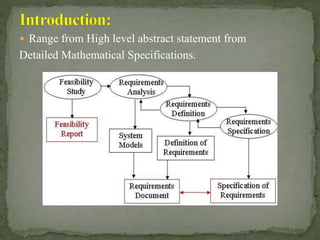
The document discusses the key steps in the requirements engineering process: inception to gather initial information, elicitation to identify stakeholders and understand needs, elaboration to further analyze functions and constraints, negotiation to resolve conflicts, specification to formalize requirements, validation to ensure requirements are unambiguous, and management of requirements throughout the project. Some challenges of requirements engineering include defining system boundaries, understanding technical domains, and handling volatile requirements that may change over time.