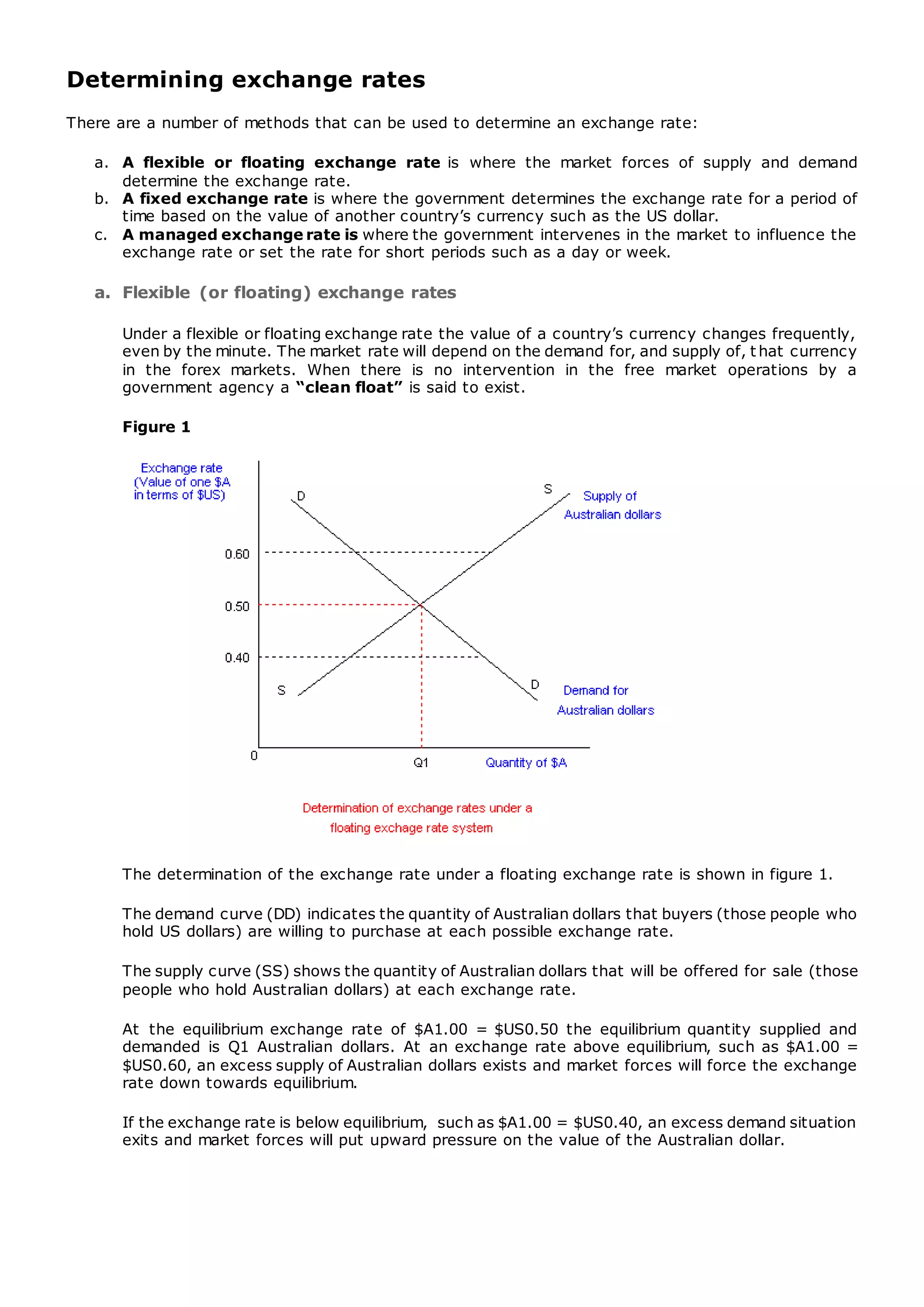
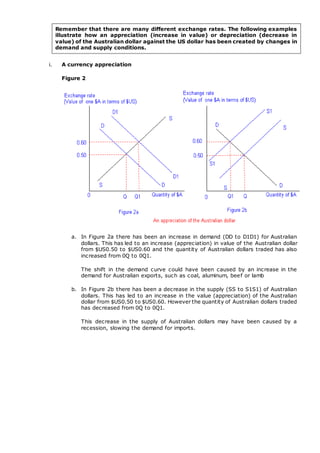
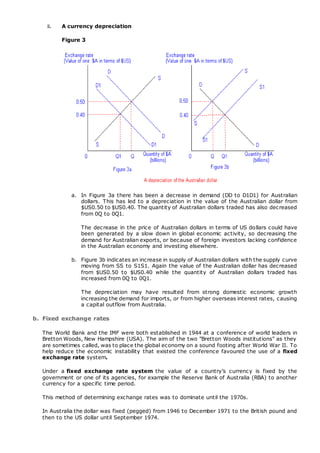
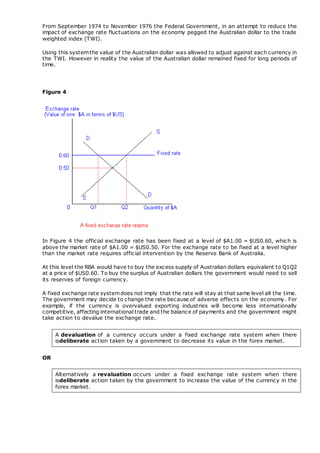
There are three main methods for determining exchange rates:
1) Flexible or floating exchange rates, where market forces of supply and demand determine the rate without government intervention.
2) Fixed exchange rates, where a government pegs its currency to another currency at a set rate for a period of time.
3) Managed exchange rates, where a government intervenes periodically in currency markets to influence exchange rates within a target zone or band.