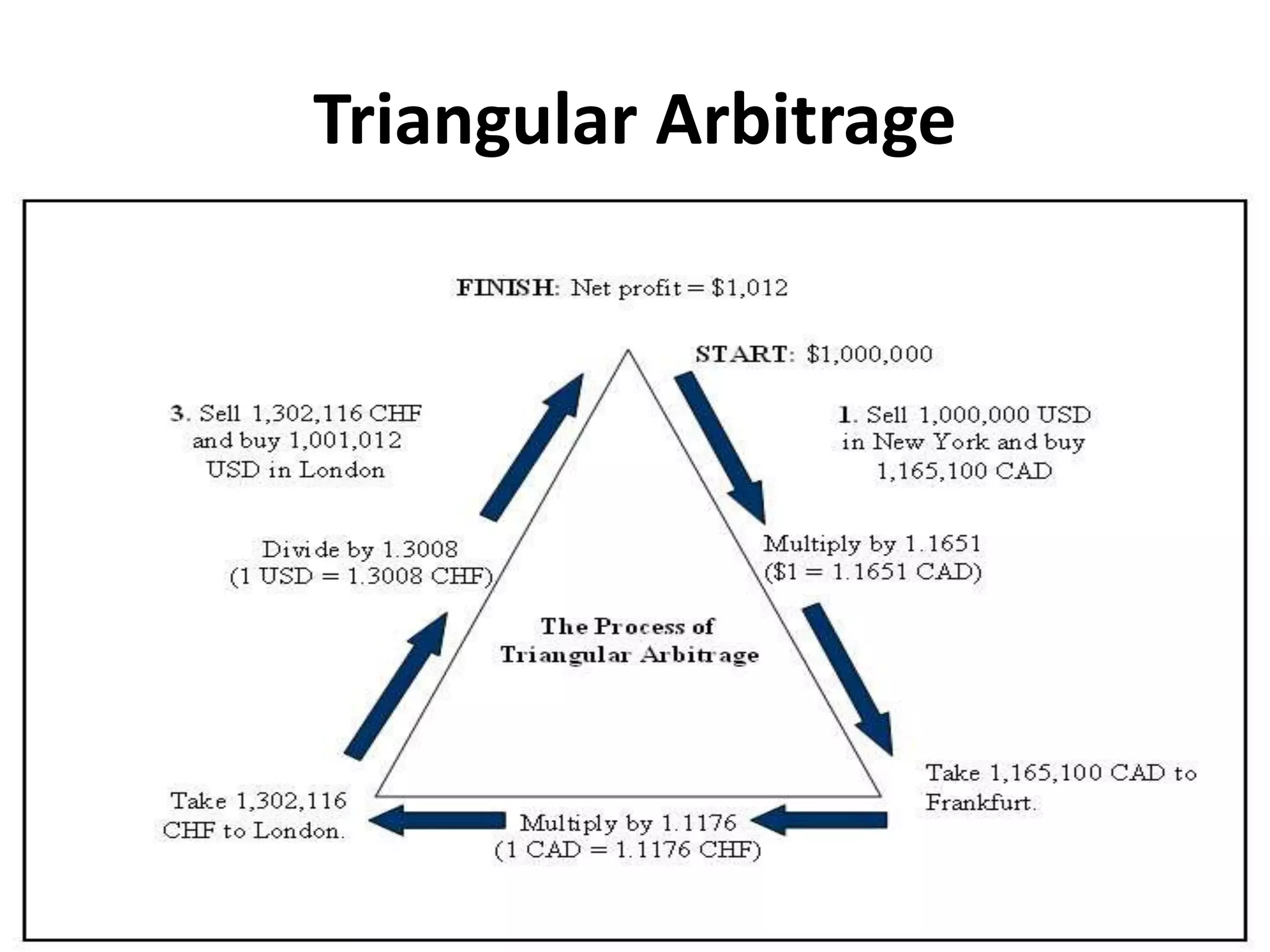
Arbitrage involves purchasing currency where it is cheaper and immediately reselling it where it is more expensive to make a profit. There are different types of arbitrage depending on the number of currencies and locations involved. Covered interest arbitrage moves funds between countries to exploit interest rate differences while hedging exchange rate risk using forward contracts. The international Fisher equation establishes a relationship between exchange rates and interest rates such that any arbitrage profits will be offset over time as markets adjust rates.














![Interest Rate Parity
• Any exchange gains / losses incurred by simultaneous
purchase / sale in spot and forward markets are offset
by interest rate differential on similar assets.
RHS = [{SX(1+p)}/S] * (1+ic) = (1+ic) * (1+p)
Where, p = forward premium.
p= [(1+i$)/(1+ic)] - 1 = [(i$- ic)/(1+ic)]
• In approximated form, p = i$- ic, provides a reasonable
estimate when the interest rate differential is small.
• Interest Rate Parity hold when the Covered Interest
Arbitrage does not exist.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coveredinterestarbitrage12-201204131924/75/Covered-interest-arbitrage-1-2-16-2048.jpg)



