This document discusses several exchange rate theories, including the traditional or elasticities approach, purchasing power parity (PPP), and interest rate parity (IRP).
The traditional approach assumes an equilibrium exchange rate where a country's imports balance its exports. If imports exceed exports, the exchange rate will fall to make the country's exports cheaper and imports more expensive, balancing trade.
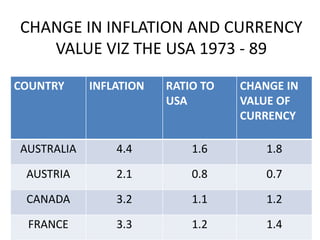
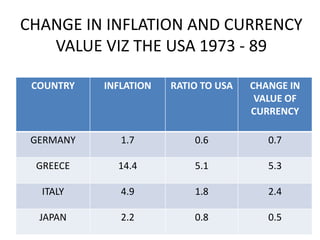
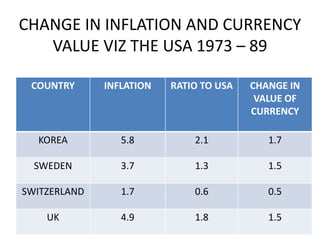
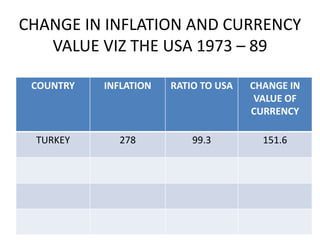
PPP has both an absolute and relative form. In absolute PPP, similar goods should have the same price in different currencies. Relative PPP recognizes market imperfections but holds that inflation rates between countries will offset exchange rate changes over time.
IRP links exchange and money markets, stating that interest rate differences between countries should equal forward exchange