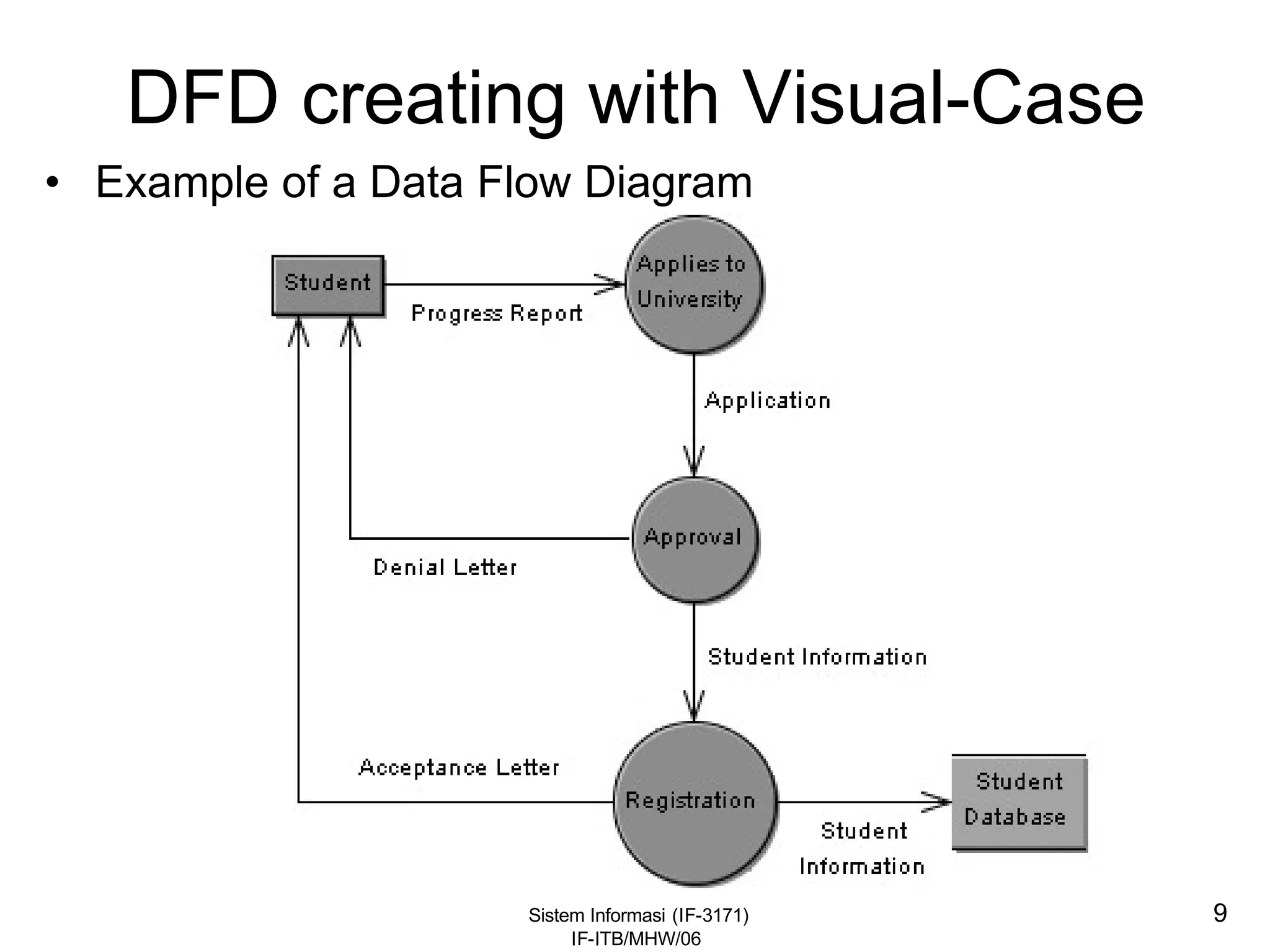
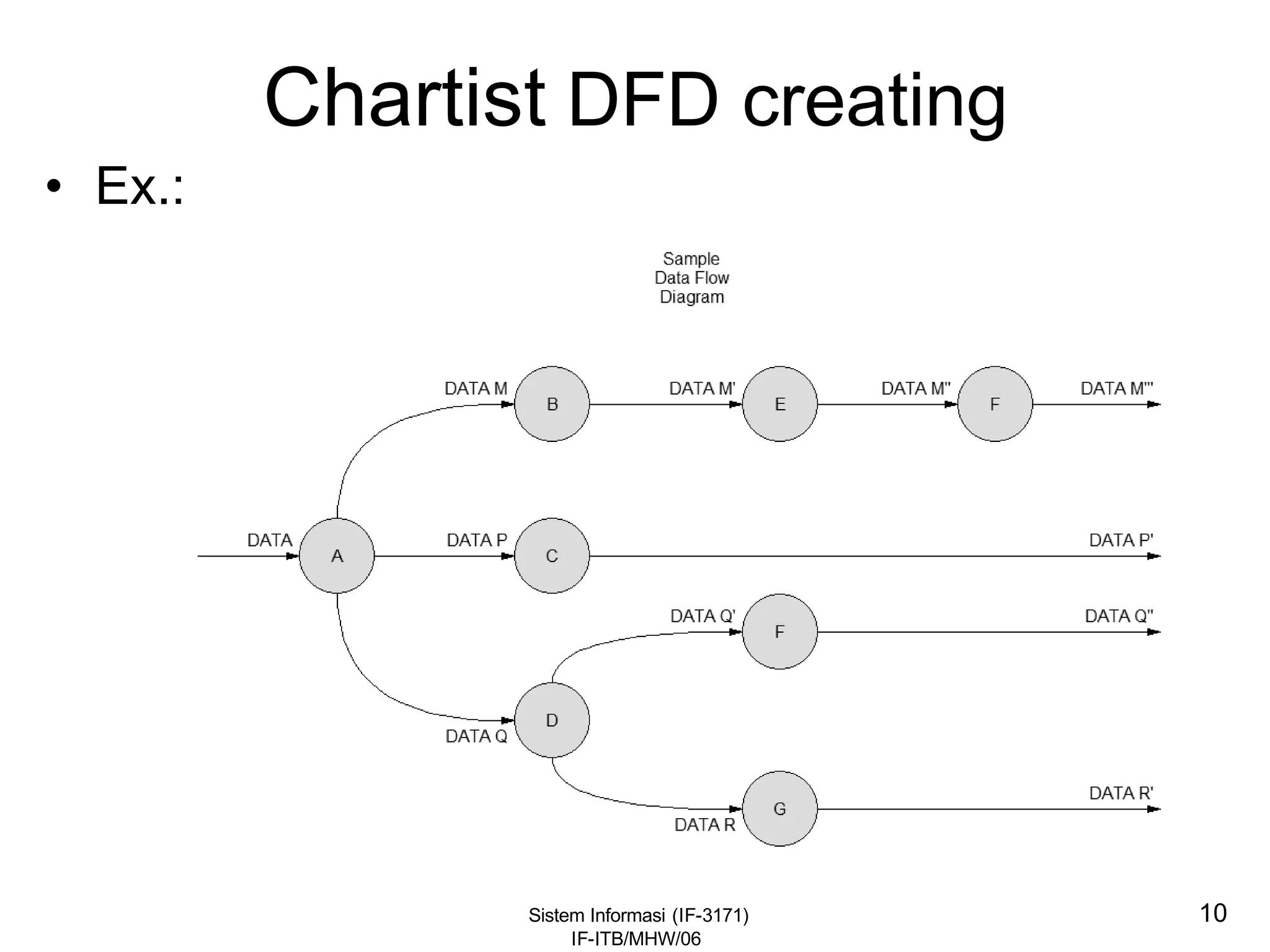
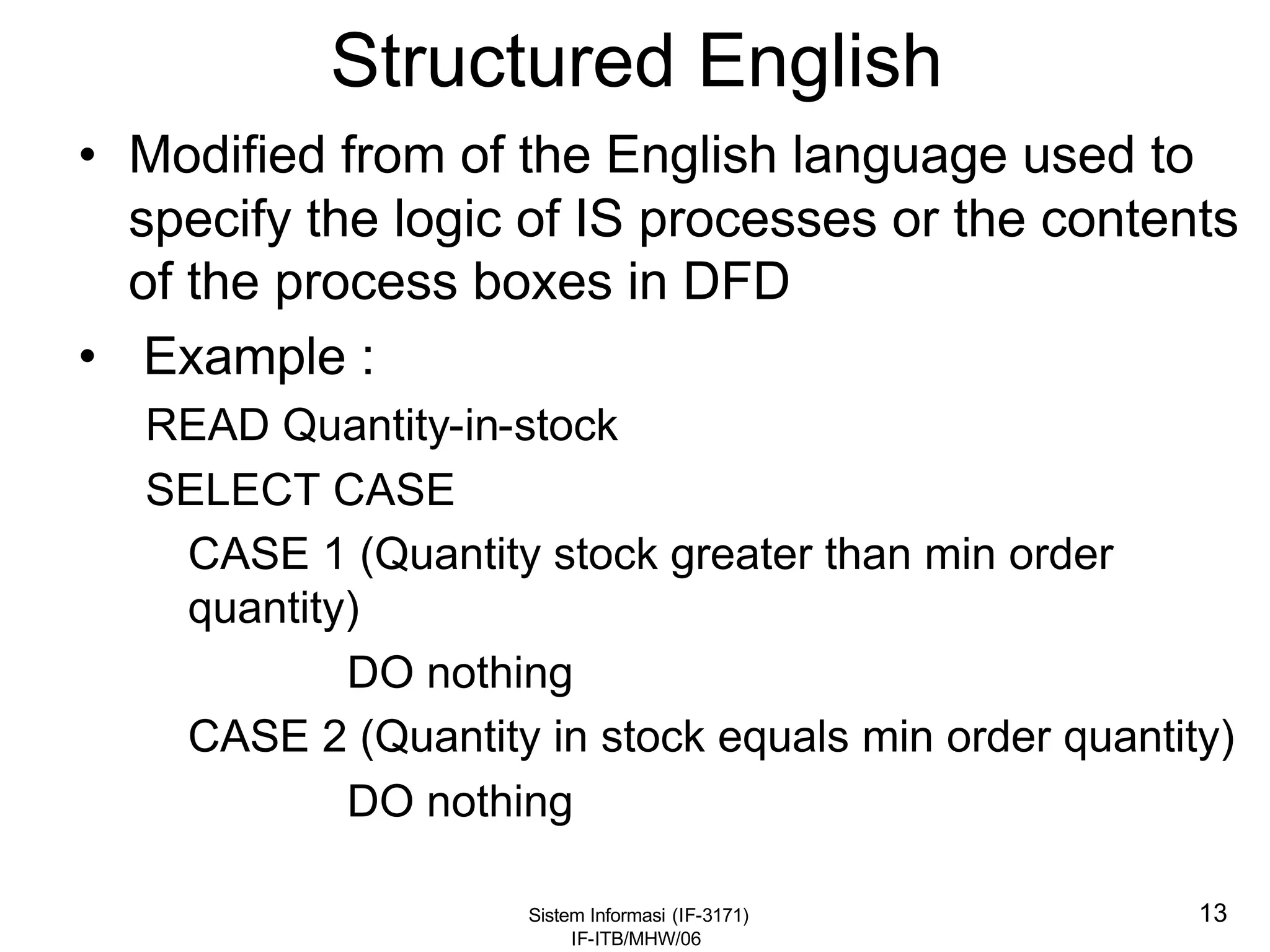
