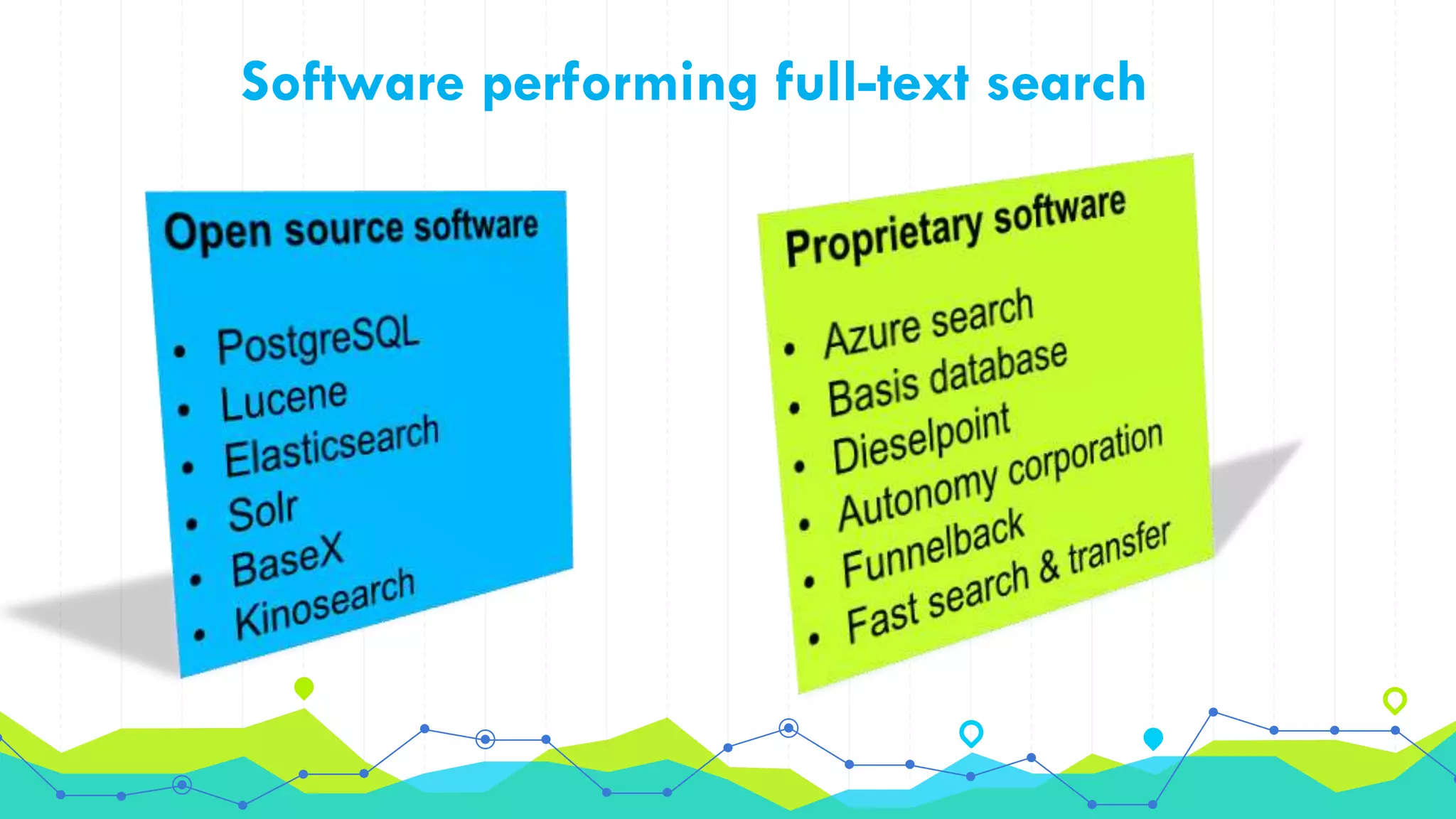
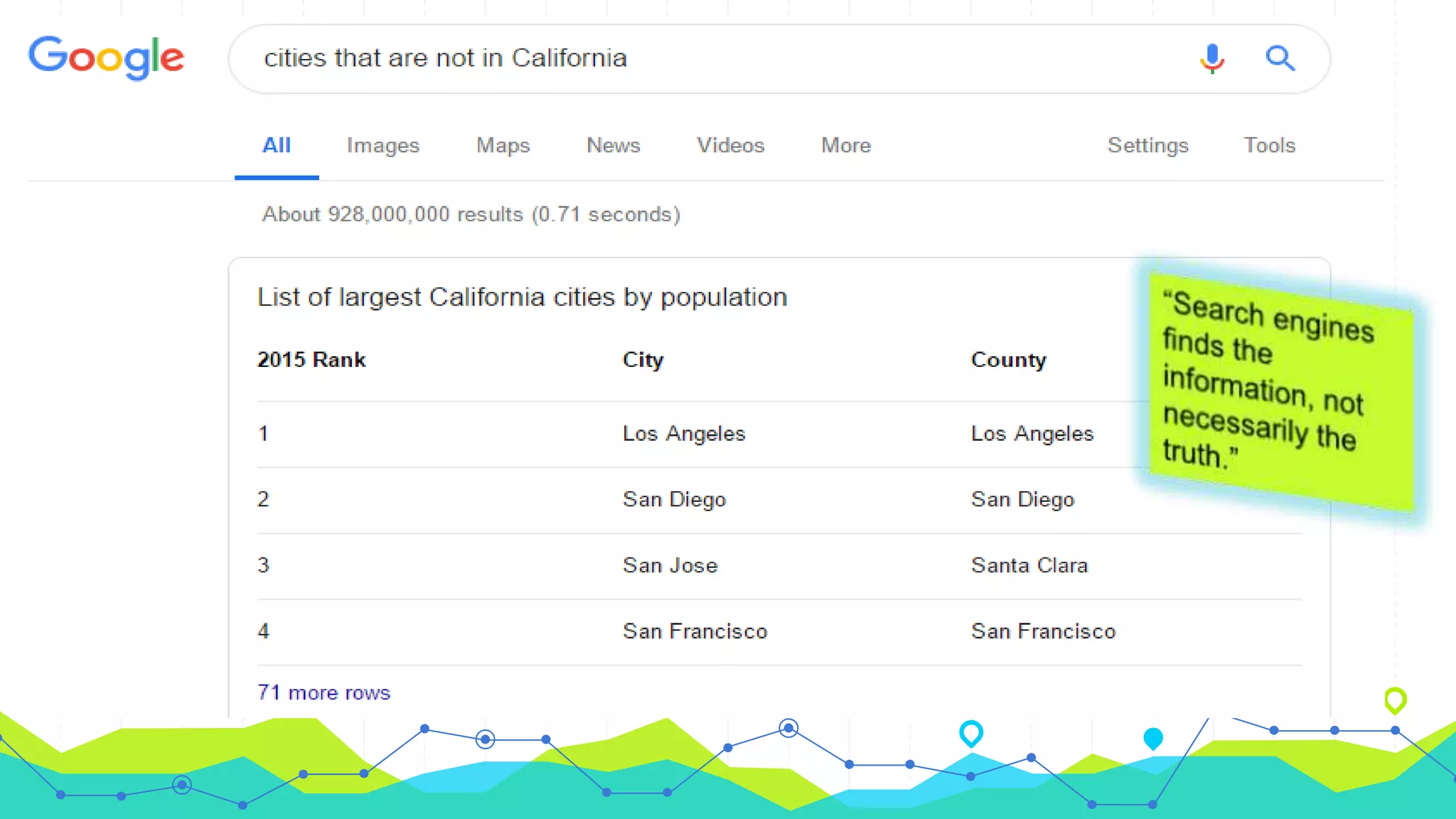
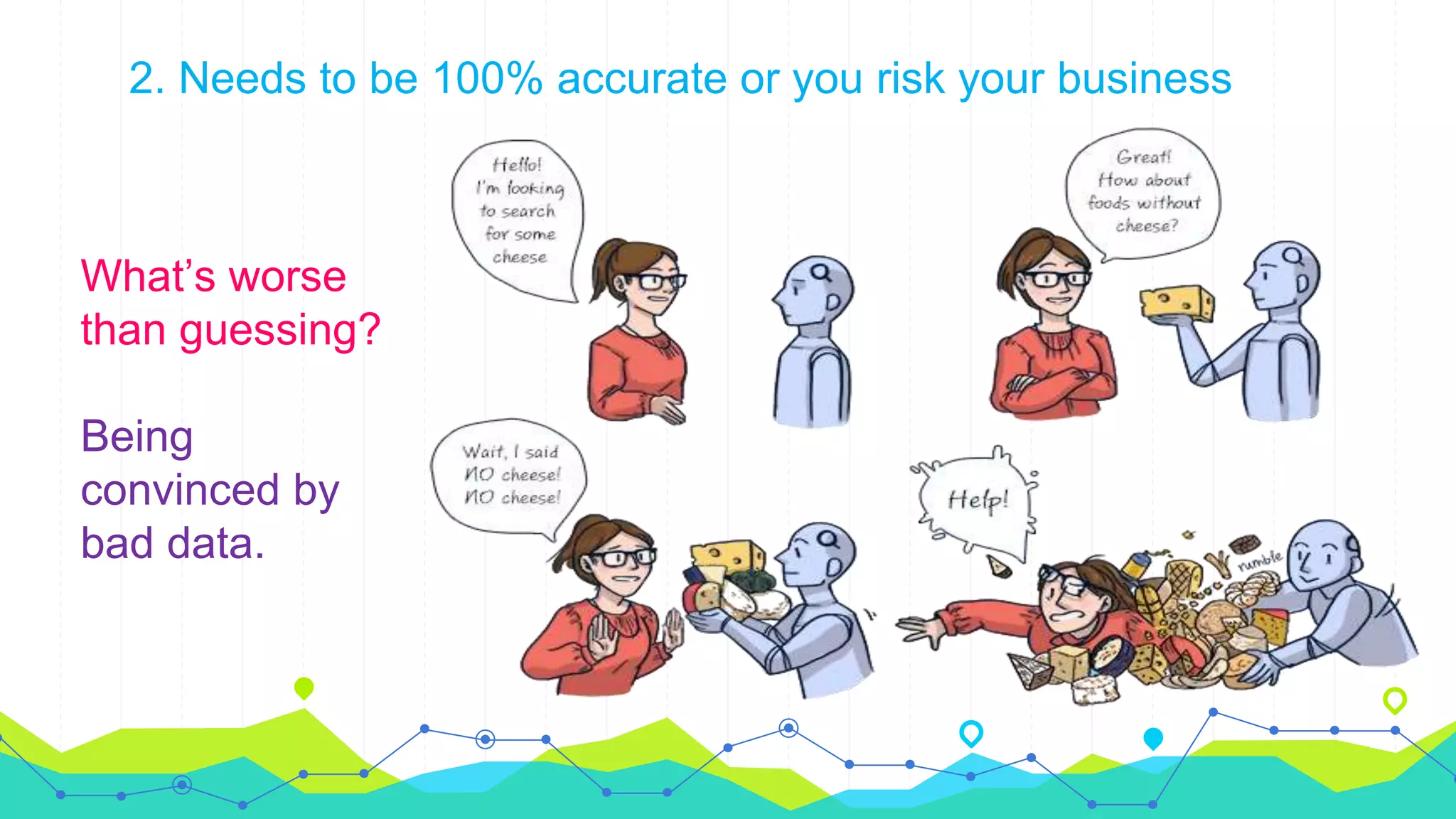
The document discusses full-text search and relational search. It notes that full-text search involves indexing documents and building a list of search terms, while relational search allows for more accurate and relevant searches of complex business data by accounting for relationships between database elements. However, relational search is more difficult due to the complicated nature of enterprise data and the need for 100% accuracy and fast search times when working with business-critical information.