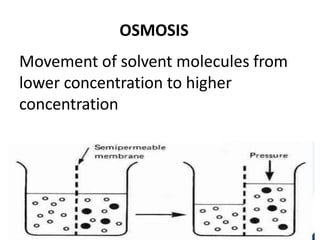
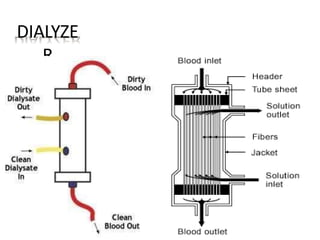
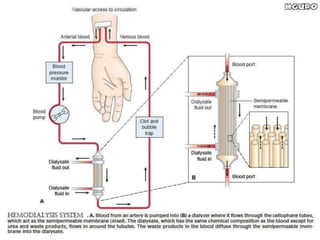
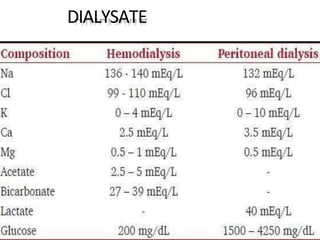
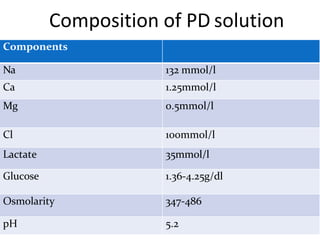
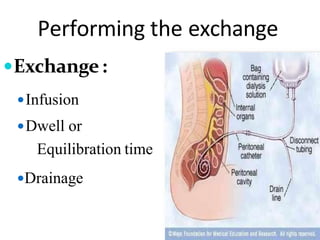
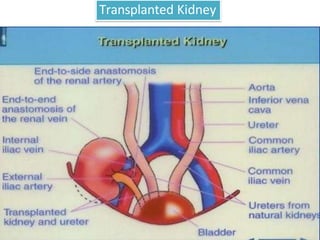
Dialysis is a process that removes waste and excess water from the blood when the kidneys fail. It uses diffusion and osmosis across a semi-permeable membrane as an artificial replacement for kidney function. There are two main types: hemodialysis which cleanses the blood directly by passing it through a dialyzer, and peritoneal dialysis which uses the peritoneal membrane in the abdomen as a filter. Both aim to maintain fluid, electrolyte and acid-base balance by removing toxins when the kidneys are unable to do so.