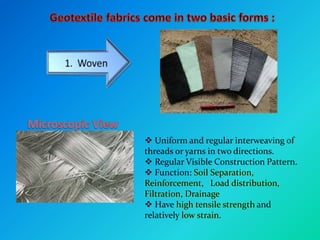
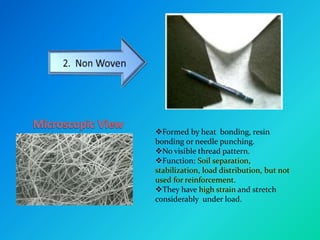
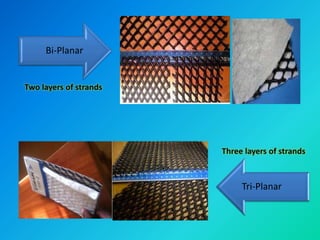
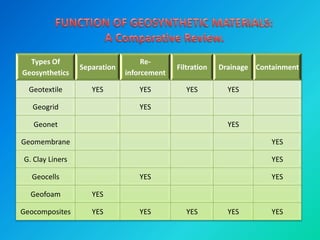
Geosynthetics are man-made materials made from polymers that are used with soil and rock in civil engineering projects to improve their behavior. There are many types of geosynthetics that each have different properties and uses, including geotextiles, geogrids, geonets, geomembranes, geosynthetic clay liners, geocells, geofoam, and geocomposites. Common applications include roads, embankments, retaining walls, reservoirs, landfills, erosion control, and more. Each type has distinct characteristics that make it suitable for functions like separation, reinforcement, filtration, drainage, and containment.