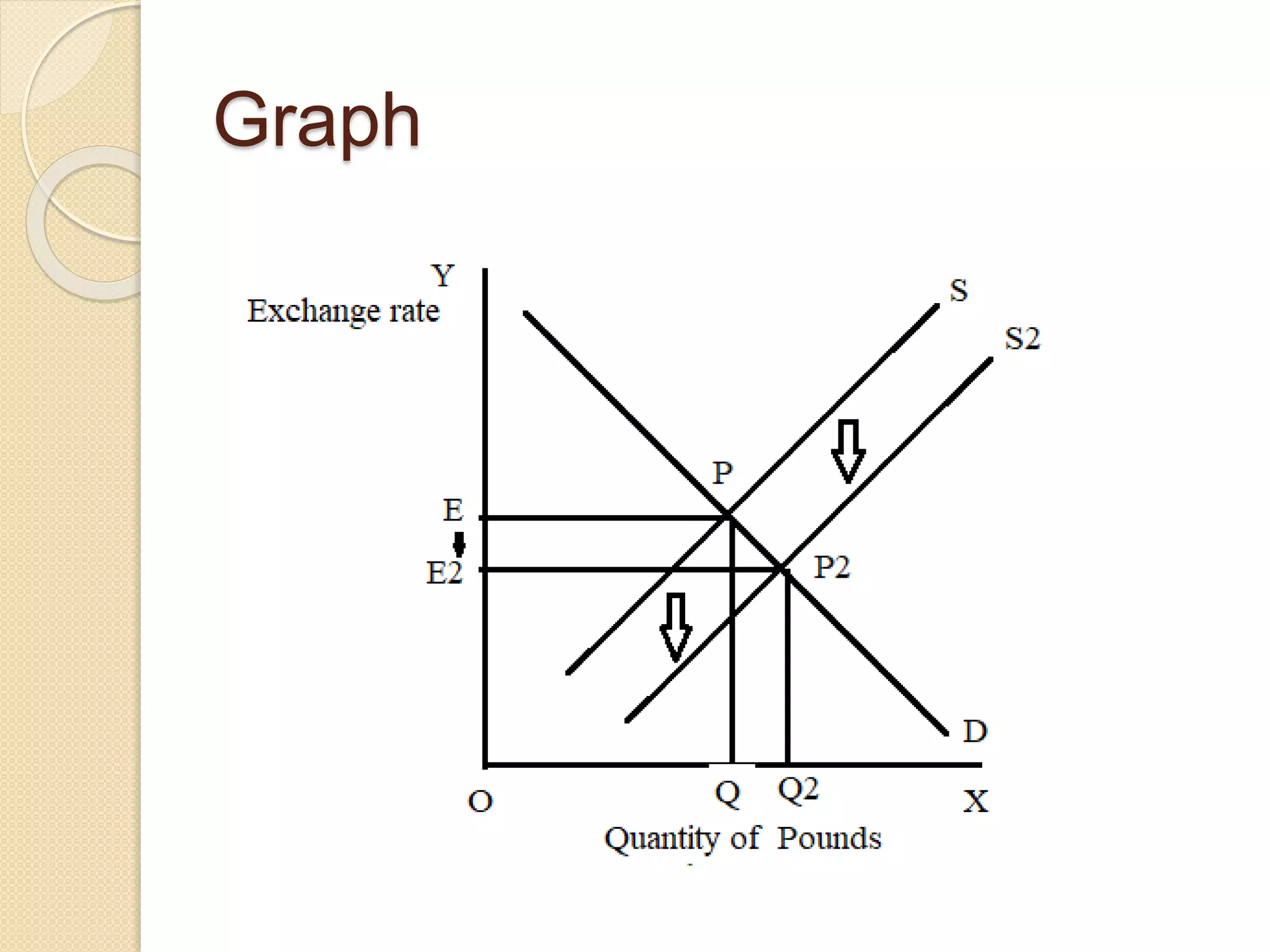
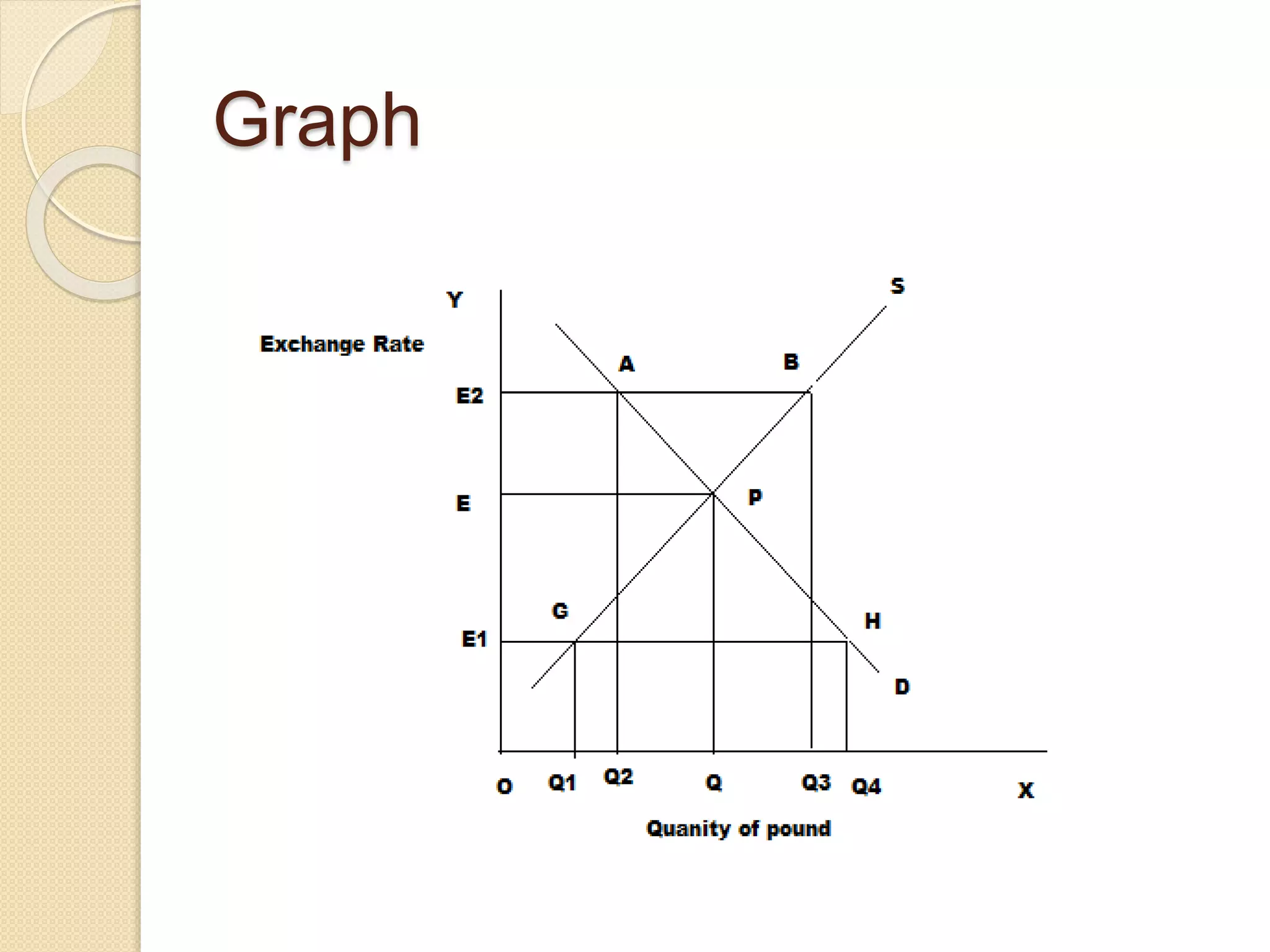
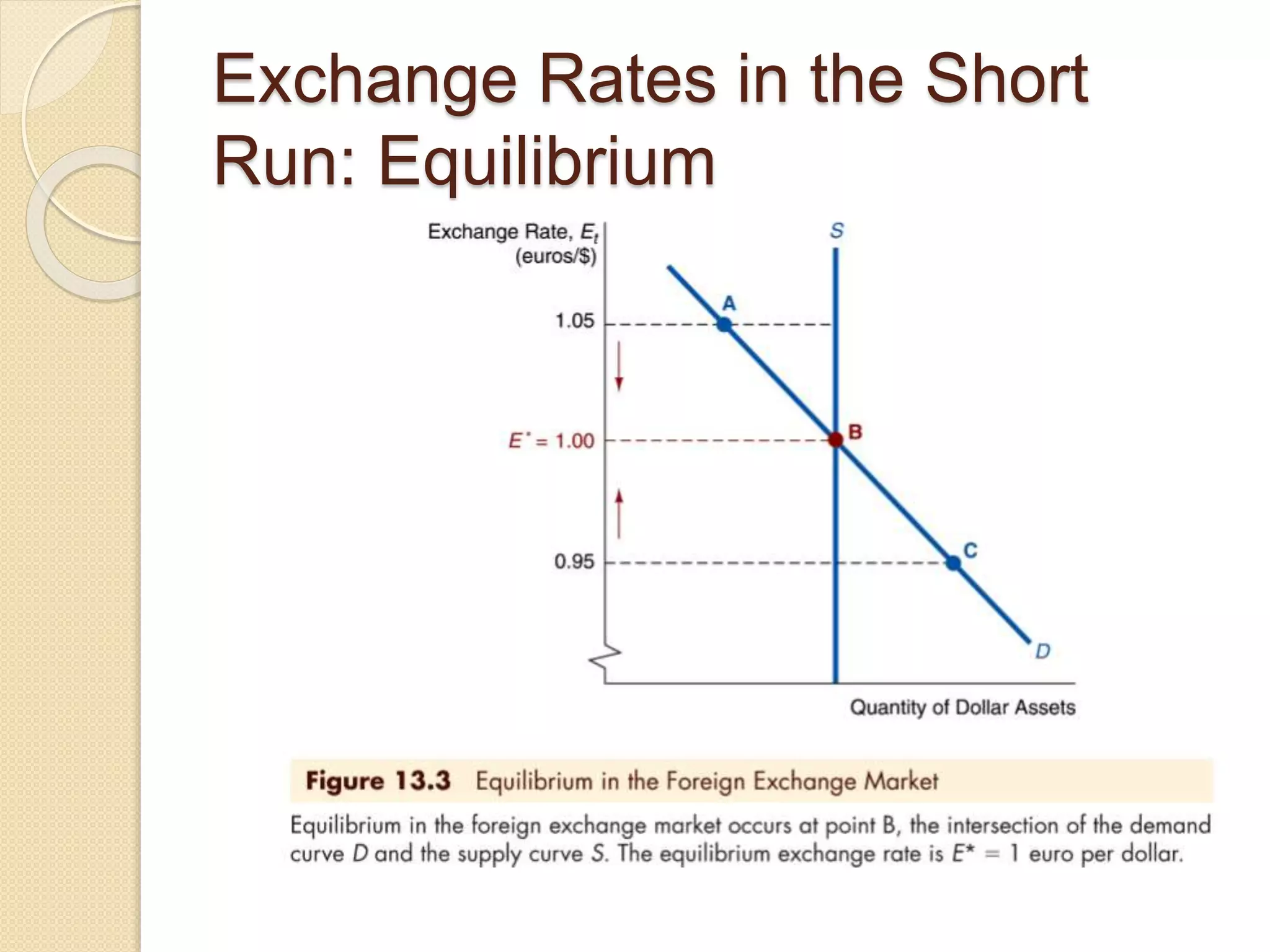
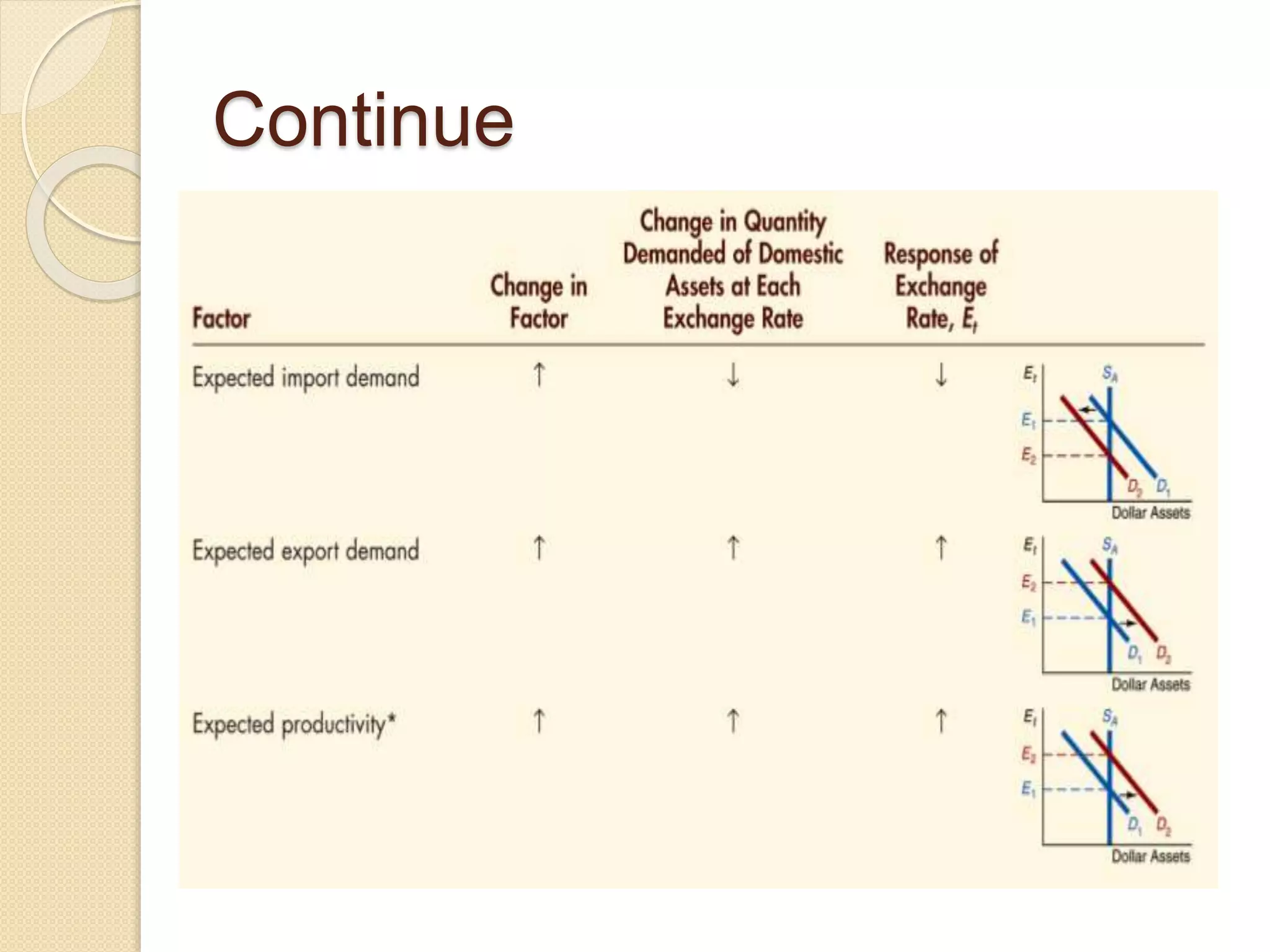
The foreign exchange market determines exchange rates and facilitates international trade and investment. It is a decentralized global market where multiple currencies are traded. Participants include banks, central banks, companies, investors and more. The purpose is to allow businesses to convert one currency to another to facilitate international trade. Under a fixed exchange rate system, a country's central bank pegs its currency value to another currency and intervenes to maintain the peg. A floating system allows market forces to determine exchange rates without central bank intervention. Countries consider factors like financial depth, trade openness and volatility when deciding their exchange rate regime.