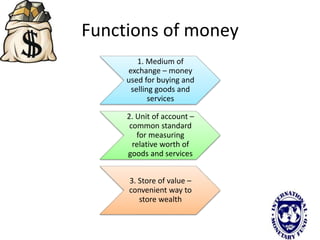
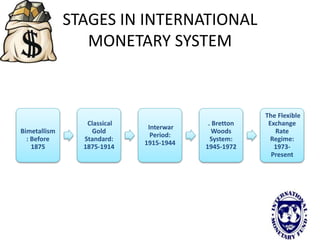
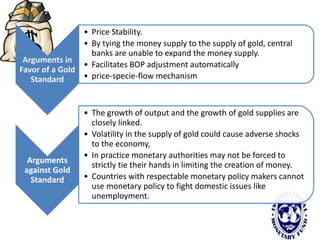
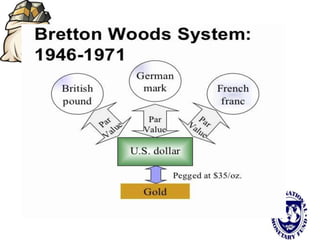
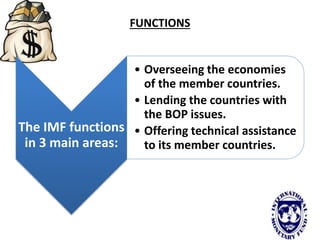
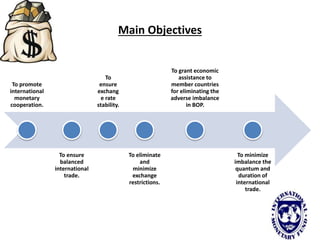
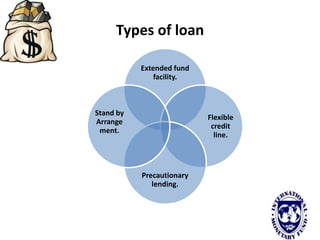
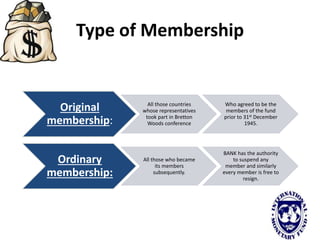
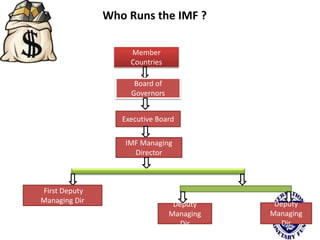
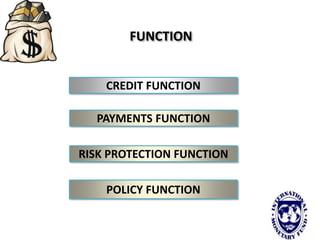
The international monetary system refers to the global network of governments and financial institutions that govern international payments, capital flows, and currency exchange rates. It aims to facilitate international trade and investment. Historically it has taken different forms, including the gold standard (1875-1914), the Bretton Woods system (1945-1972), and currently a flexible exchange rate regime. The International Monetary Fund was established in 1945 to oversee the system and provide emergency loans to countries facing balance of payments crises. It works to promote global monetary cooperation and sustainable economic growth.