines the two main types of fatty liver disease and their risk factors. It provides details on the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).