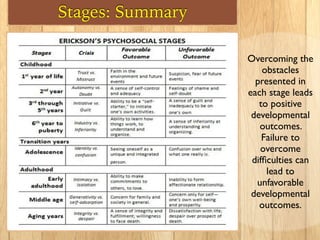
Developmental psychology studies patterns of growth and change throughout life. Two key research methods are cross-sectional research, which compares age groups, and longitudinal research, which studies individuals over many years. Erik Erikson's influential theory of psychosocial development proposed that people progress through eight stages of developing trust, autonomy, initiative, identity and integrity. Successful completion of the challenges in each stage leads to healthy development.