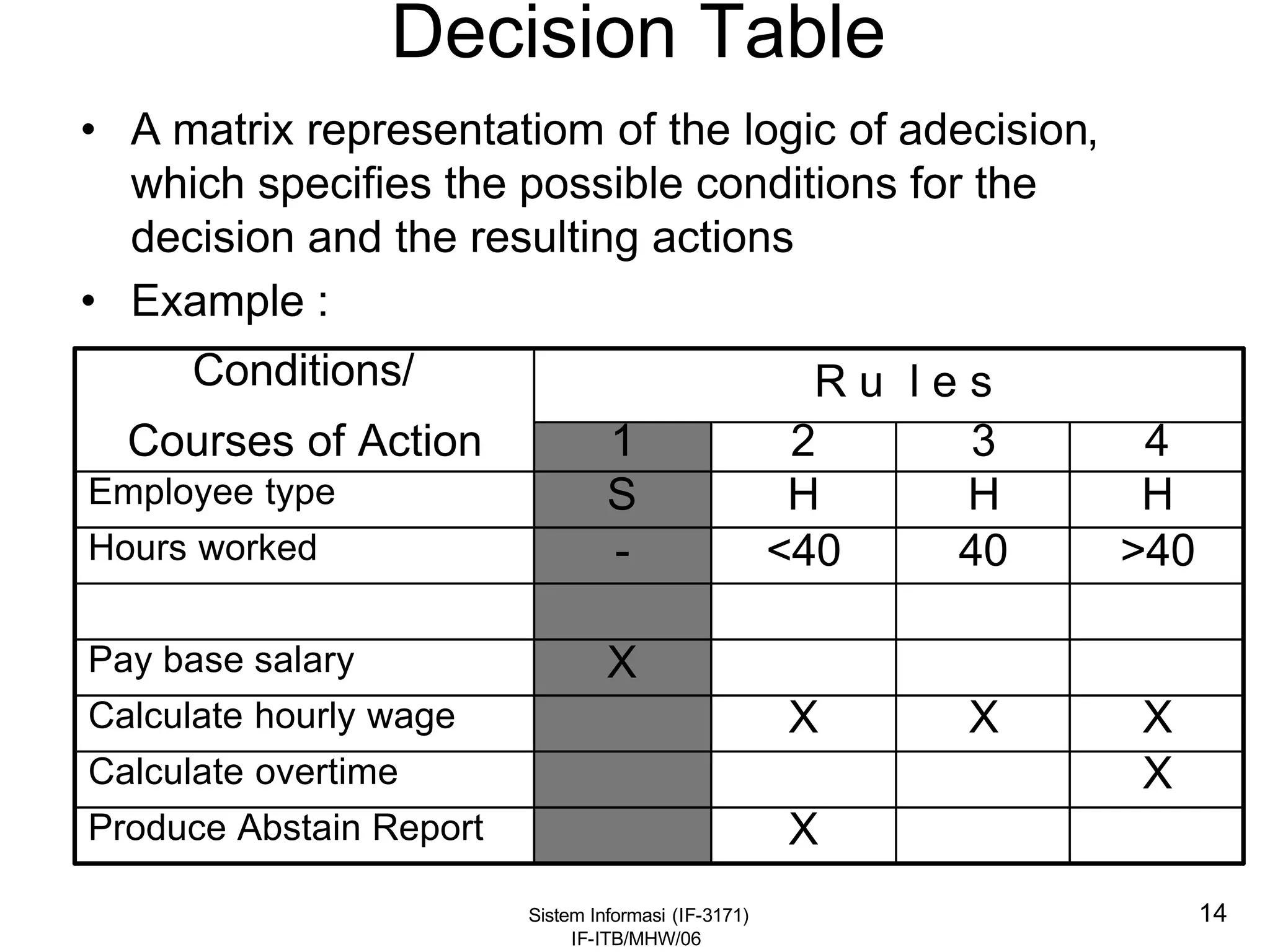
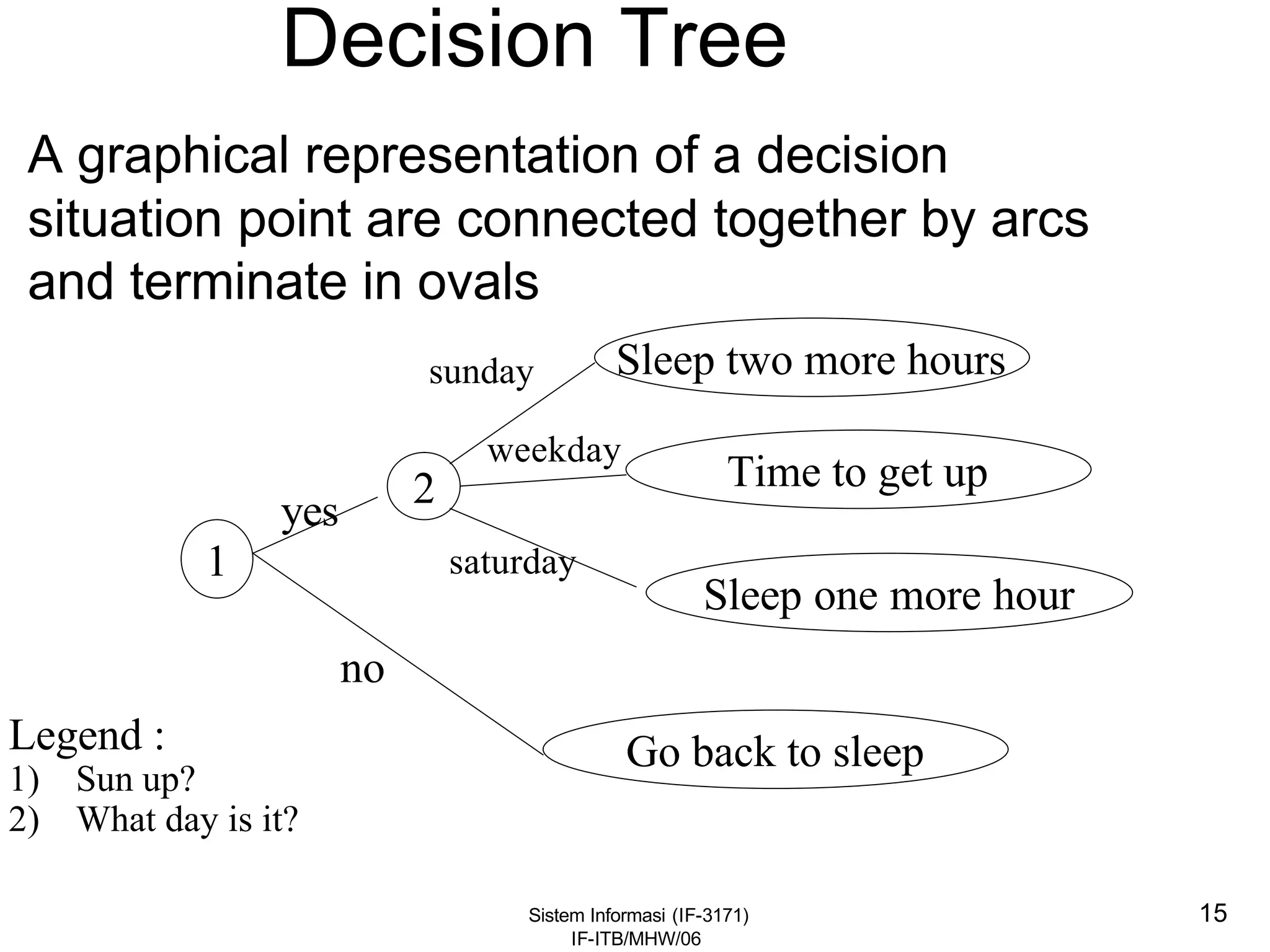
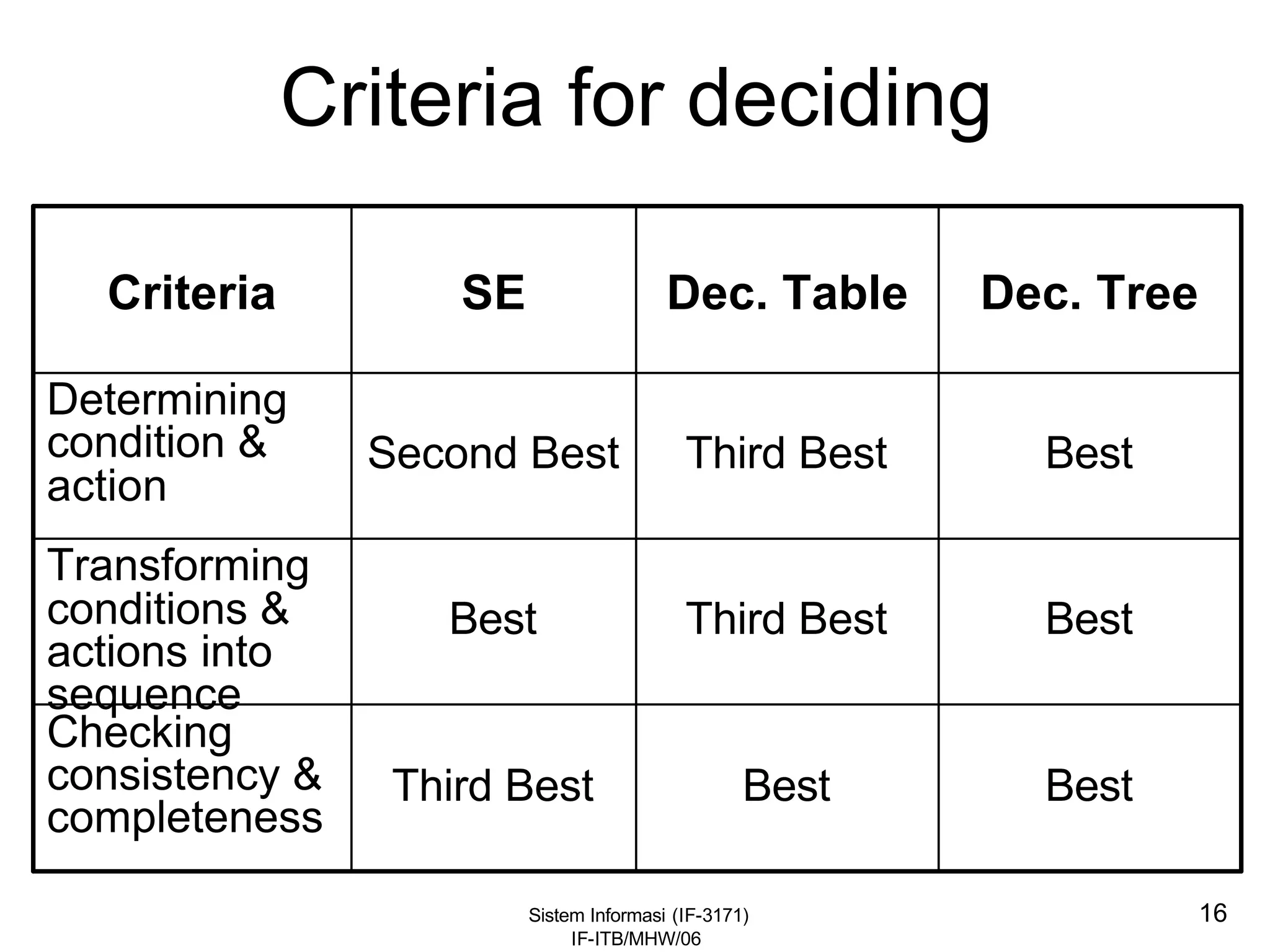
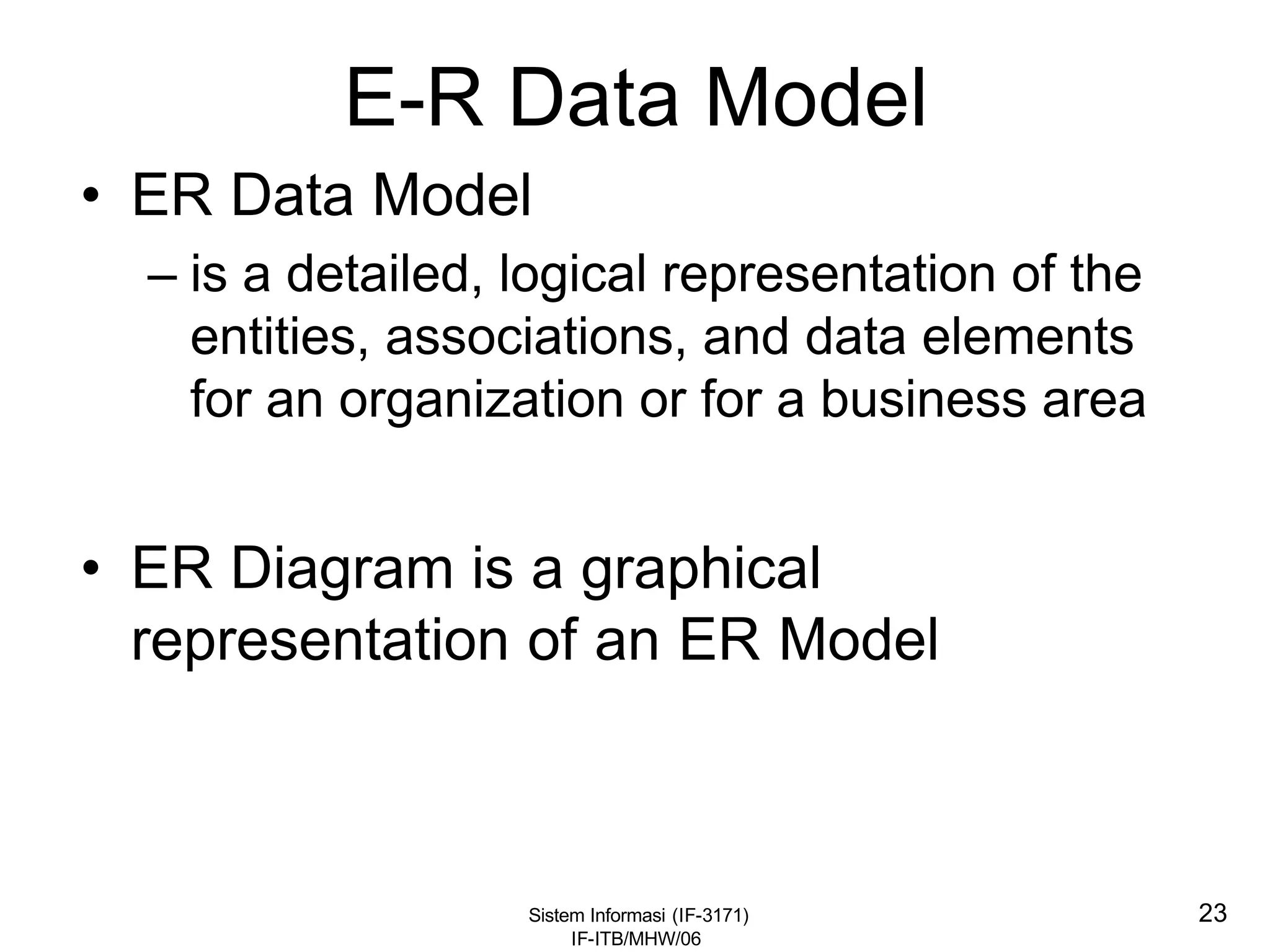
