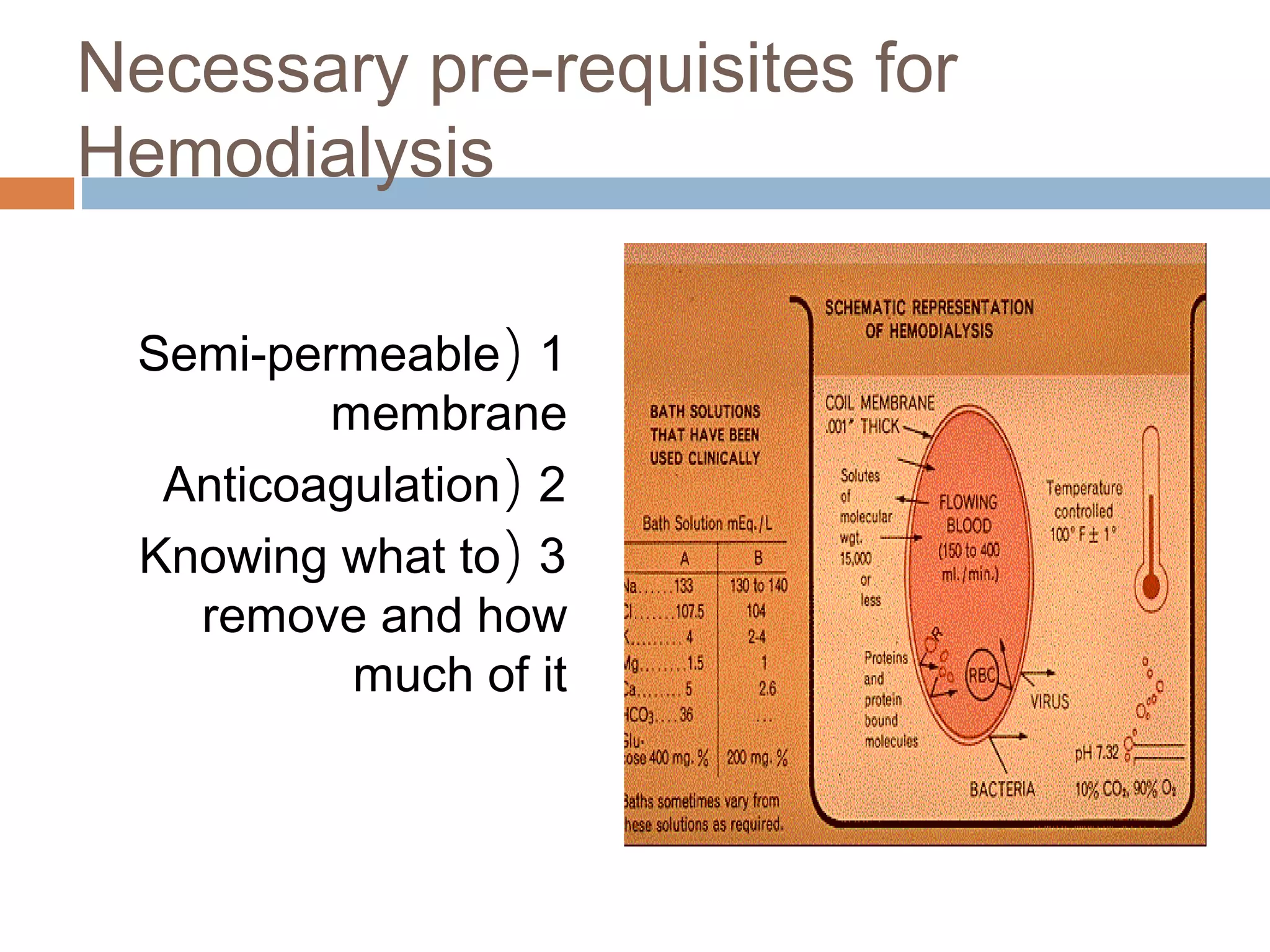
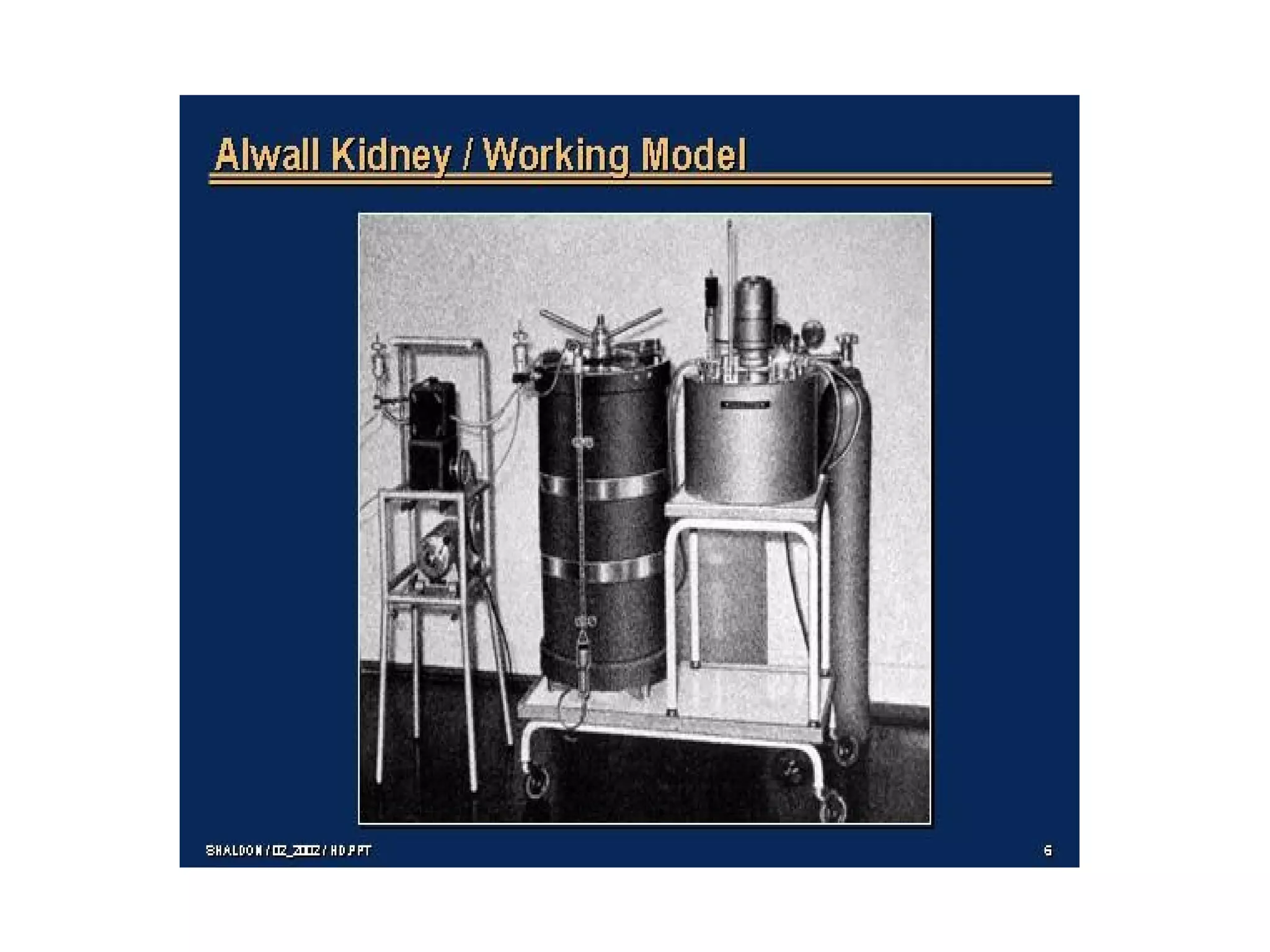
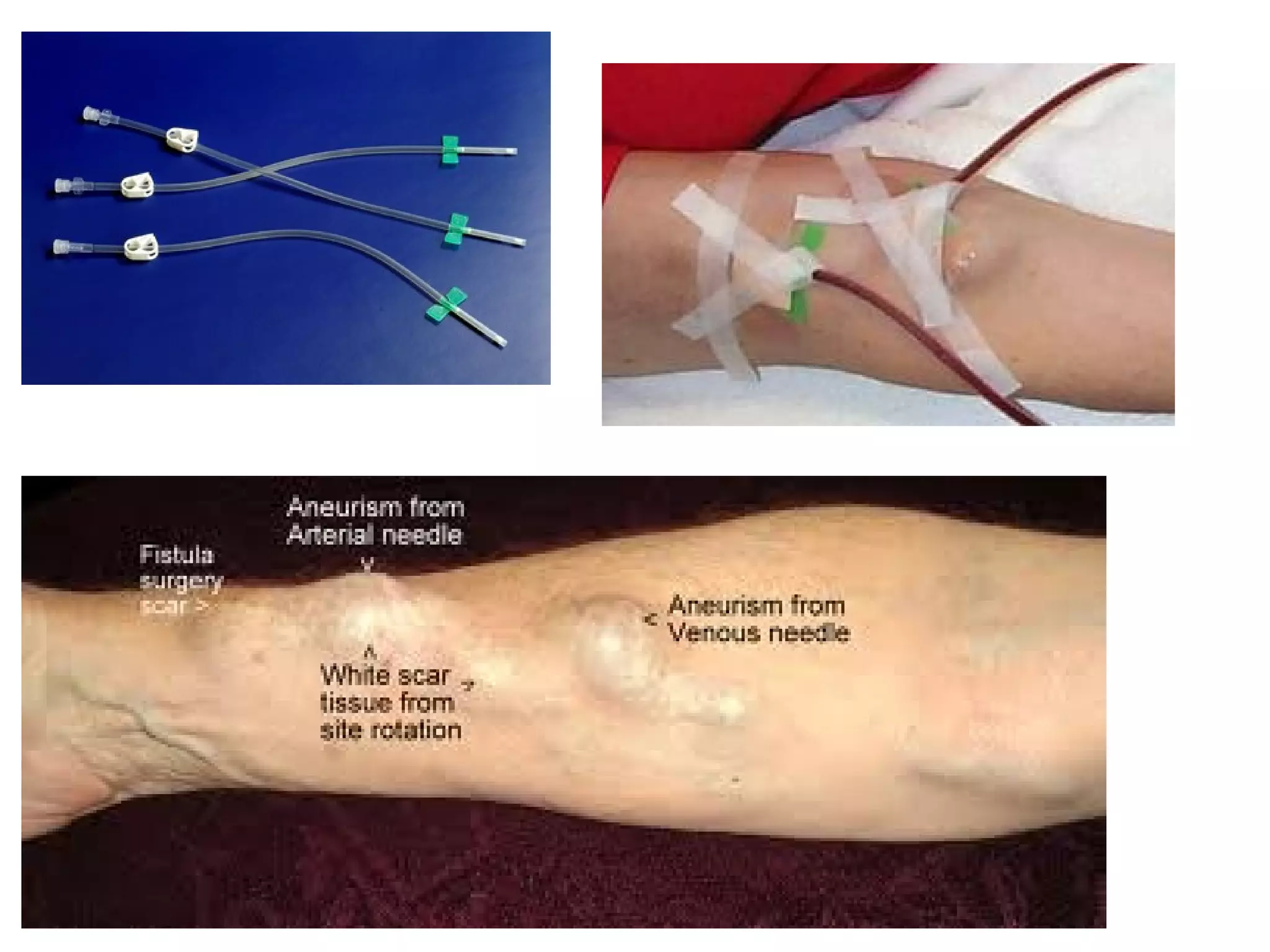
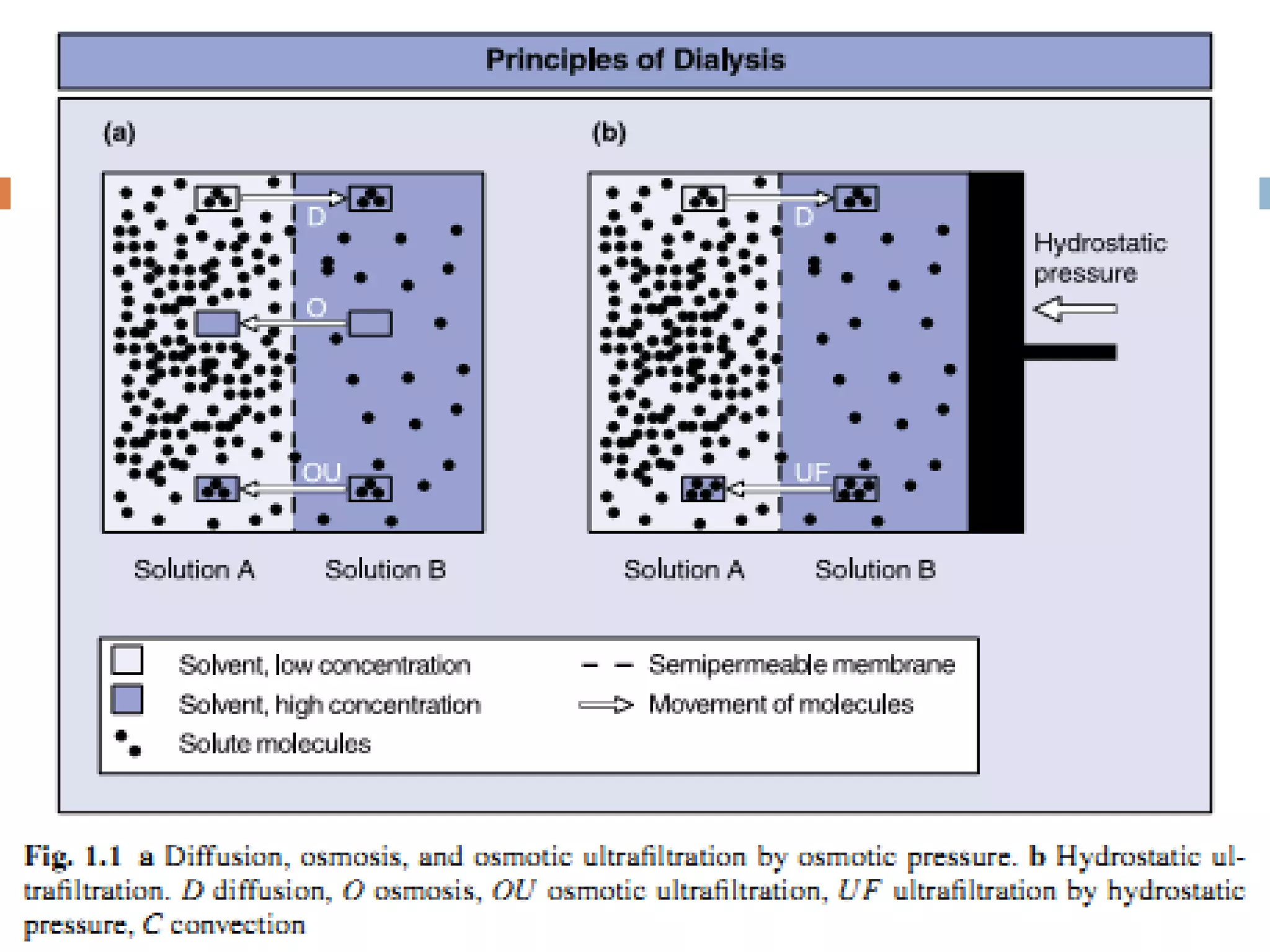
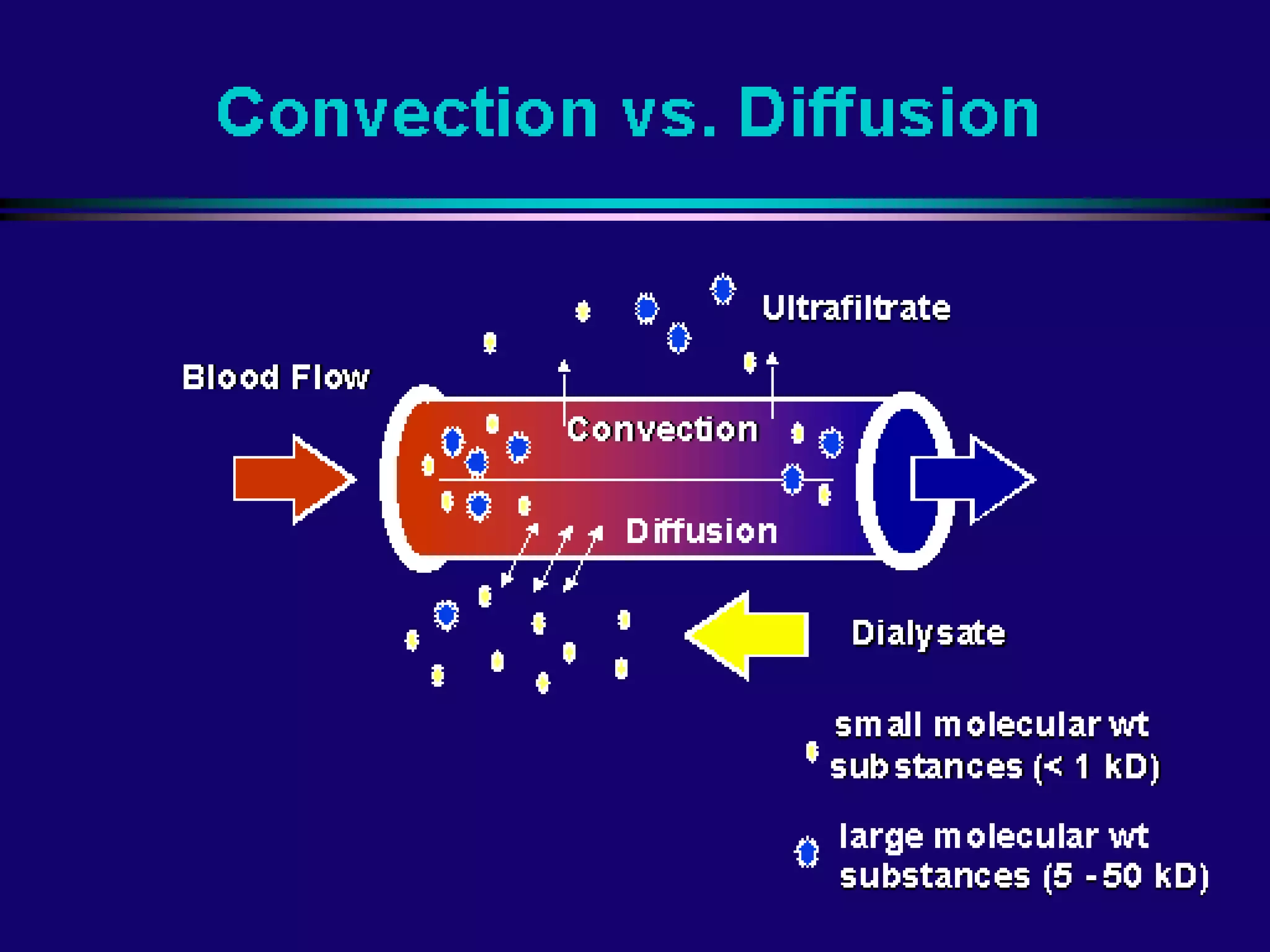
