Embed presentation
Downloaded 16 times


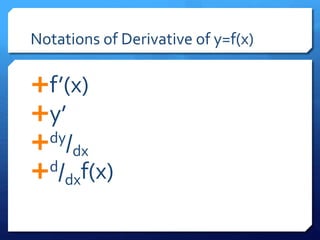


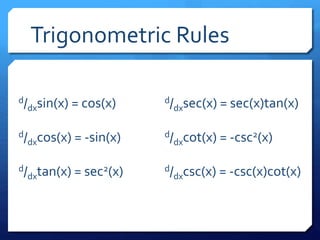


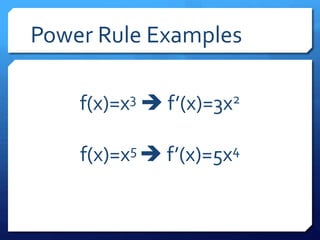

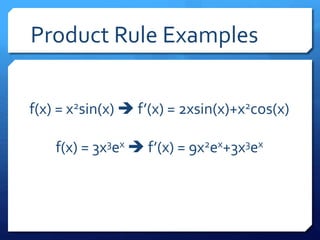
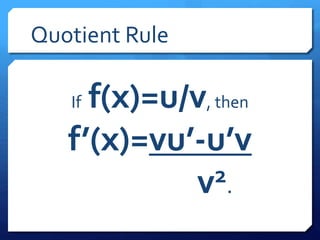
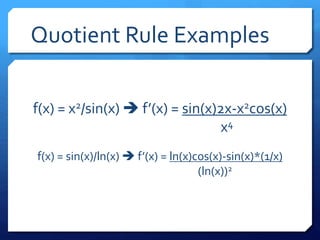

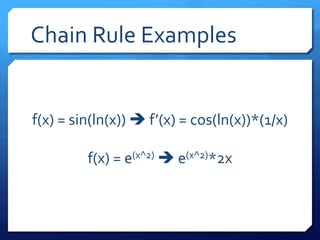
The document provides an overview of derivatives, defining them as the instantaneous slope of a function and outlining various notations for representation. It details methods for finding derivatives, including the power rule, product rule, quotient rule, and chain rule, along with examples for each. Additionally, it highlights important trigonometric derivatives and general rules for differentiation.














