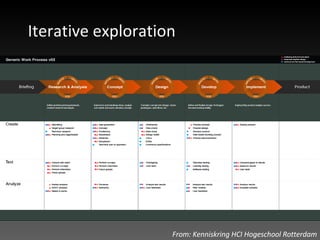
The document discusses the importance of design rationale for an iterative design process. It emphasizes that design is a collaborative effort that requires input from others. An explicit design rationale documents the design process, key decisions, and underlying reasons for those decisions based on research. This helps prevent locking into early decisions as requirements change and promotes a shared understanding of the design.