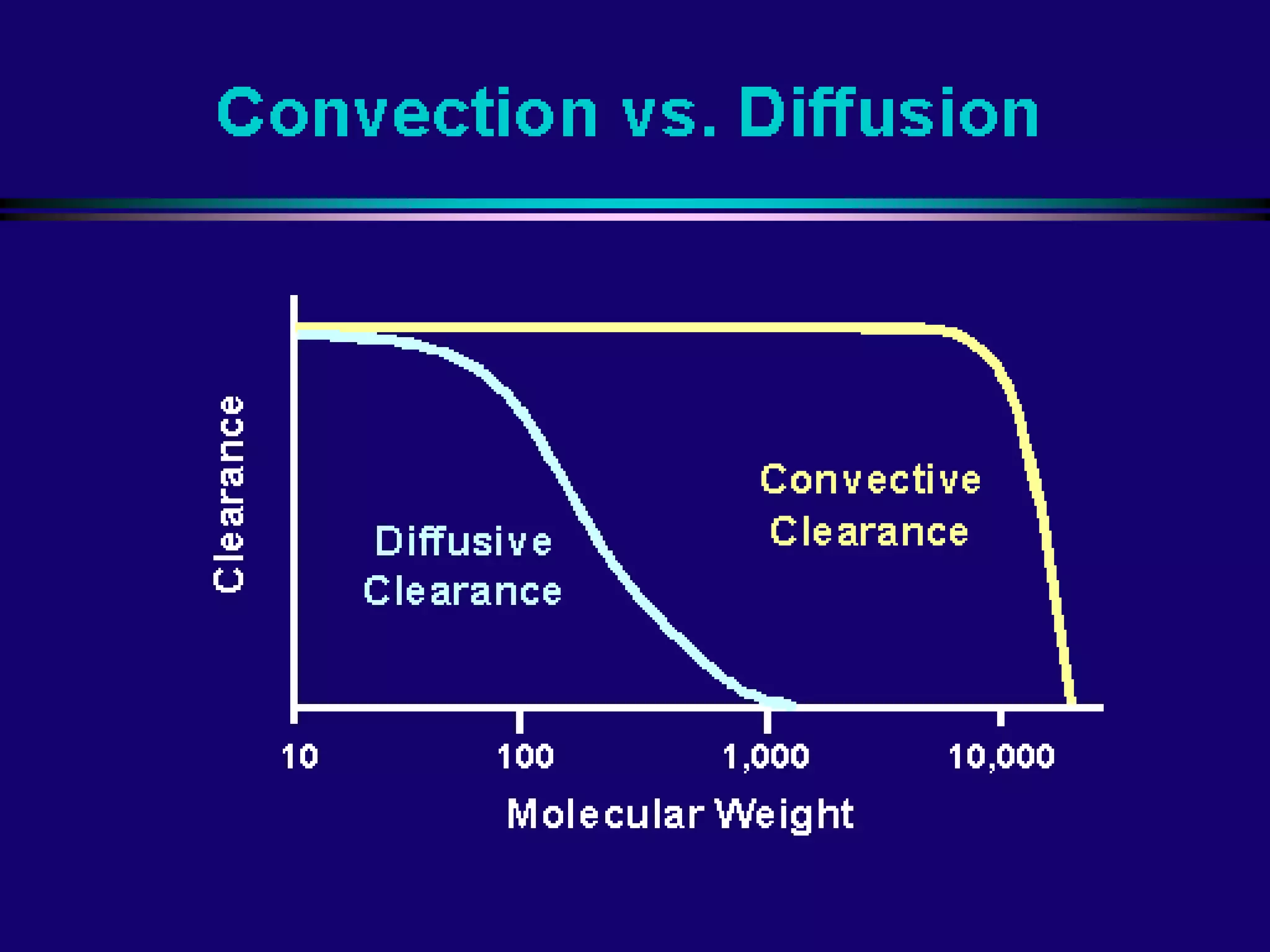
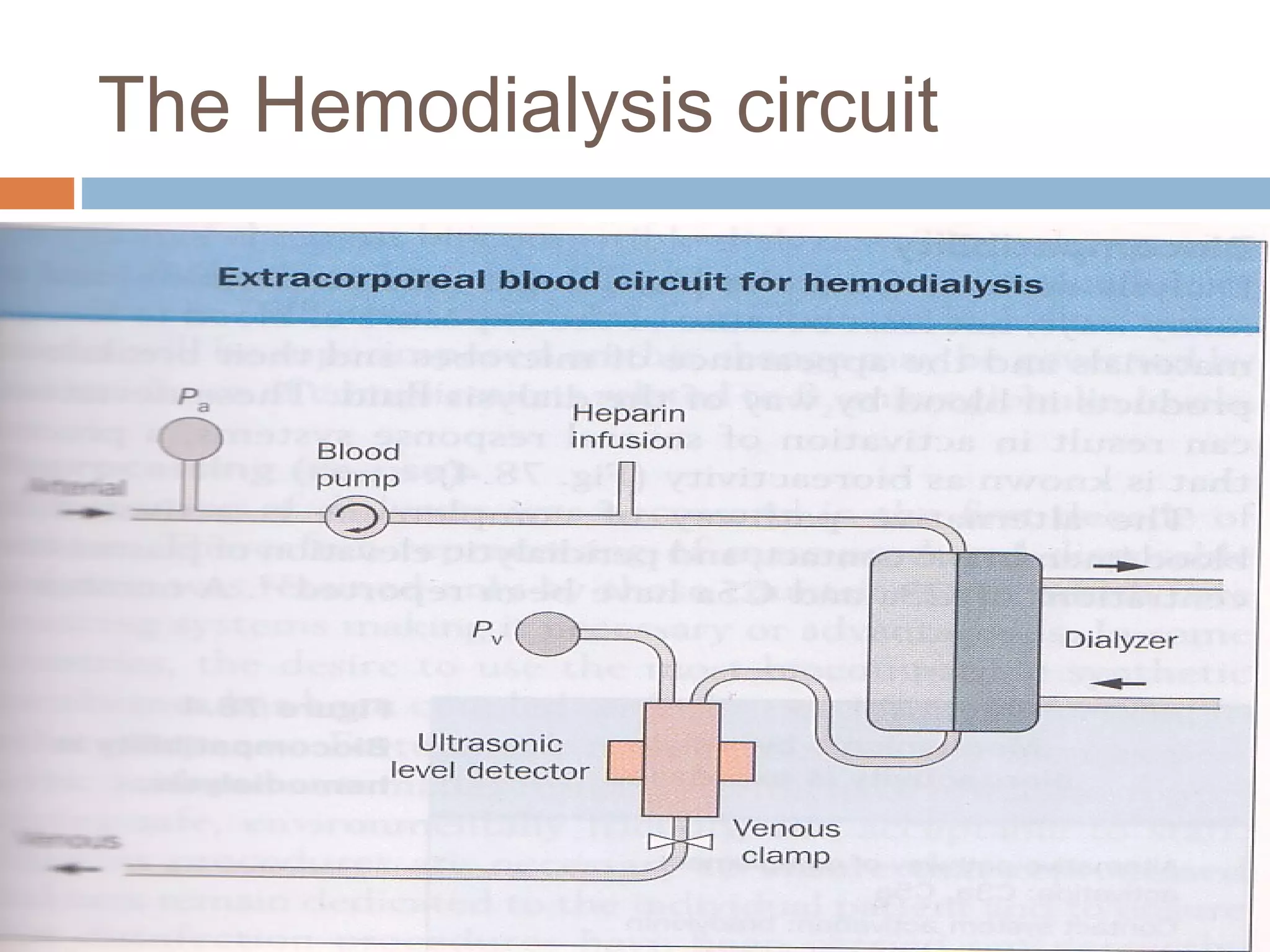
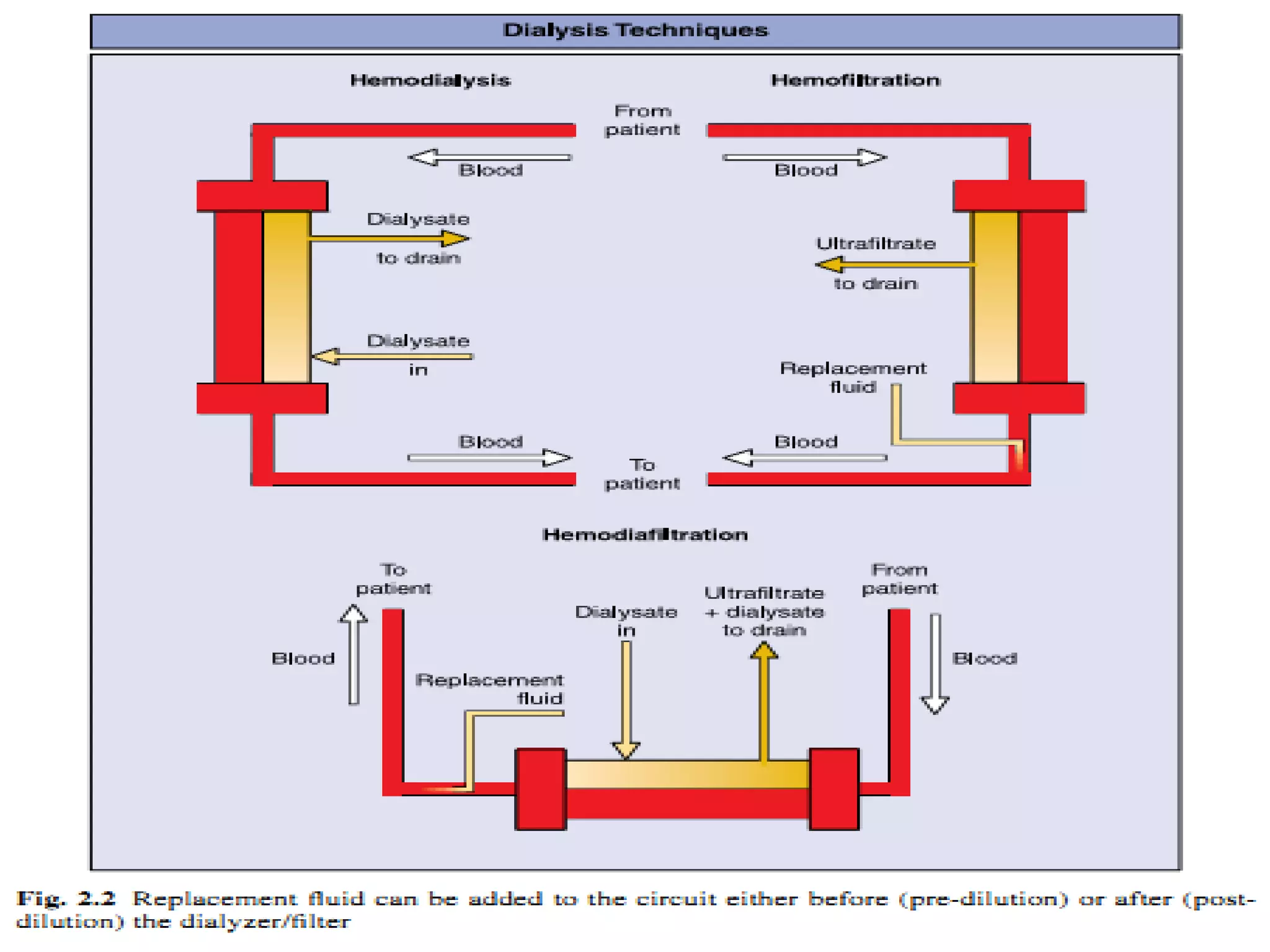
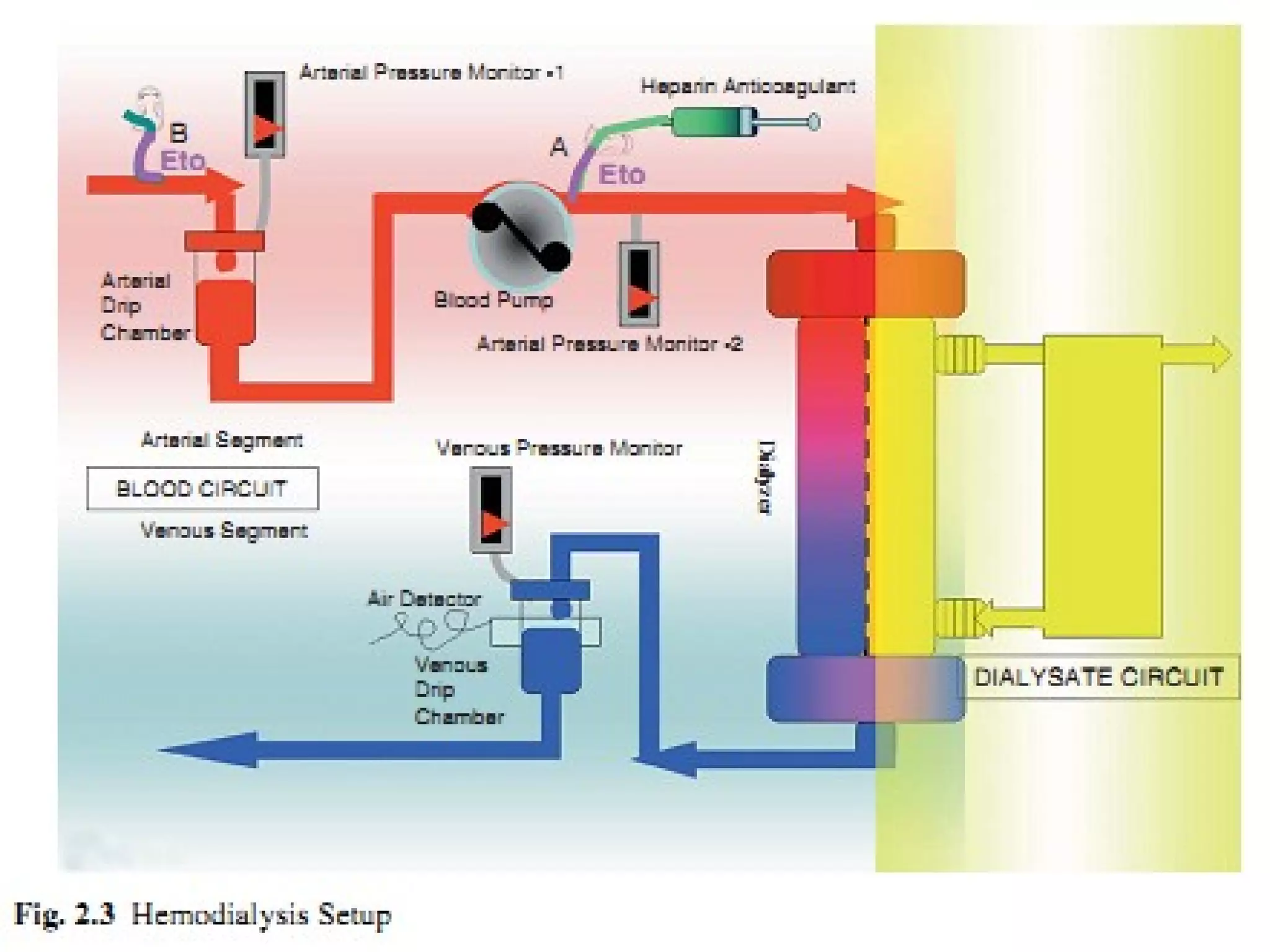
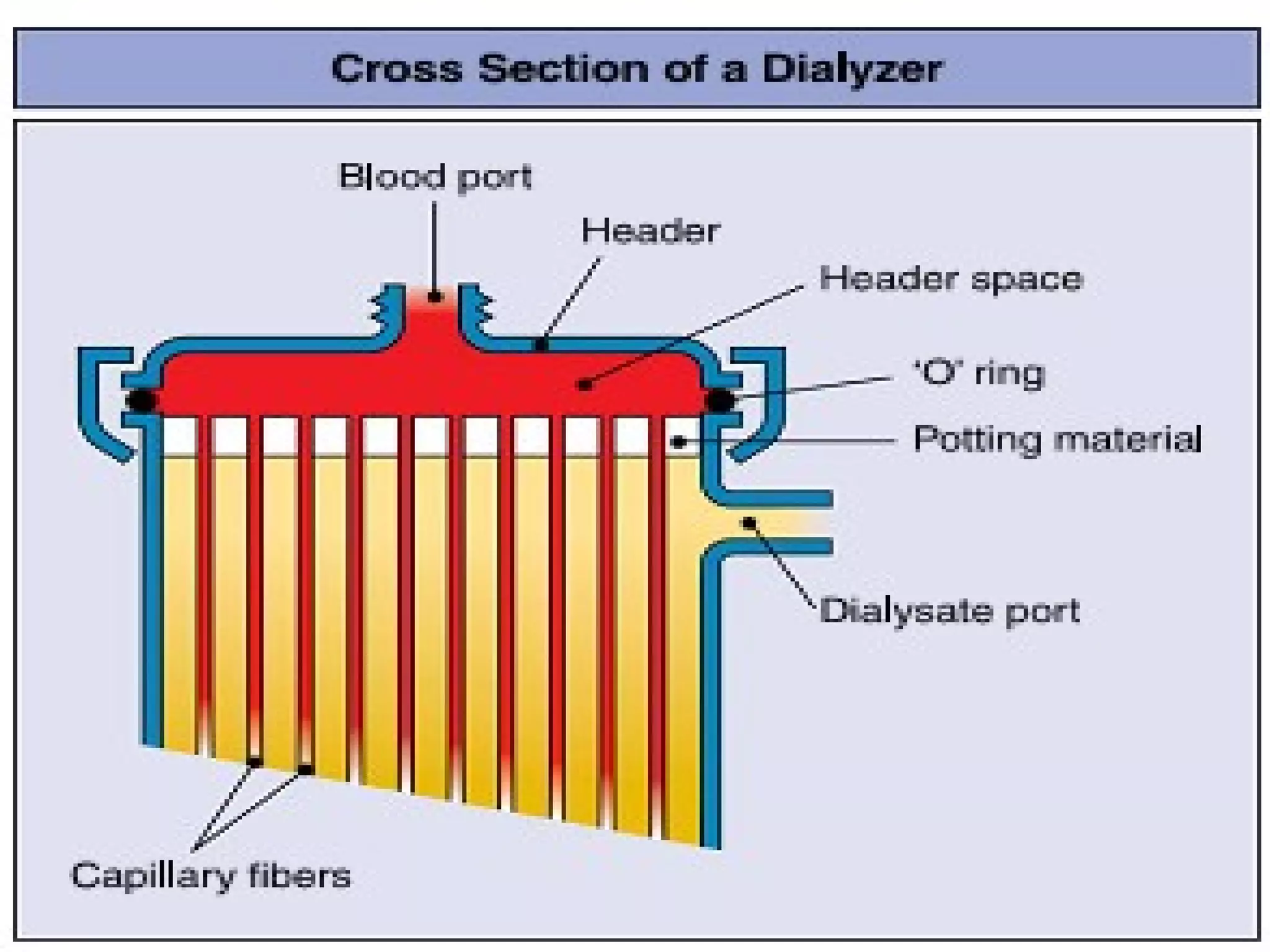
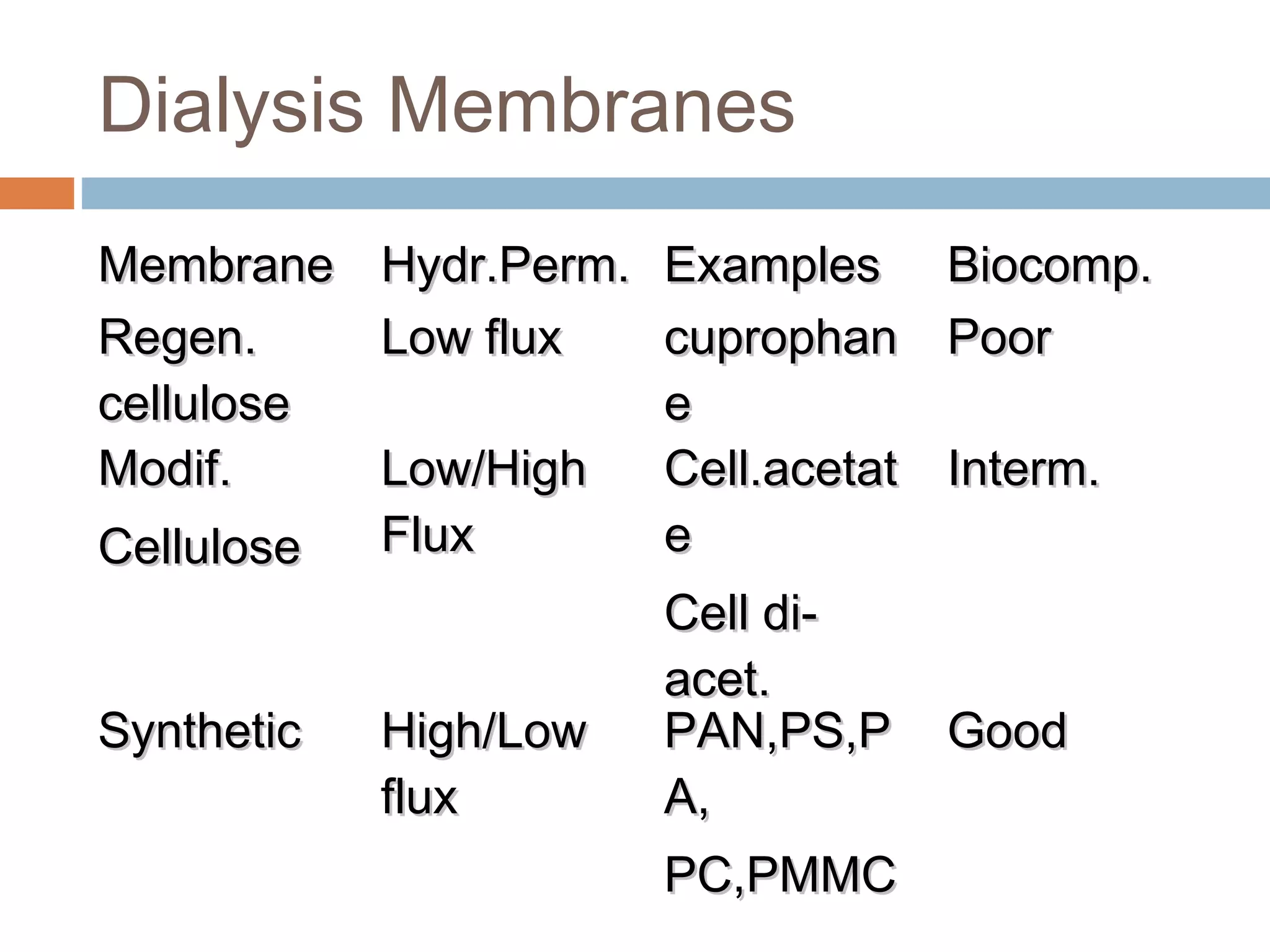