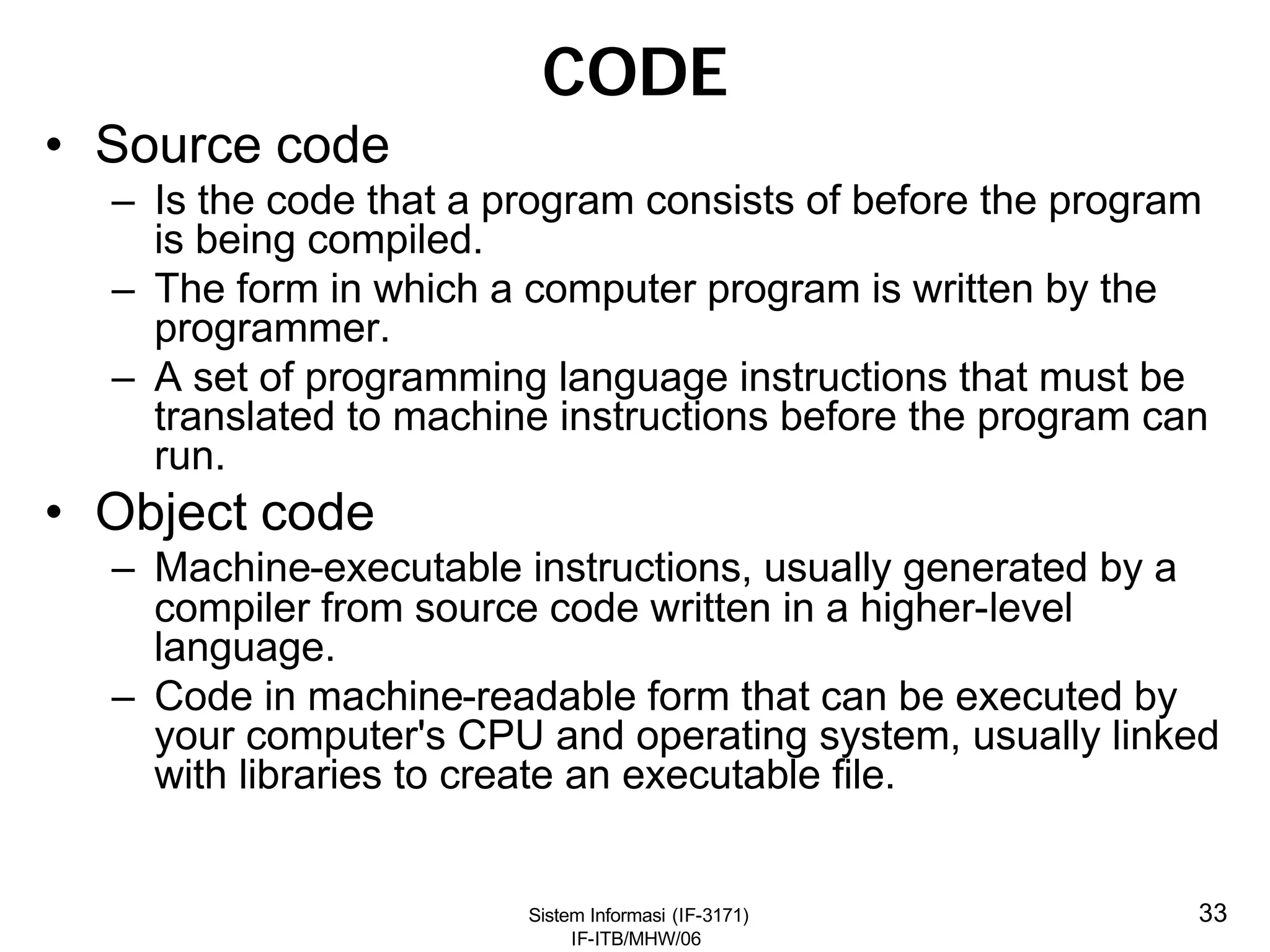
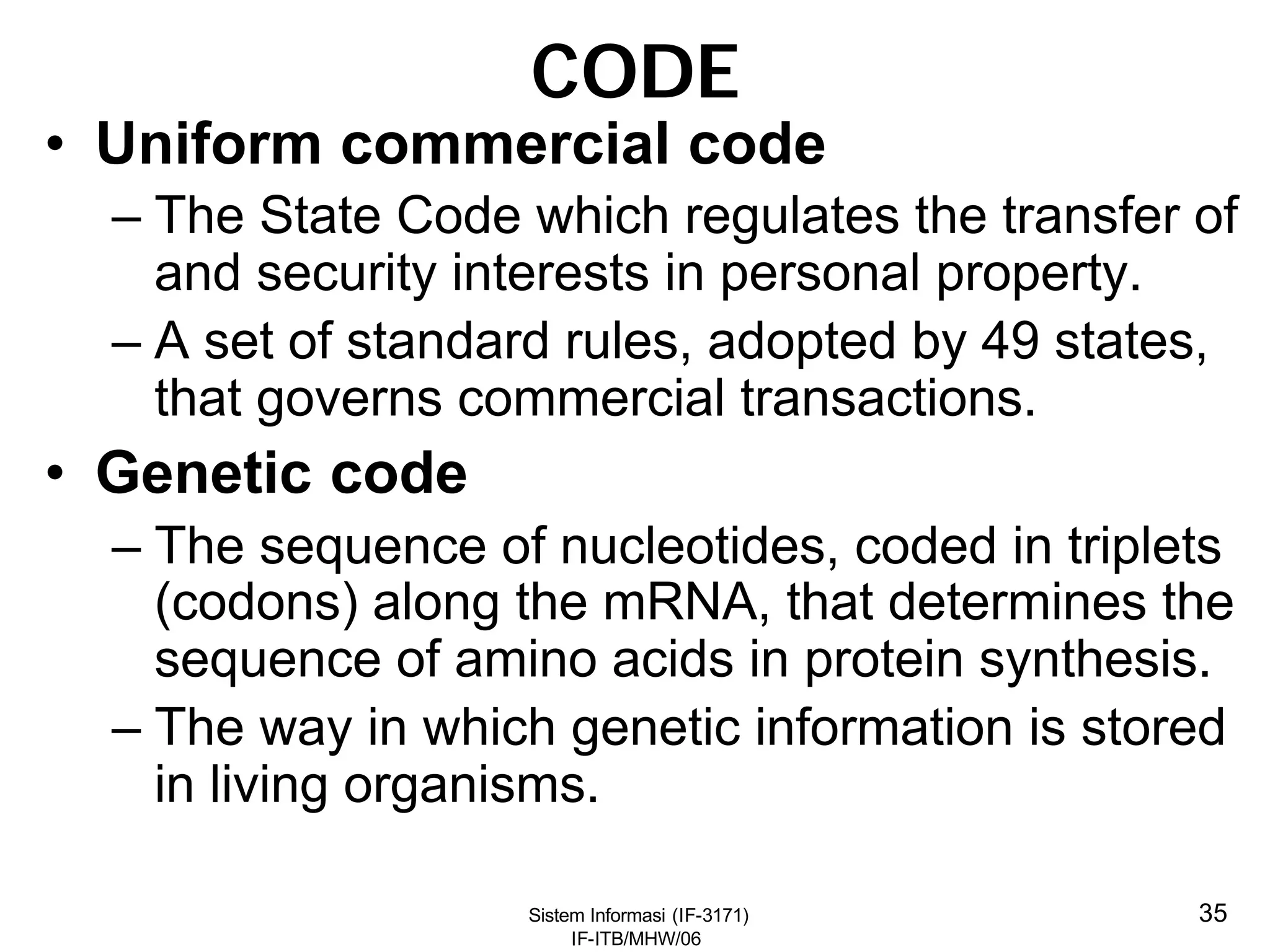
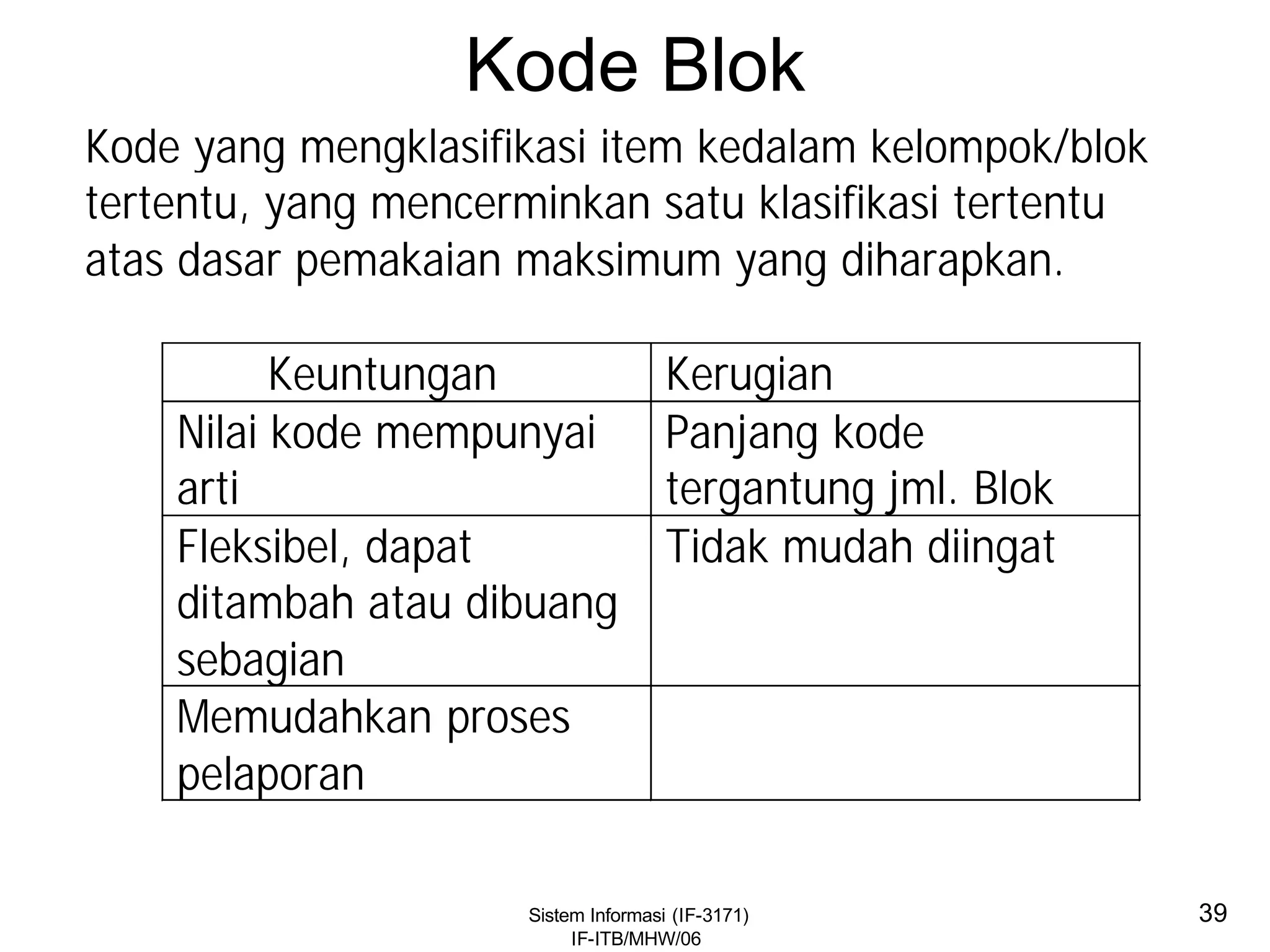
