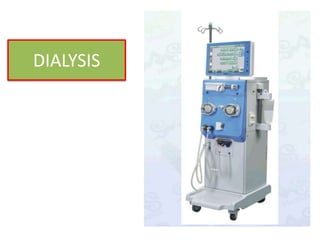
Dialysis involves the artificial filtration and removal of waste from the bloodstream through diffusion, osmosis, and ultrafiltration. There are two main types: hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Hemodialysis is performed using an artificial kidney machine to filter blood through a dialyzer, usually via arteriovenous fistula or graft. Peritoneal dialysis uses the peritoneum as a natural semipermeable membrane and involves manually infusing and draining a dialysate solution into the abdominal cavity. Both procedures help remove waste and excess fluid but come with risks like infection, hypotension, and disequilibrium.