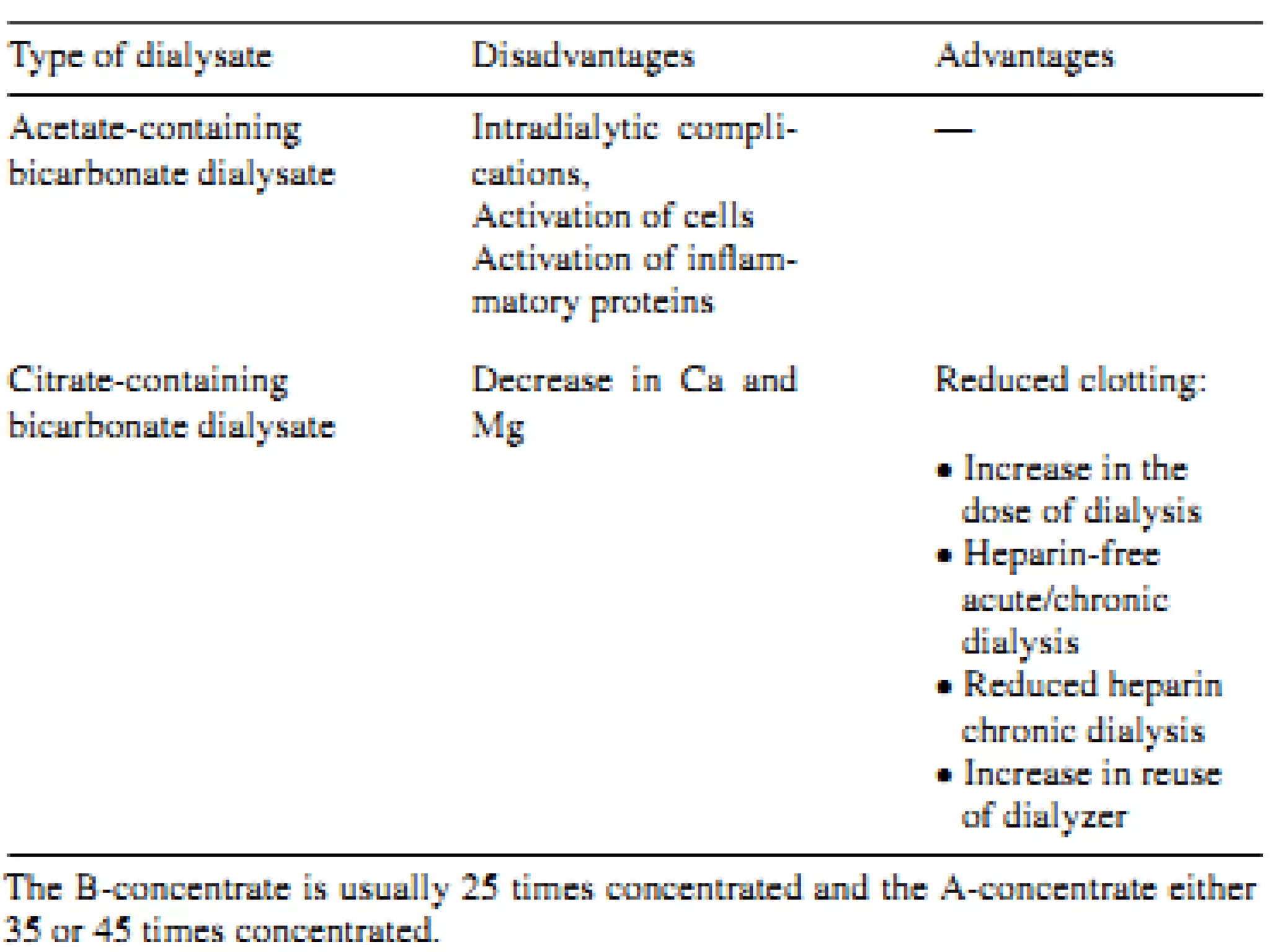
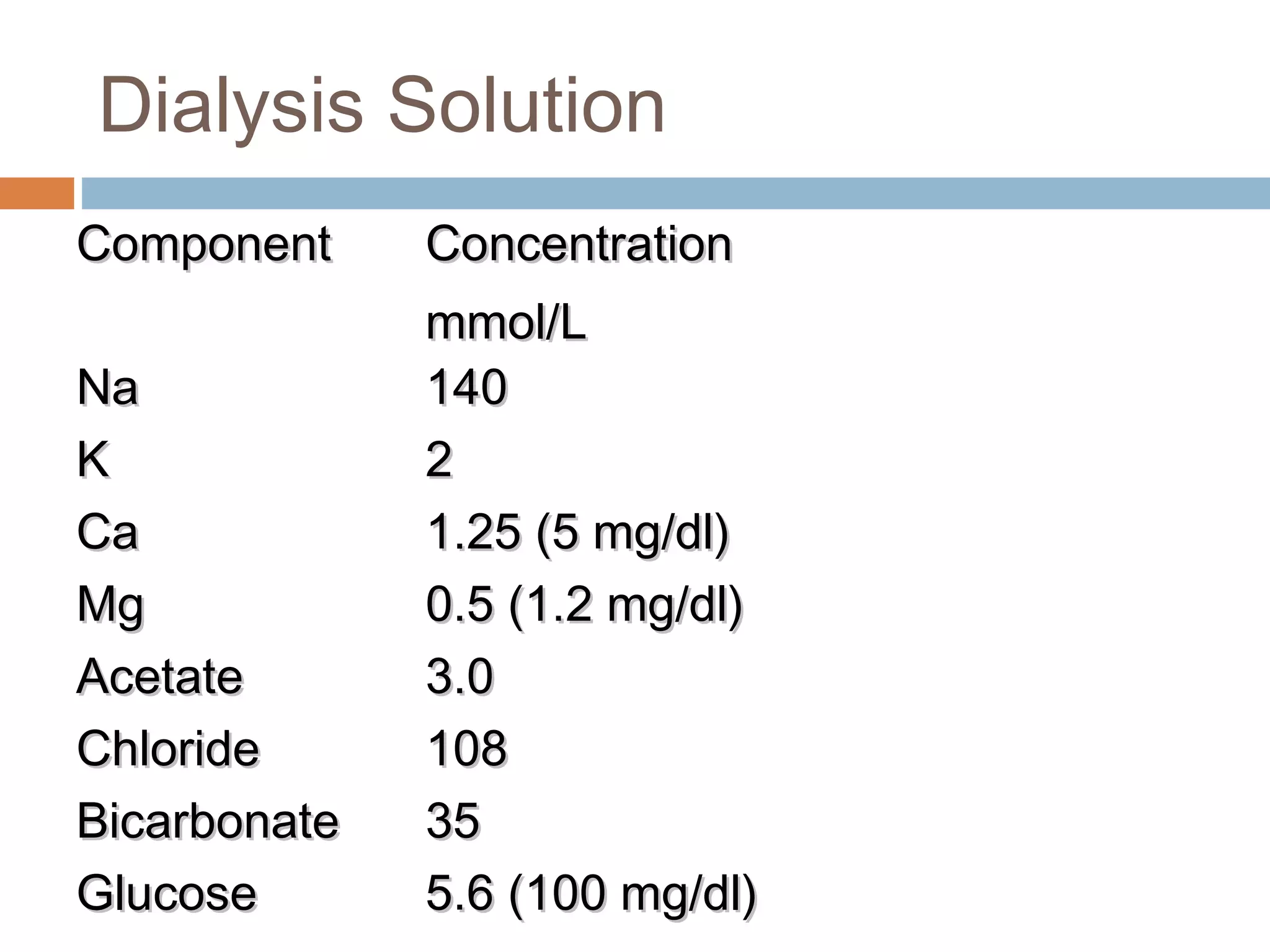
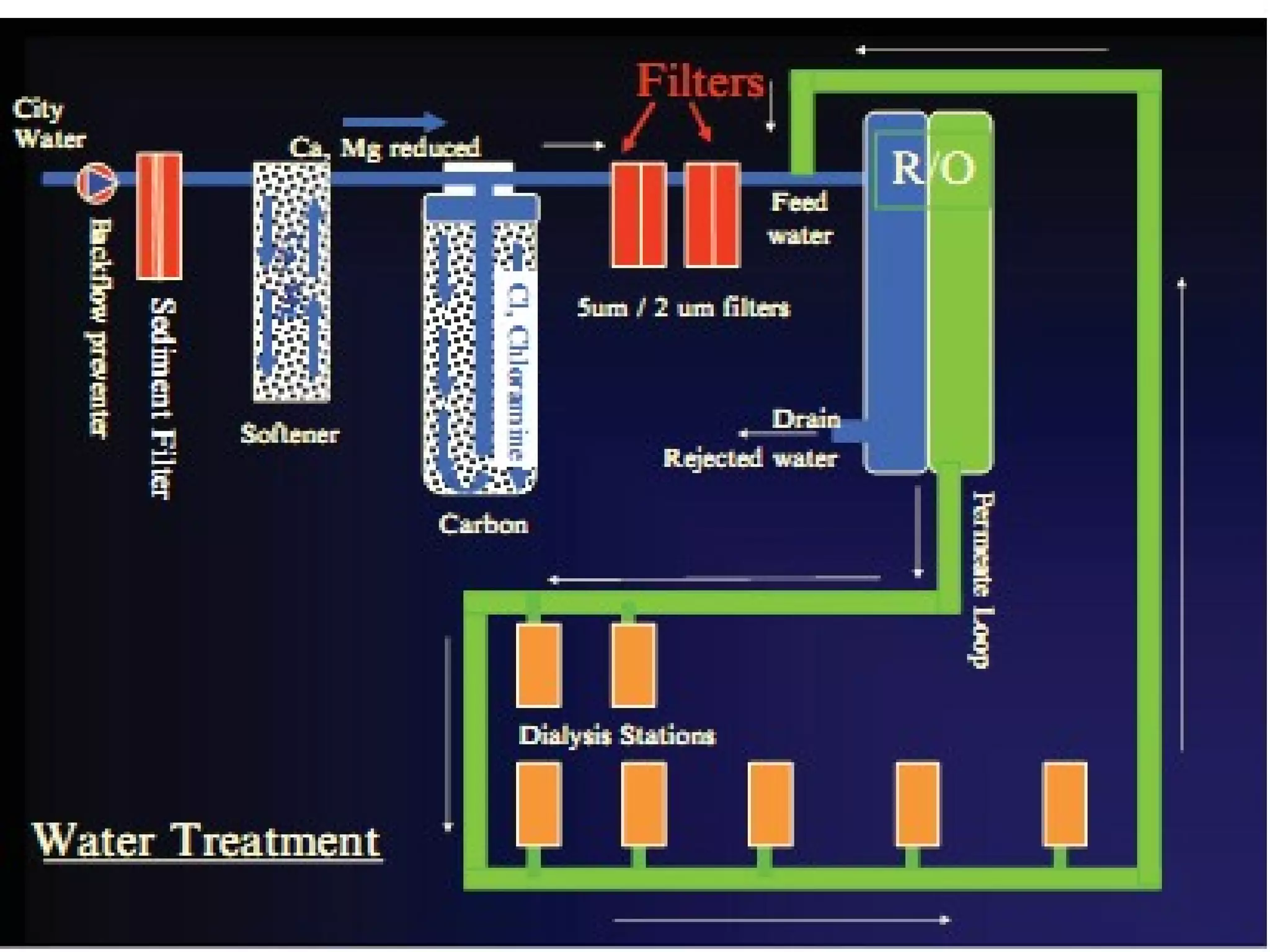
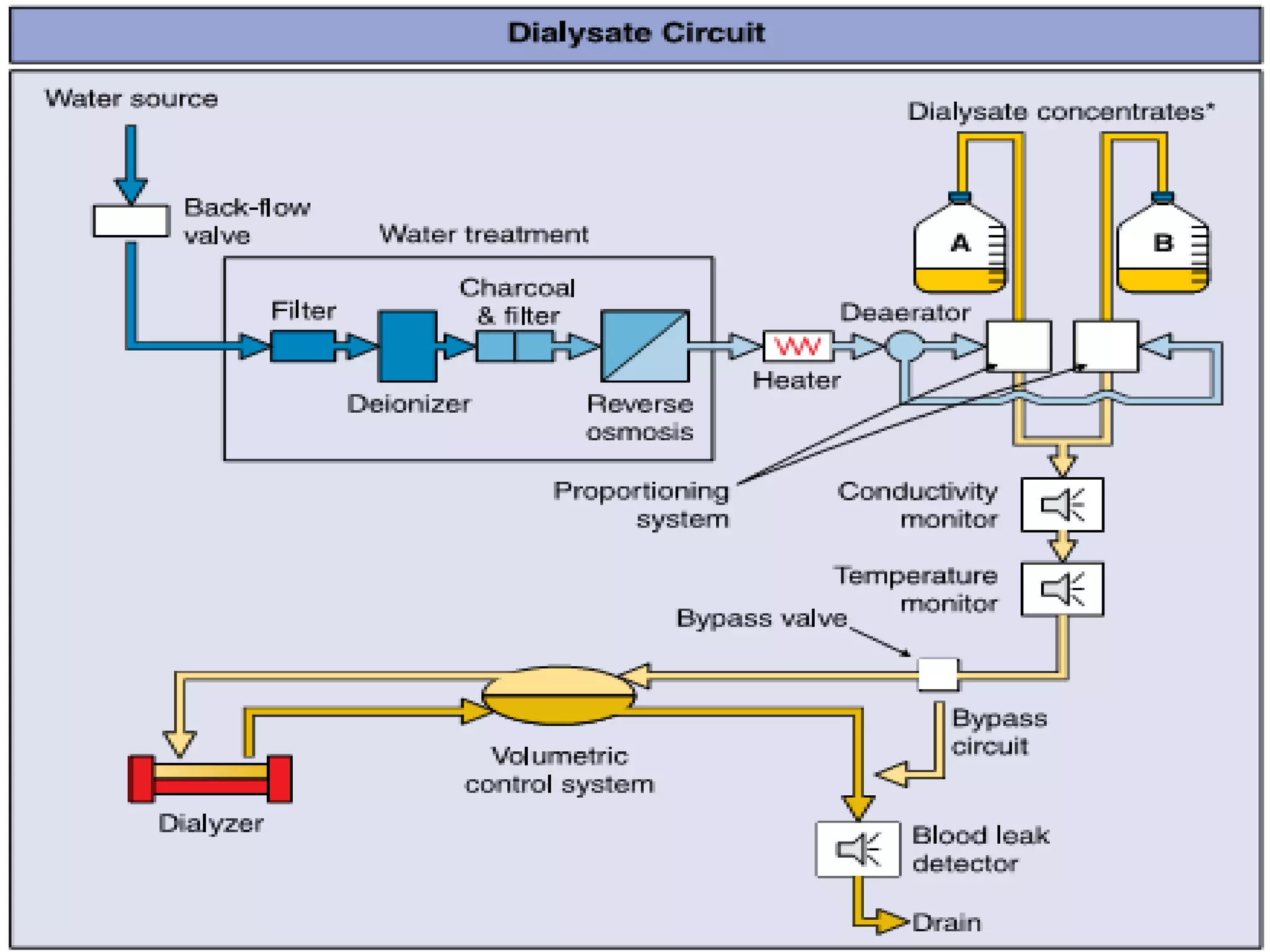
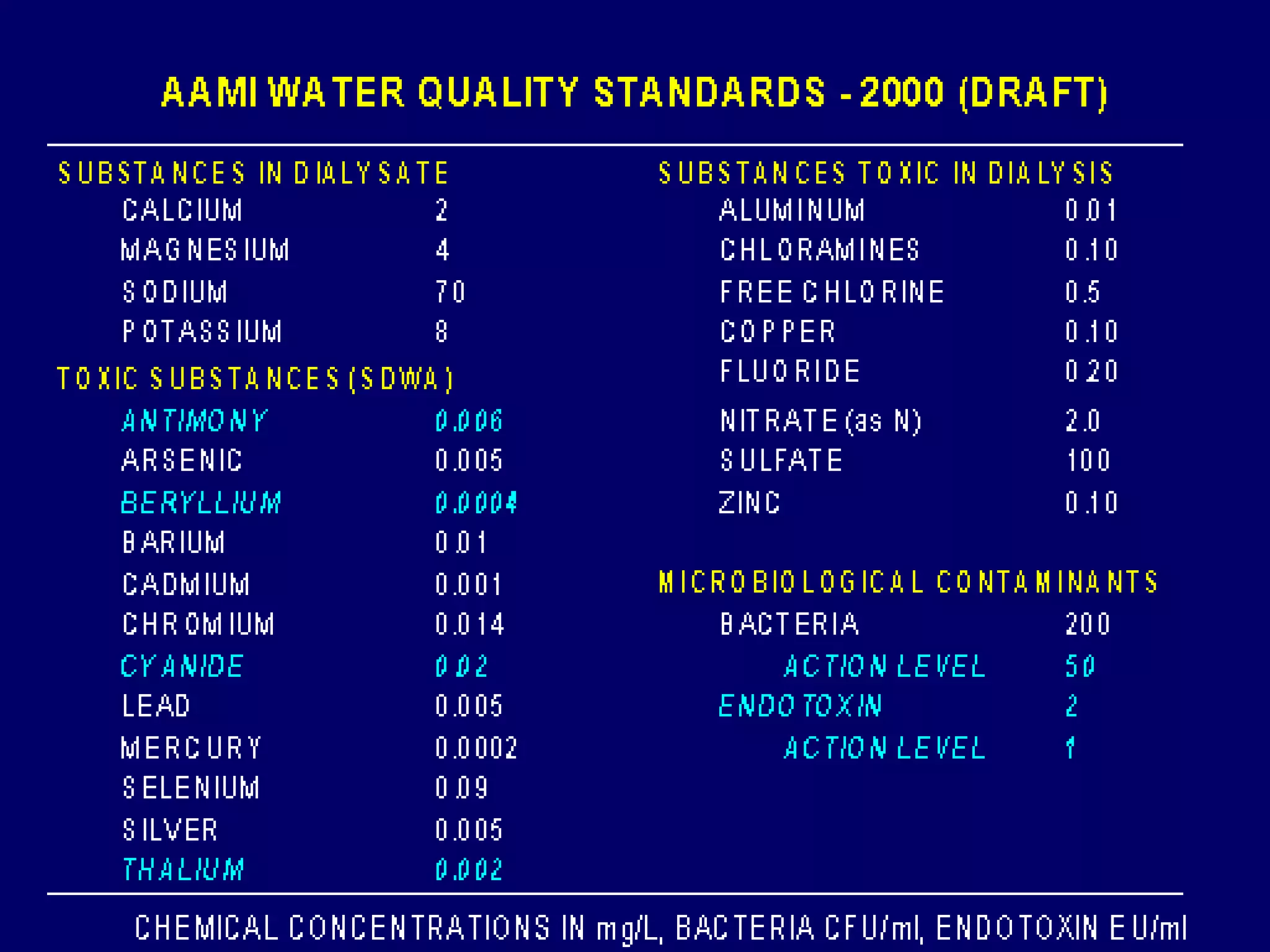
