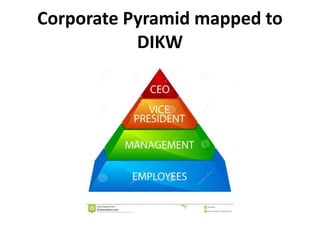
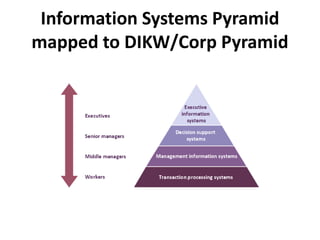
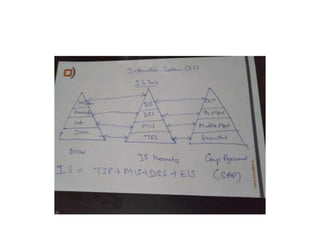
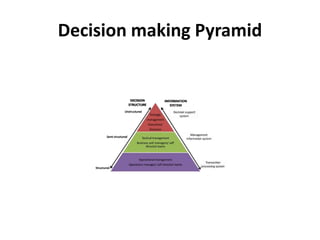
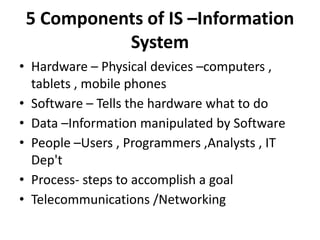
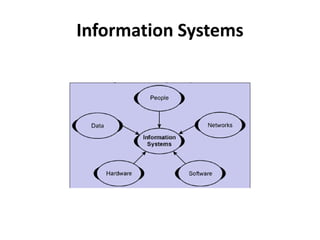
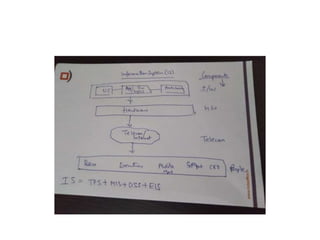
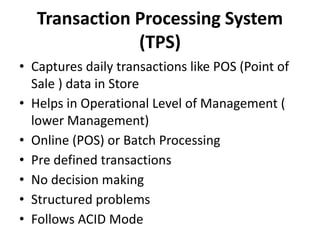
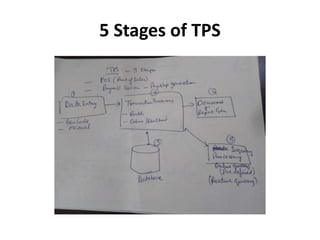
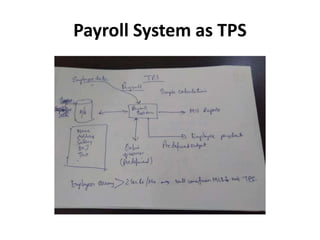
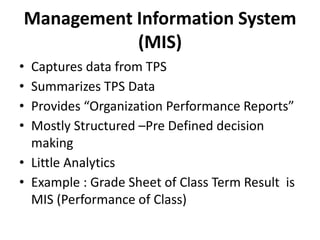
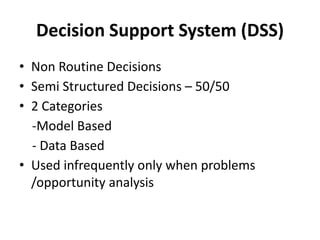
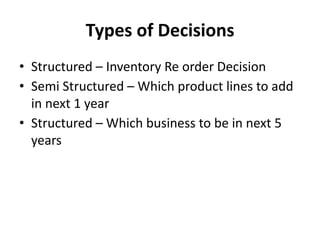
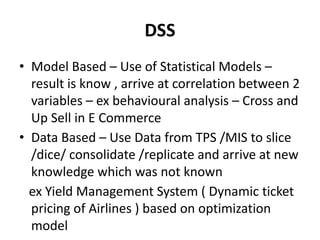
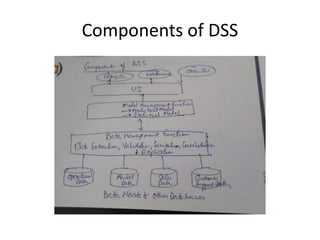
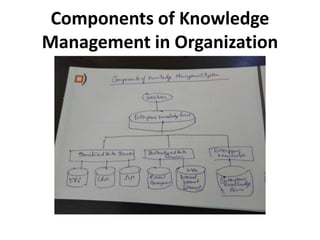
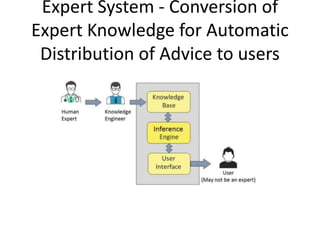
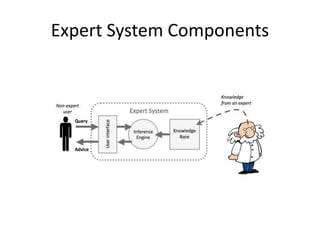
This document provides an introduction to information systems for non-technical managers. It discusses how information systems are designed to help managers understand the implications of technology and prepare for advances like artificial intelligence. The document then outlines several key topics that will be covered, including data, information, knowledge, and different models that illustrate their relationships. It also defines what an information system is and distinguishes between information technology and information systems.