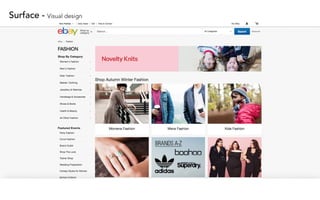
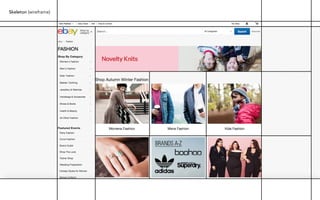
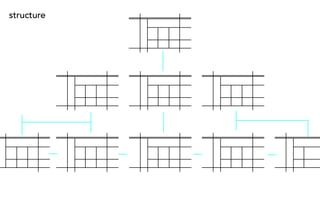
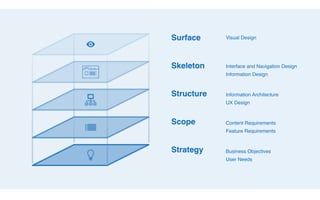
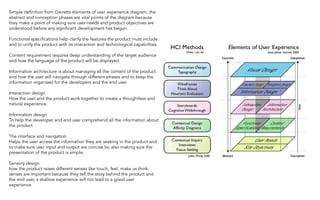
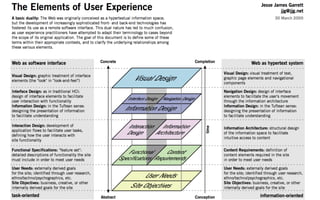
Jesse James Garrett created an influential model for user experience design called "The Elements of User Experience". This model lays out a hierarchy for designing from the ground up in UX. The presentation will use examples to explain insights gained from investigating Garrett's book of the same title. Garrett's model includes the surface/visual design, the skeleton/wireframe underneath, and the interface/navigation. It also encompasses the less visible levels of scope, structure and strategy to define the user needs, product vision, and development process from an experience-focused perspective.