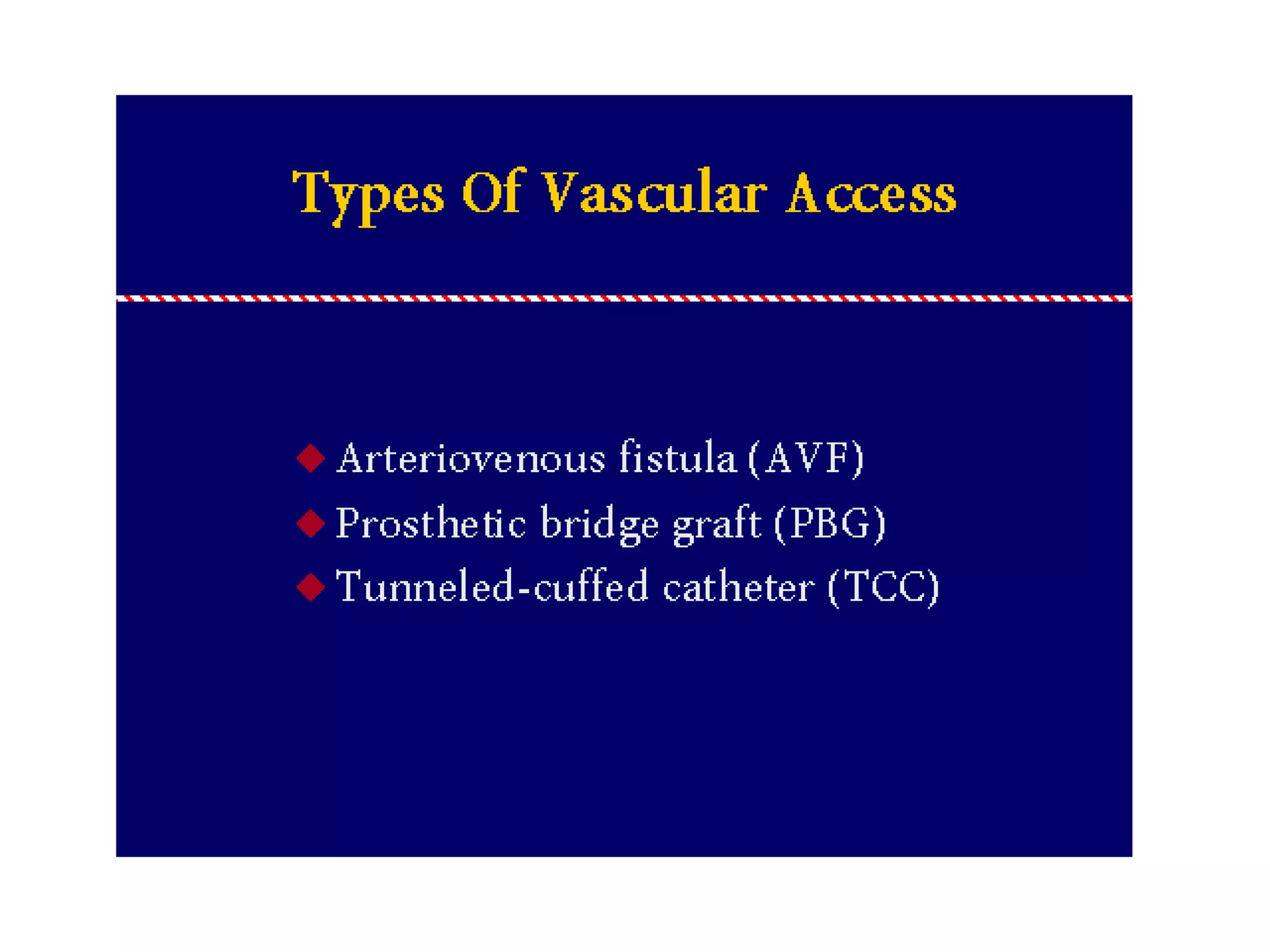
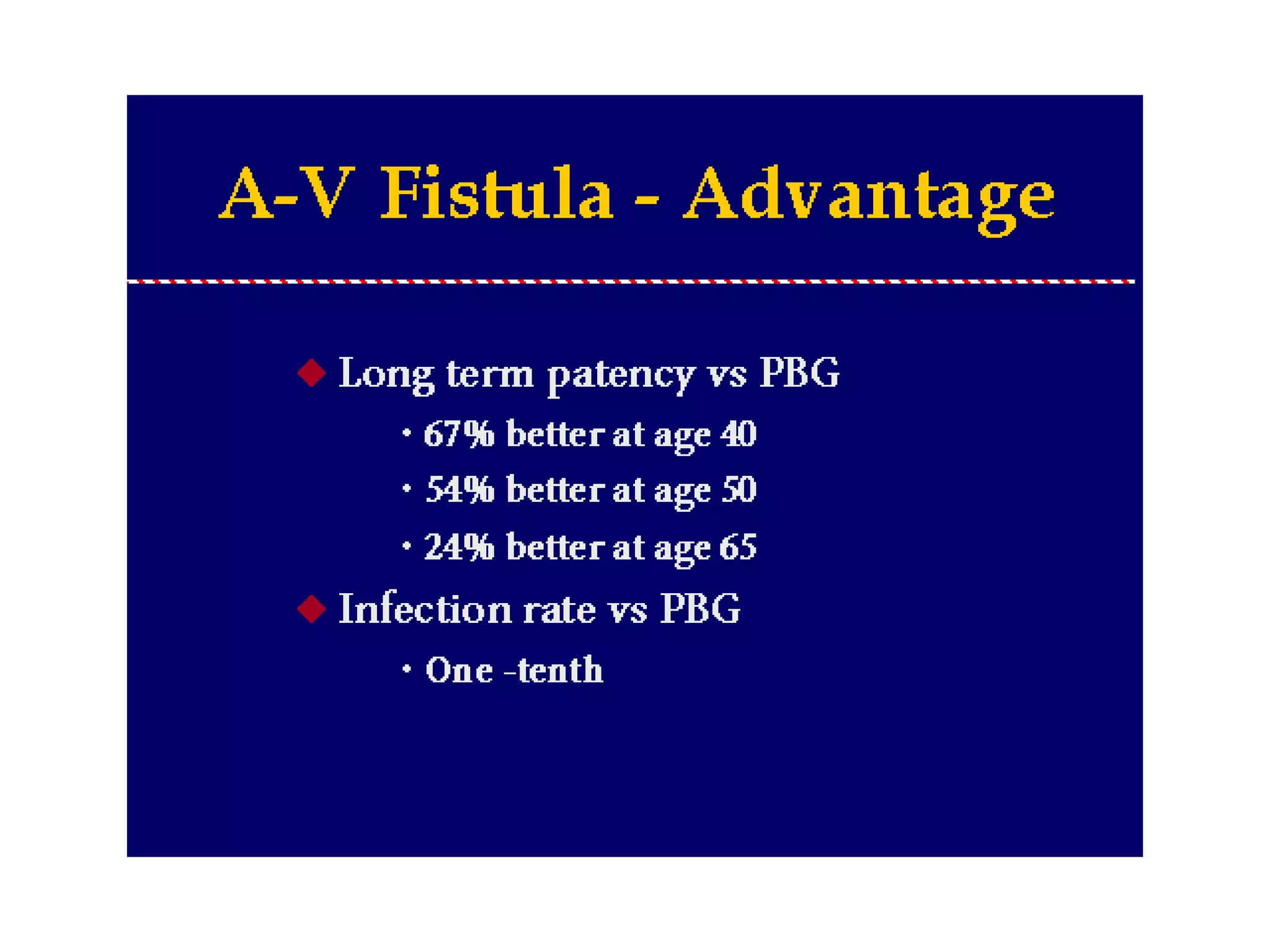
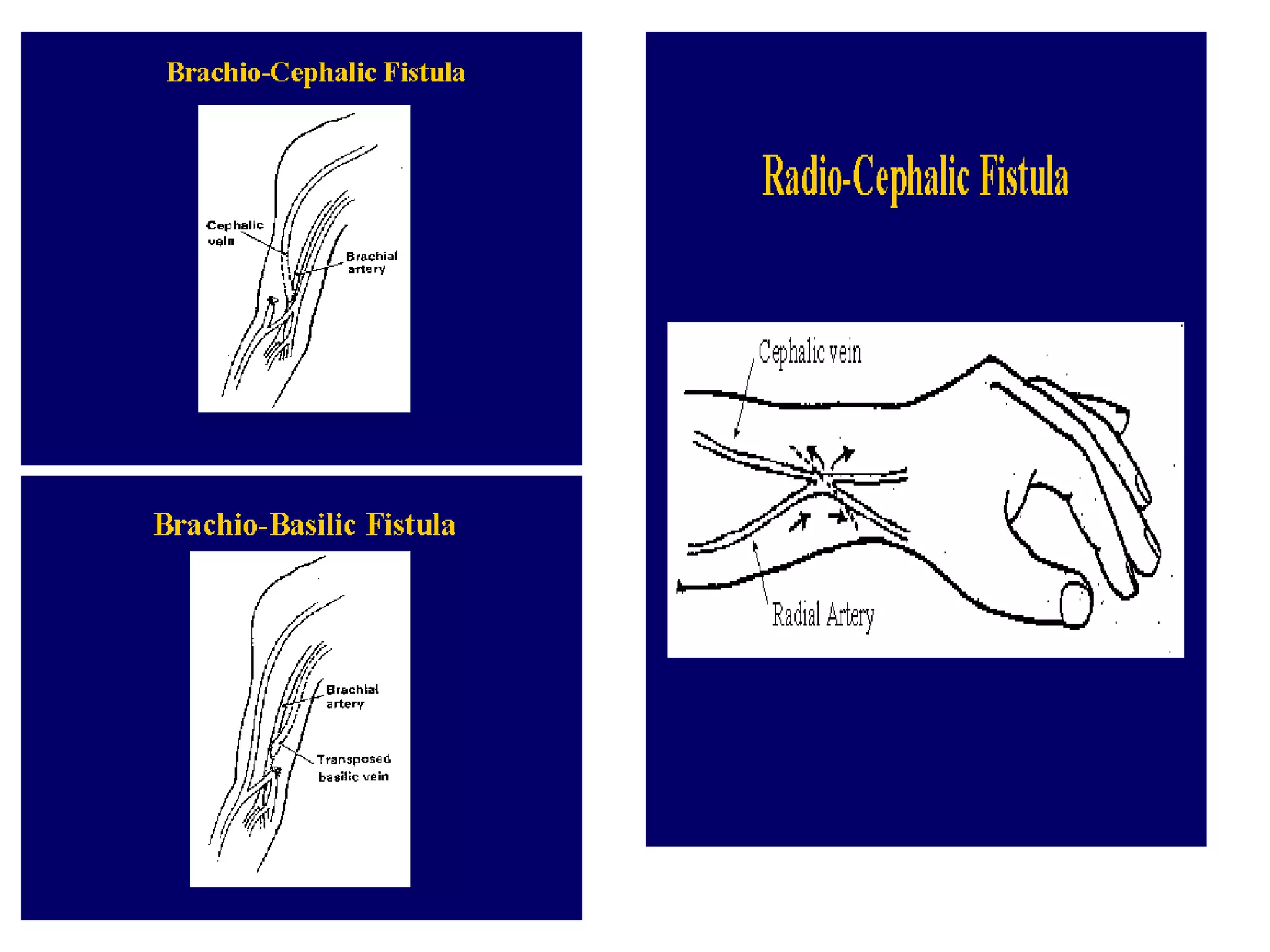
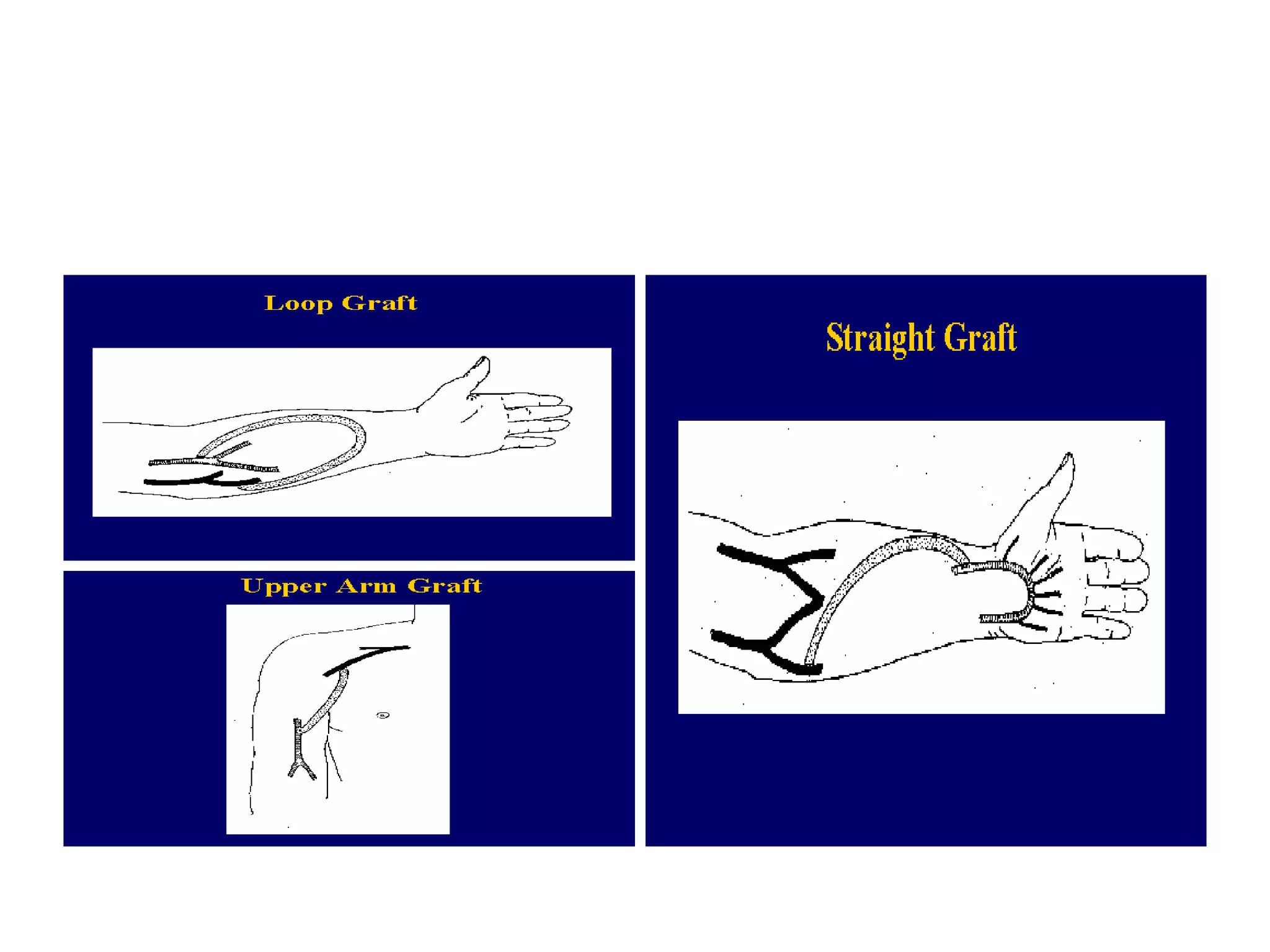
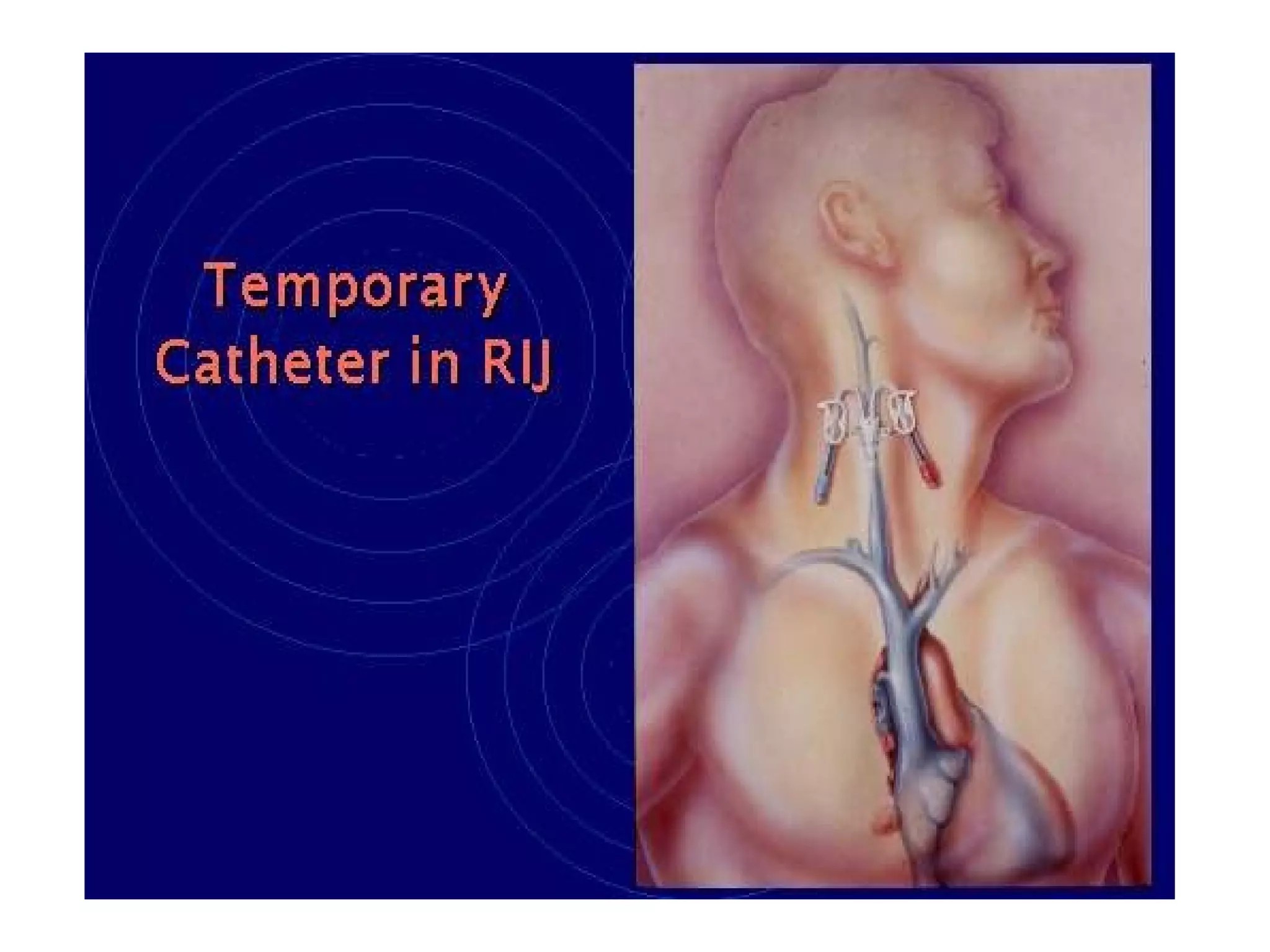
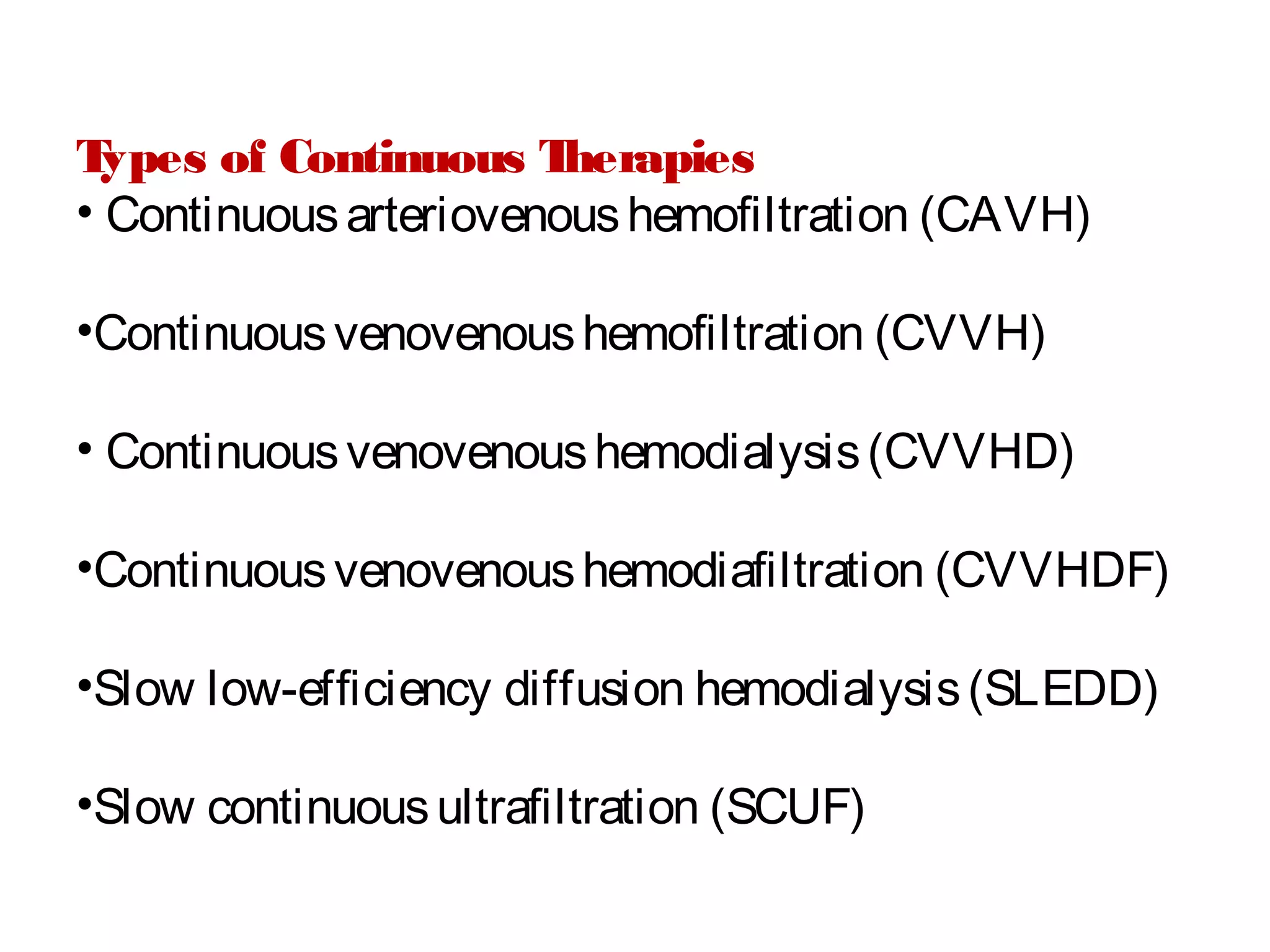
