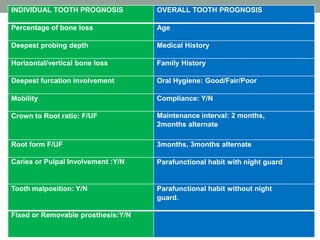
This document discusses prognosis in periodontal disease. It defines prognosis as the prediction of the course and outcome of a disease based on general knowledge of pathogenesis and risk factors. Prognosis is classified on a scale from excellent to hopeless based on factors like bone loss, patient cooperation, and systemic conditions. Key prognostic factors include disease severity, plaque control, smoking, diabetes, genetic factors, tooth mobility, furcation involvement, and anatomic abnormalities. A favorable prognosis indicates periodontal stability with treatment, while an unfavorable prognosis means further breakdown is likely despite therapy. Prognosis for gingivitis is generally good if plaque is controlled, while prognosis for periodontitis depends on the severity and controllability of local and