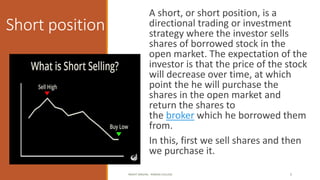
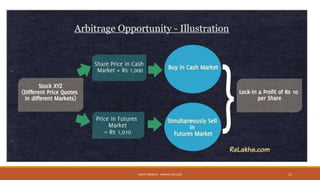
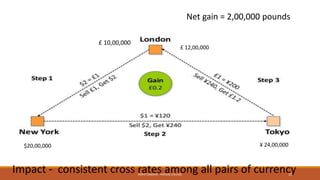
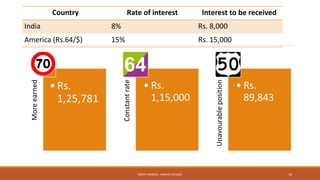
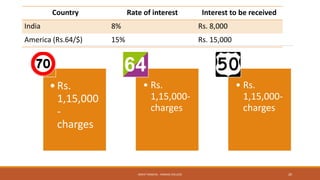
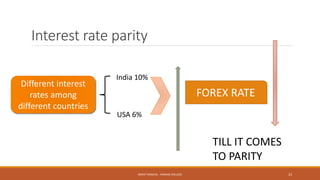
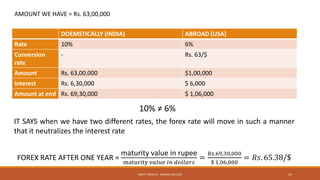
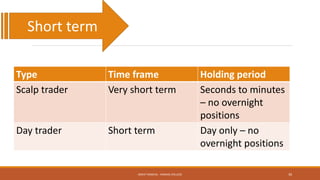
The document provides an overview of essential terms in forward markets, explaining concepts like forward rates, long and short positions, forward premium and discount, and arbitrage. It details the mechanisms of two-point and three-point arbitrage, as well as interest arbitrage, highlighting the differences between uncovered and covered strategies. Additionally, it discusses hedging as a risk management strategy in foreign exchange trading and outlines the role of speculators in the market.