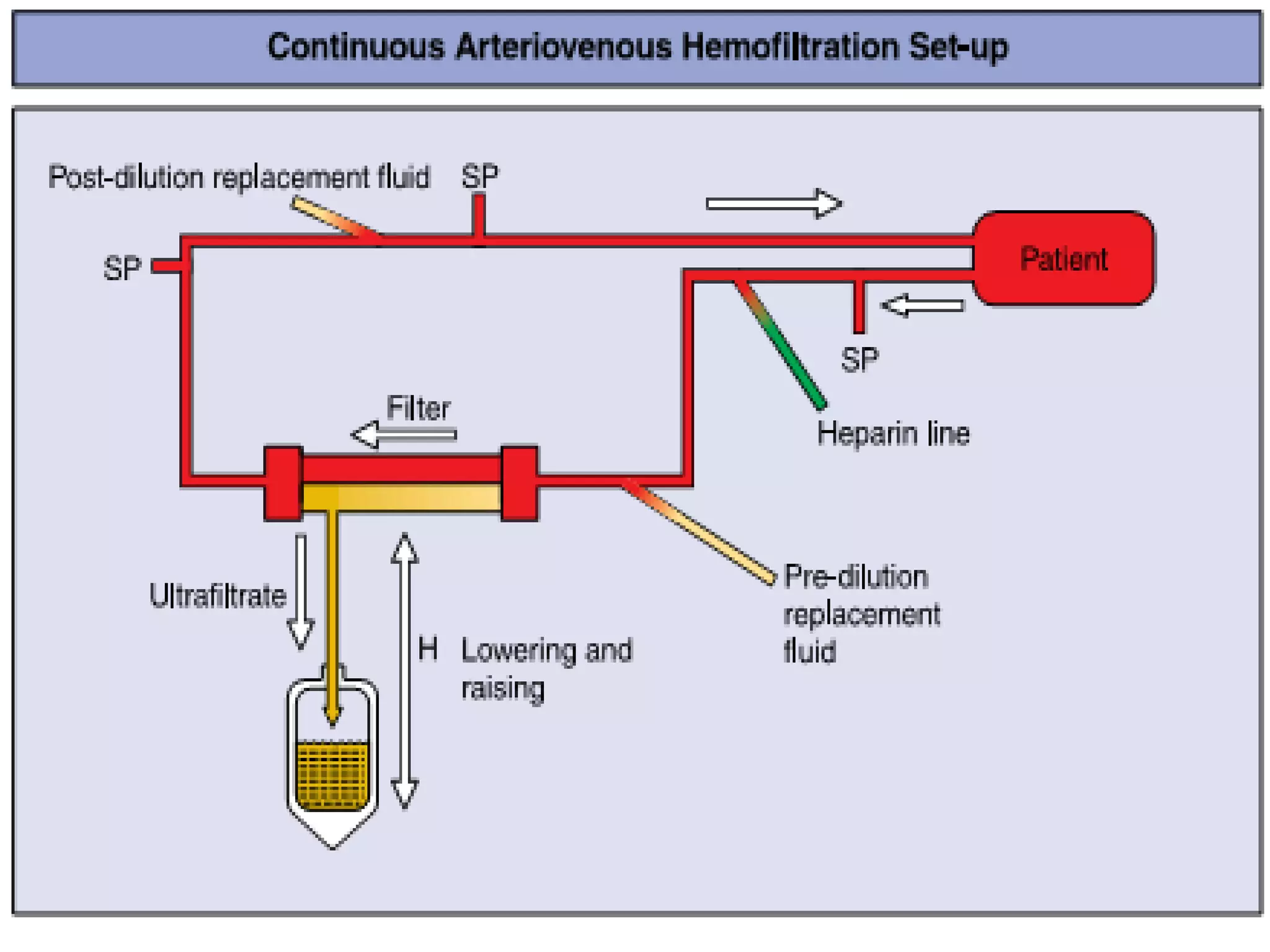
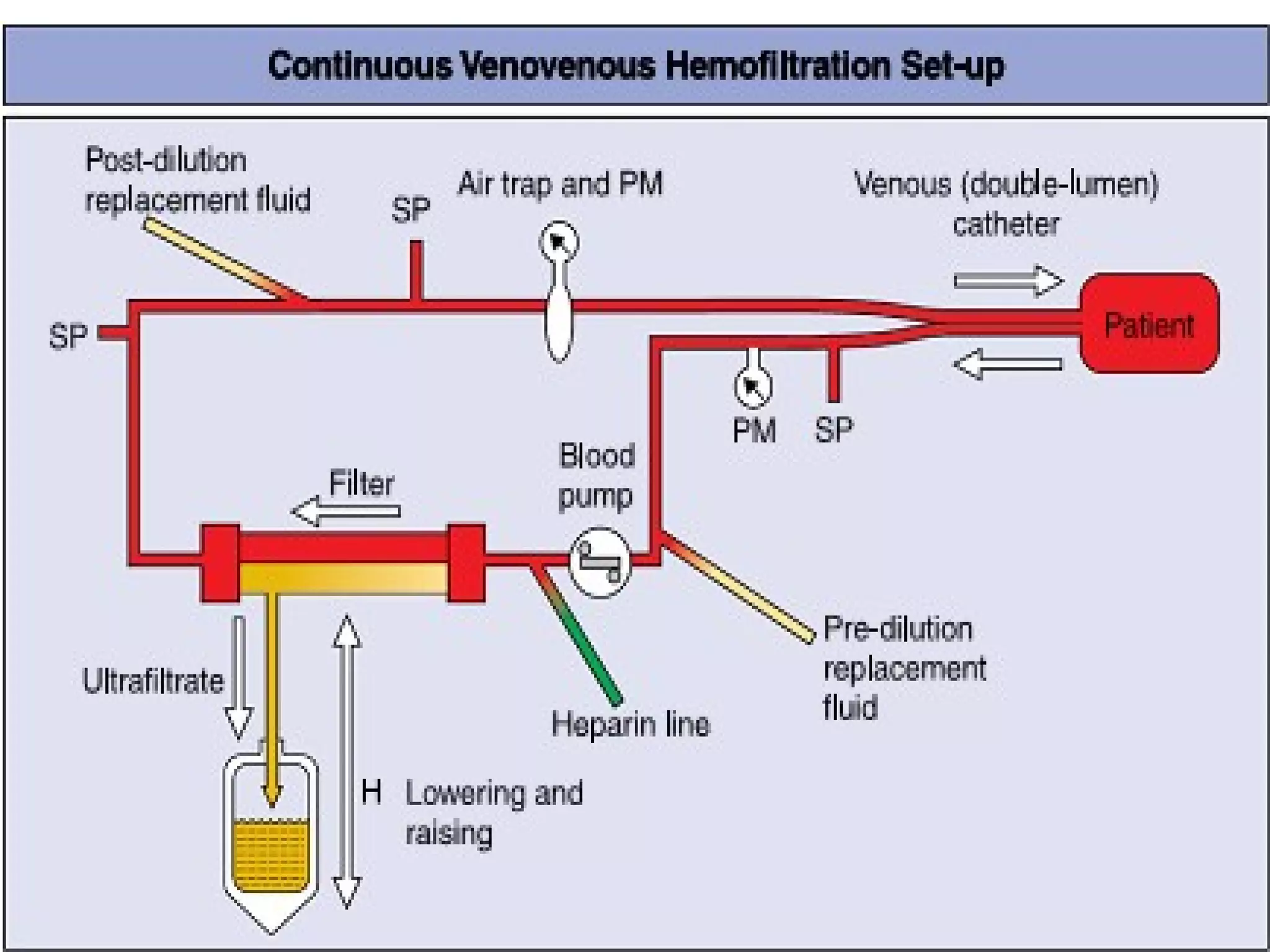
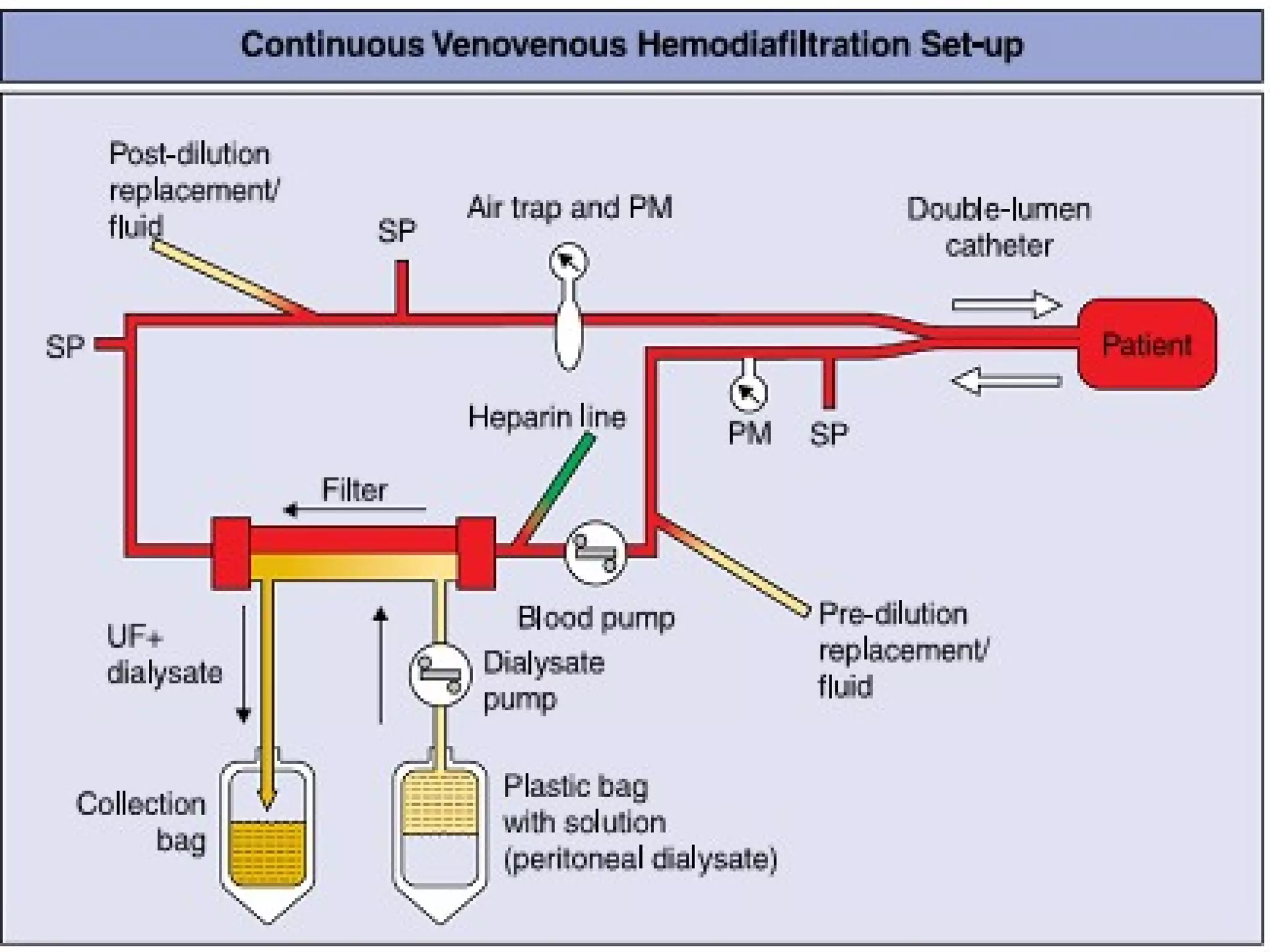
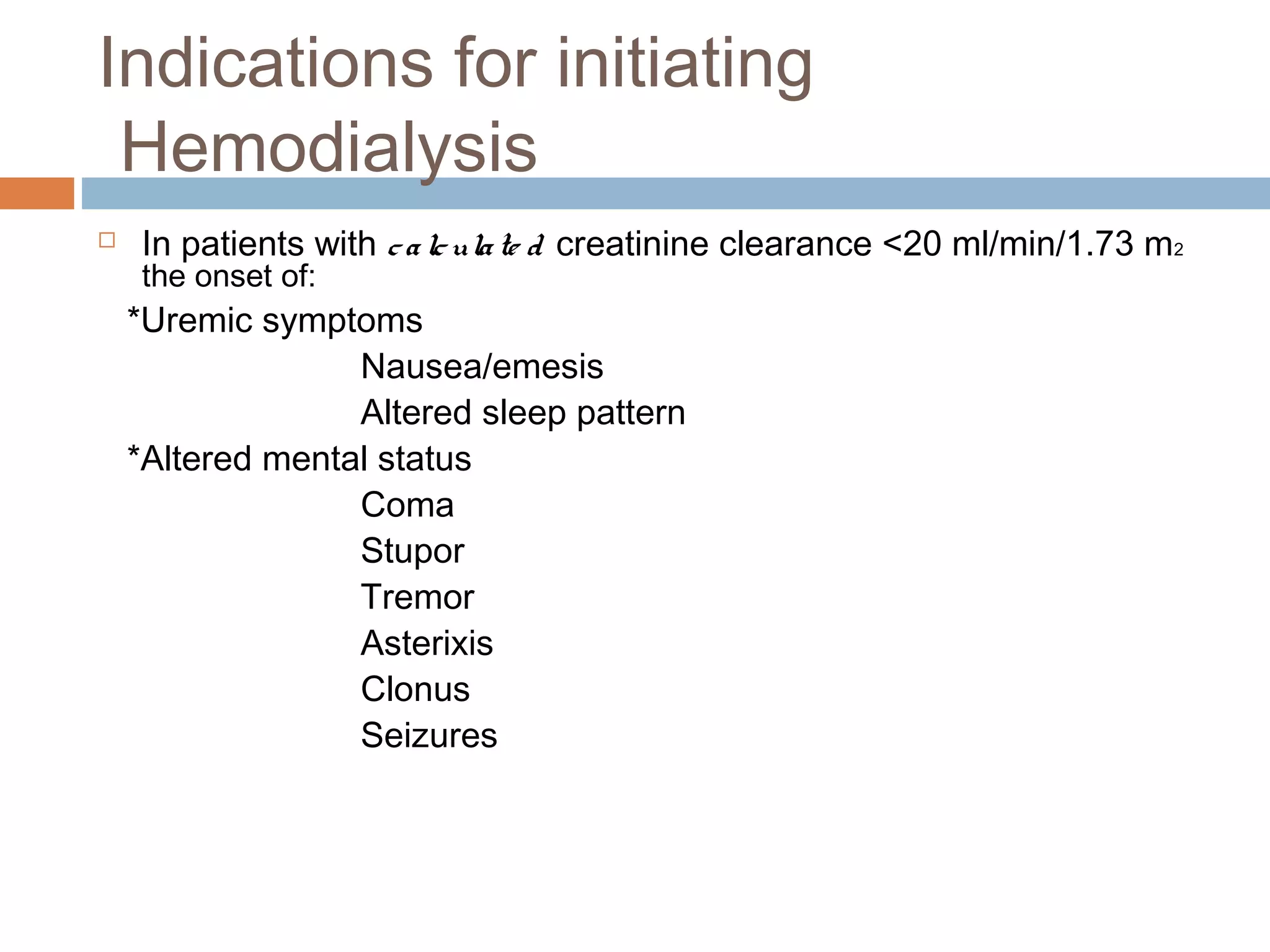
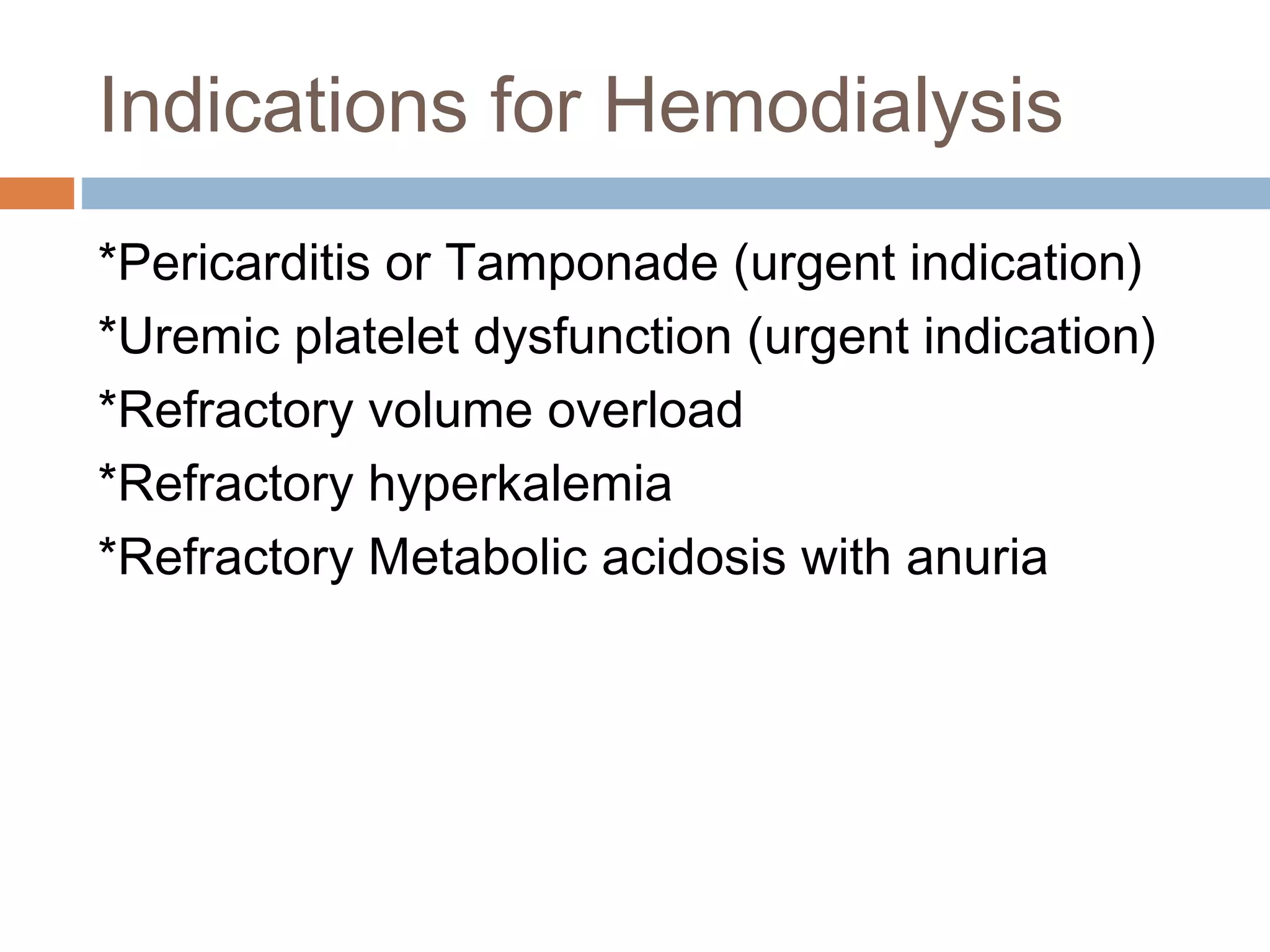
Hemodialysis is a process that uses a semi-permeable membrane to remove waste and excess fluid from the blood of patients with kidney failure. It requires anticoagulation to prevent clotting and knowledge of what substances need to be removed from the blood. Early experiments with dialysis date back to the 18th century, but the first successful hemodialysis treatment in a human was performed by Nils Alwall in 1937 using the Alwall Kidney. Modern hemodialysis utilizes synthetic high or low flux membranes and a dialysate solution to clear waste from the blood through diffusion, convection, osmosis and ultrafiltration. Indications for initiating hemodialysis include symptoms of u