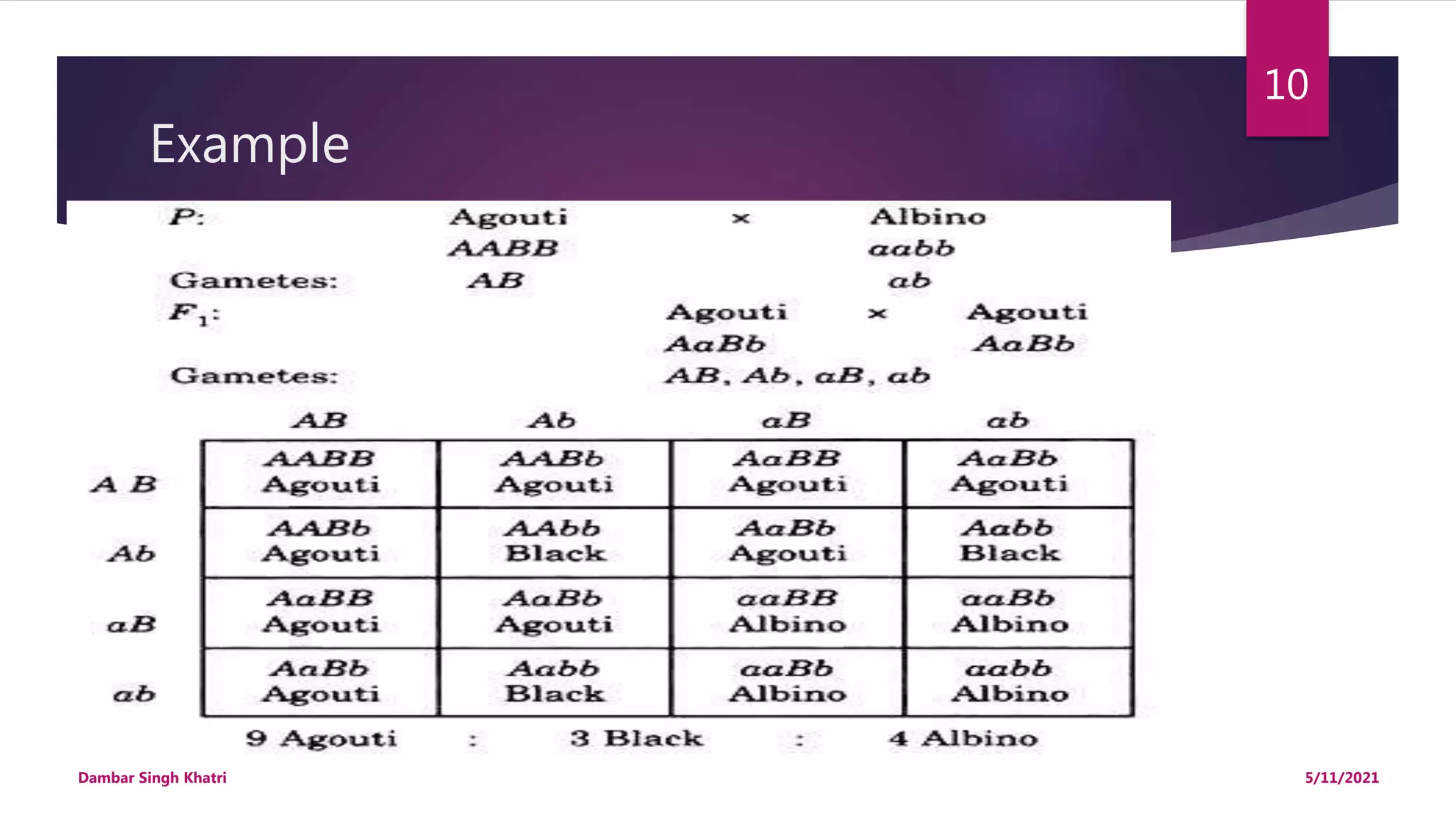
The document discusses the genetic interaction known as epistasis, defining it as a phenomenon where the expression of one gene masks or suppresses the expression of another non-allelic gene. It describes two types of epistasis: dominant epistasis, illustrated through examples in plants, and recessive epistasis, discussed in the context of mice coat color genetics. The document also includes assessments and assignments related to these concepts.