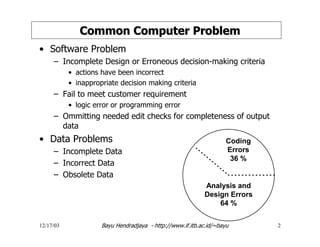
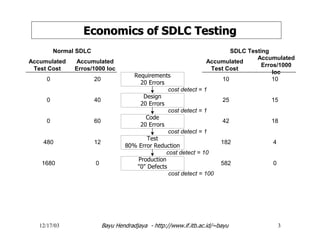
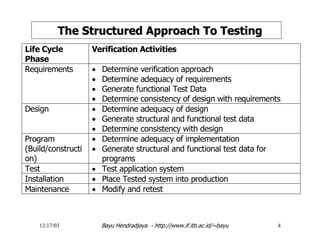
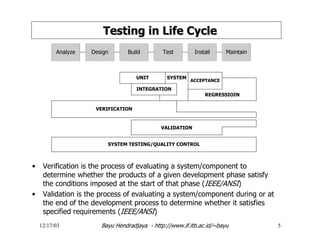
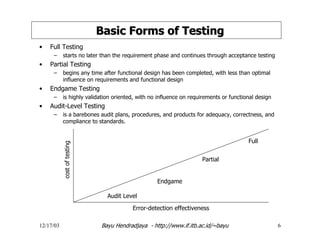
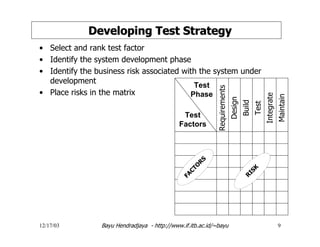
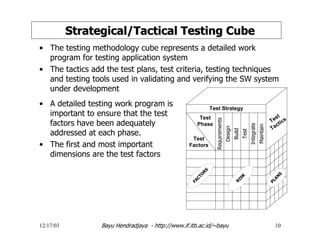
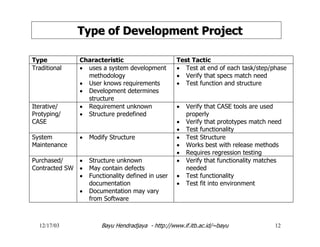
The document discusses software testing and strategies for effective testing. It explains that software problems can arise from incomplete design, erroneous criteria, or failing to meet requirements. Testing aims to reduce errors by 80% and catch them earlier in the software development lifecycle when they are cheaper to fix. A structured testing approach verifies requirements, design, code, and more across development phases. Different forms of testing provide varying levels of coverage from full testing throughout to only audit-level testing. Risks include incorrect results, security issues, and reliability problems. An effective test strategy addresses these risks through test factors and phases. Tactics then provide detailed test plans, criteria, and tools to validate and verify the system.