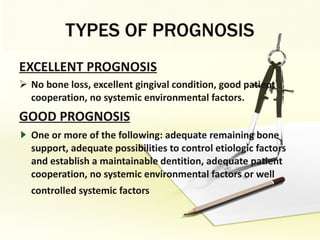
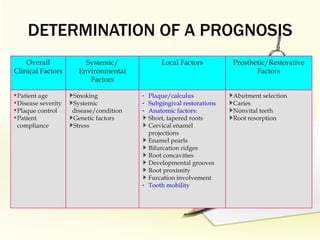
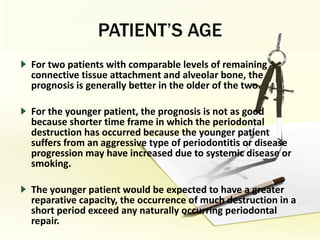
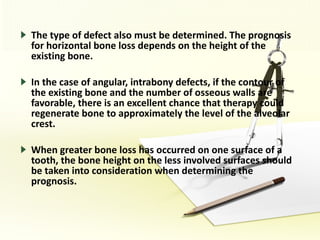
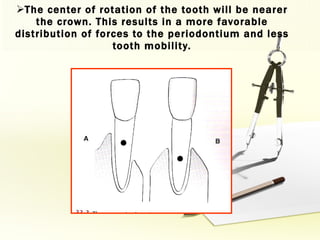
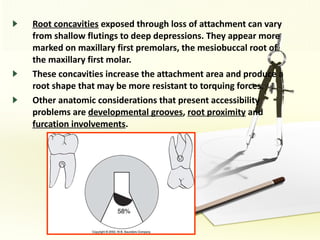
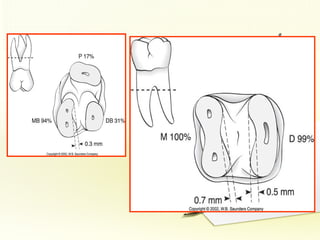
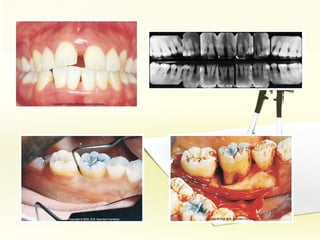
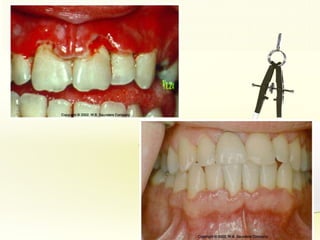
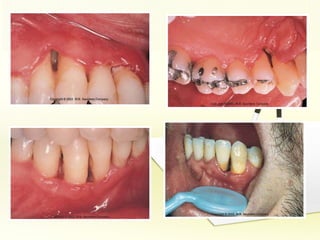
The document discusses factors involved in determining the prognosis and treatment plan for periodontal disease. It defines prognosis as a prediction of the course and outcome of a disease based on risk factors. Several types of prognoses are described from excellent to poor based on remaining bone support, tooth mobility, furcation involvement, maintenance difficulties, and presence of systemic/environmental factors. Both overall and individual tooth prognoses are considered based on patient age, disease severity, plaque control, compliance, smoking, systemic disease, genetic factors, subgingival restorations, and anatomic root factors. A favorable prognosis requires adequate bone support, control of etiologic factors, patient cooperation and absence of negative systemic influences.