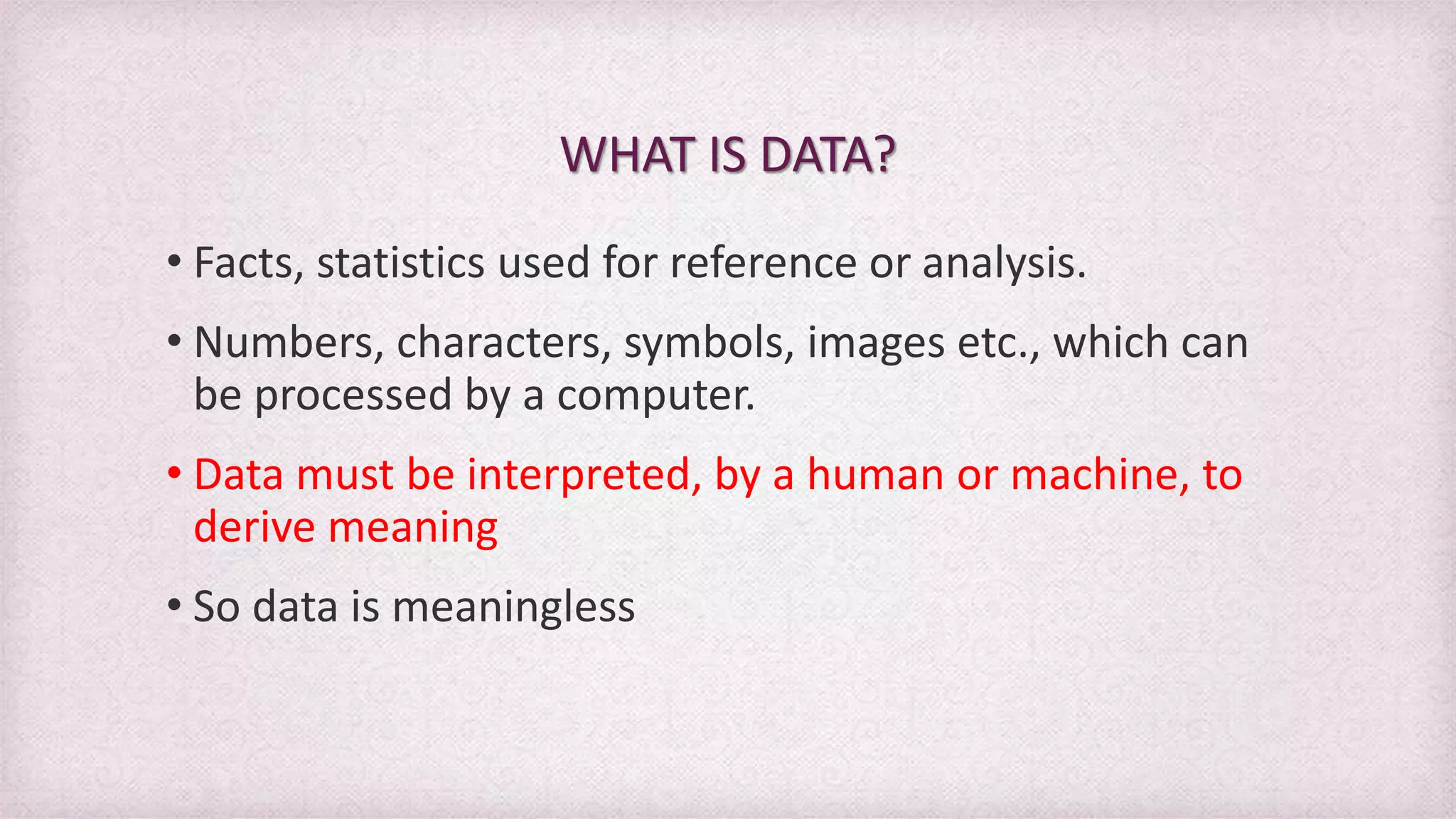
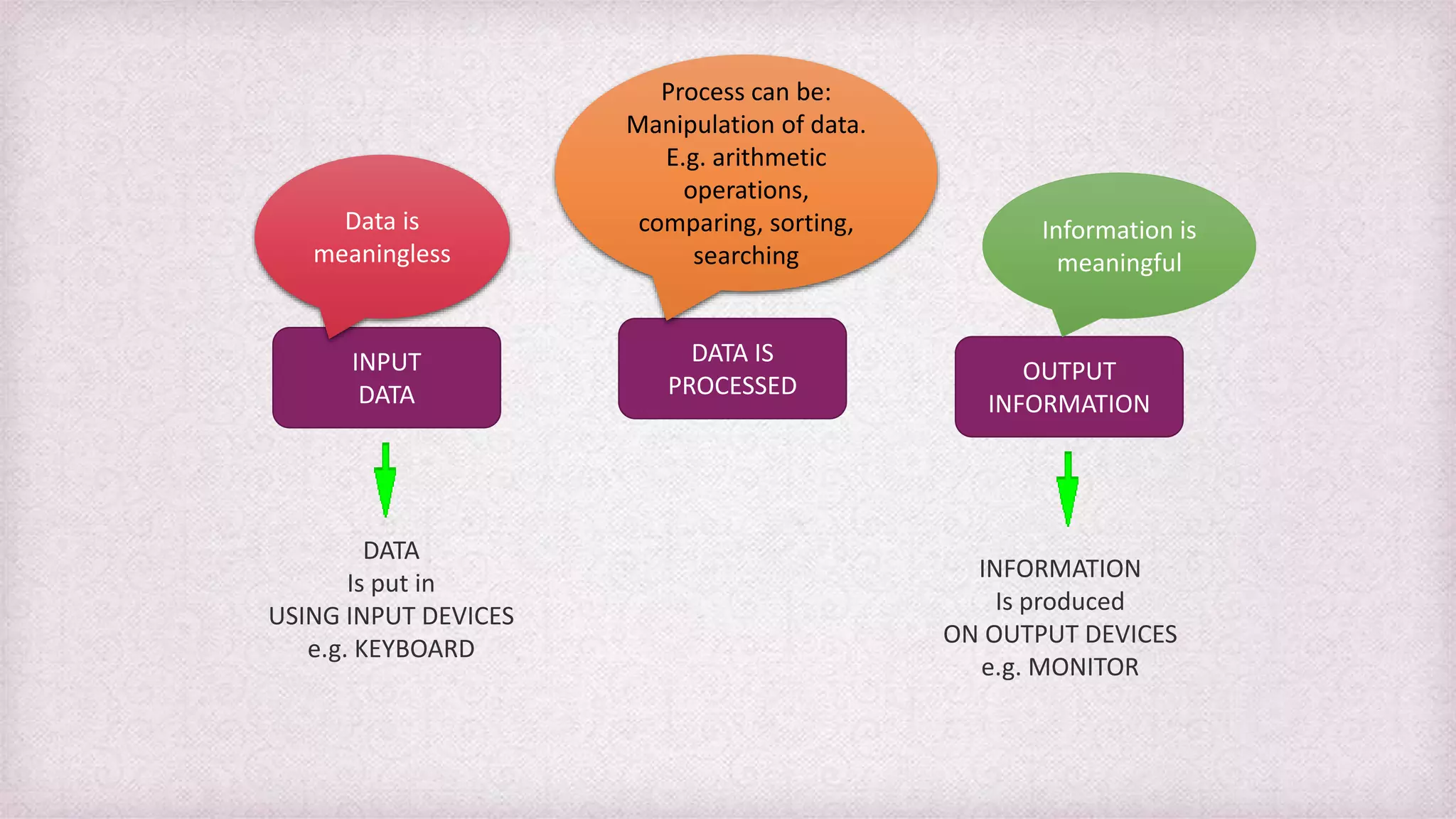
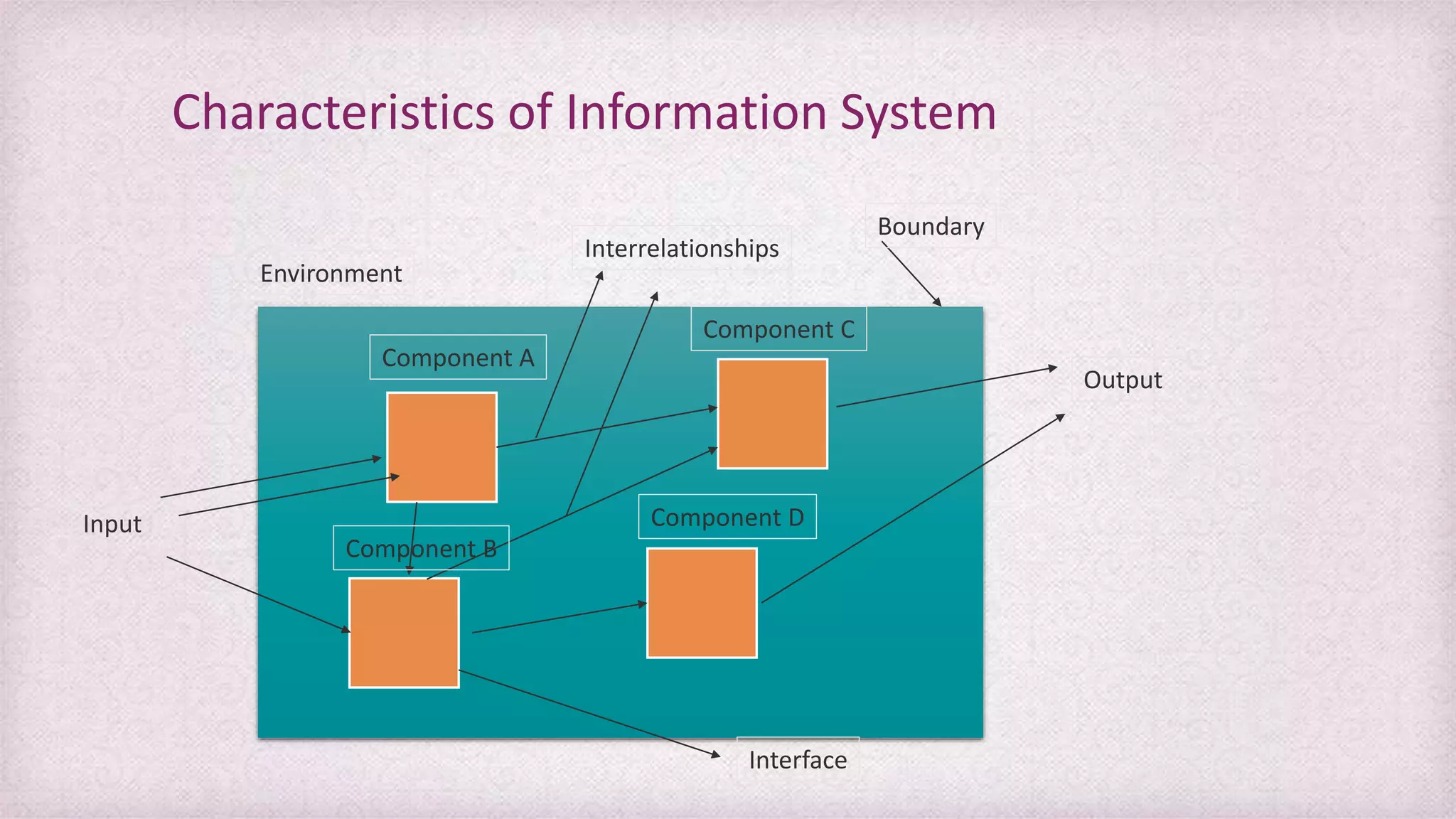
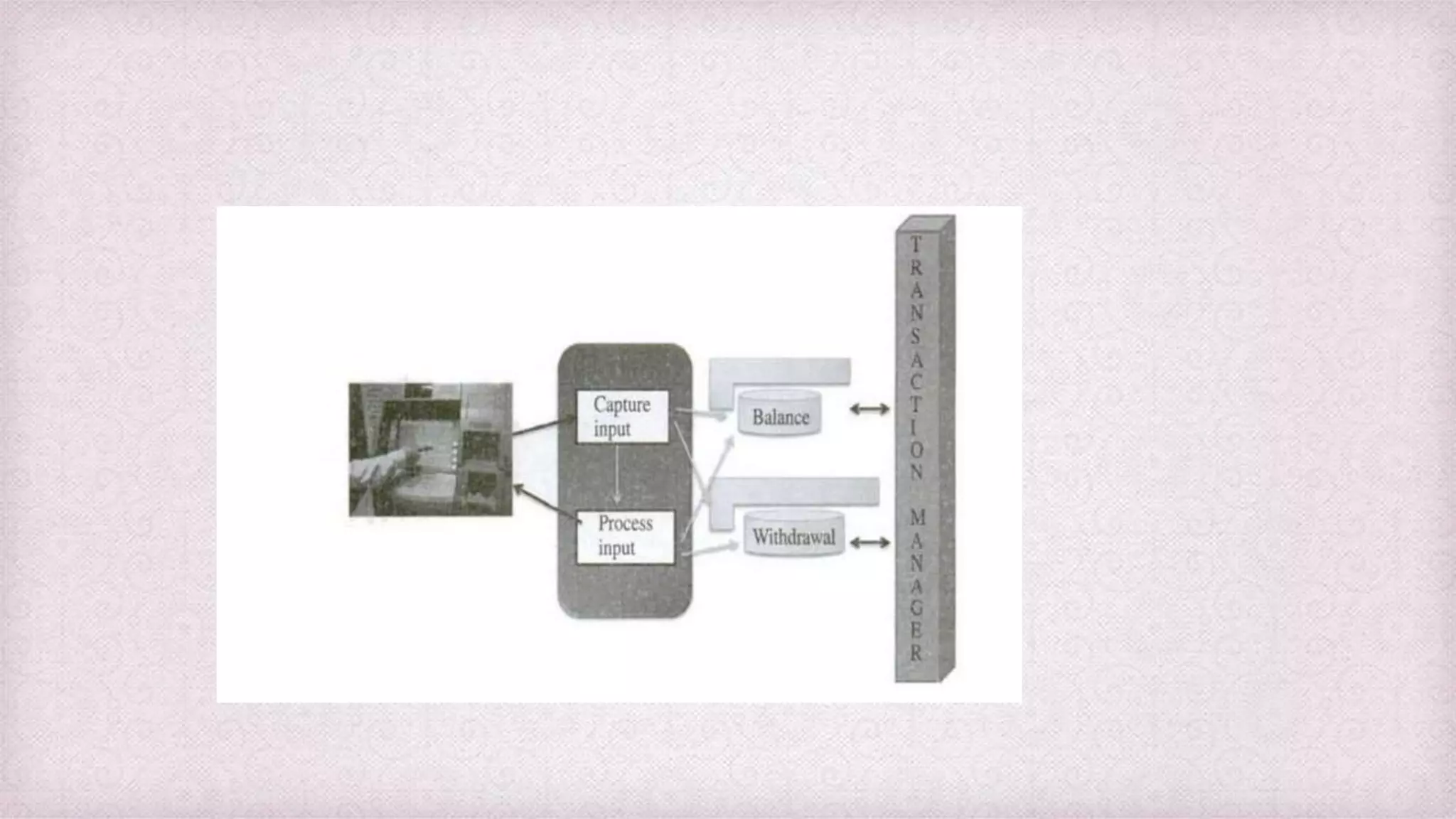
Data refers to raw facts and figures that have no inherent meaning. Information is data that has been organized and processed to give it context and meaning. There are many types of data including alphanumeric, text, images, audio. Information systems collect data, process it into information, and disseminate the results. Key components of information systems are hardware, software, databases, people, procedures, and telecommunications. Information systems support various levels of an organization from transaction processing to decision making.