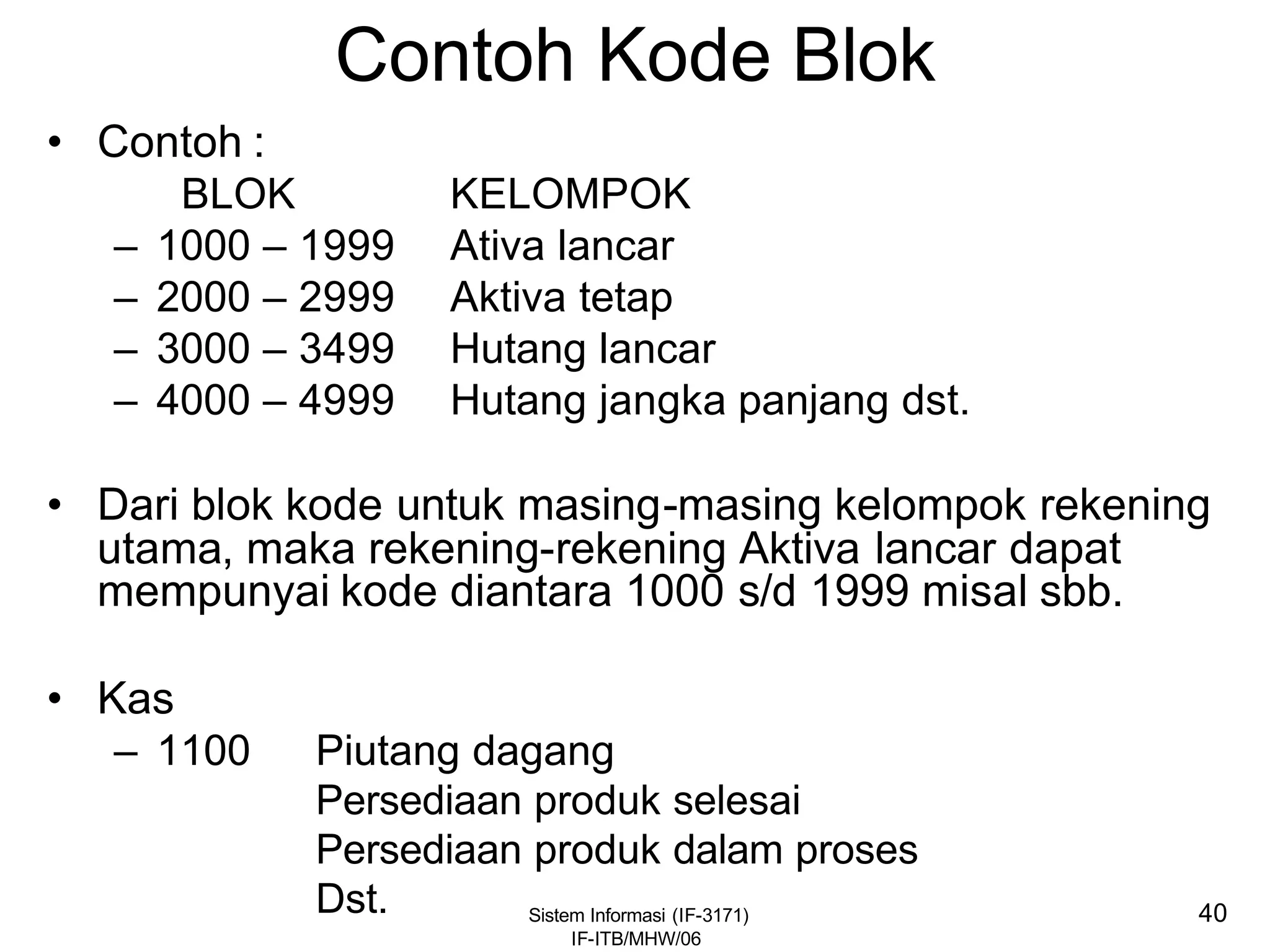
This document discusses coding systems and different types of codes. It defines source code, object code, universal product codes, barcodes, and genetic codes. It also discusses the purpose of coding which includes providing unique and concise identifiers, assigning special meanings in data processing, reducing data volume, and increasing process accuracy. Coding can use numeric, alphabetic, alphanumeric, or special characters. Considerations for code design include ease of remembering, uniqueness, flexibility, efficiency, consistency, and uniform length. Common code structures are sequential, group, block, and mnemonic codes.