Embed presentation
Downloaded 62 times


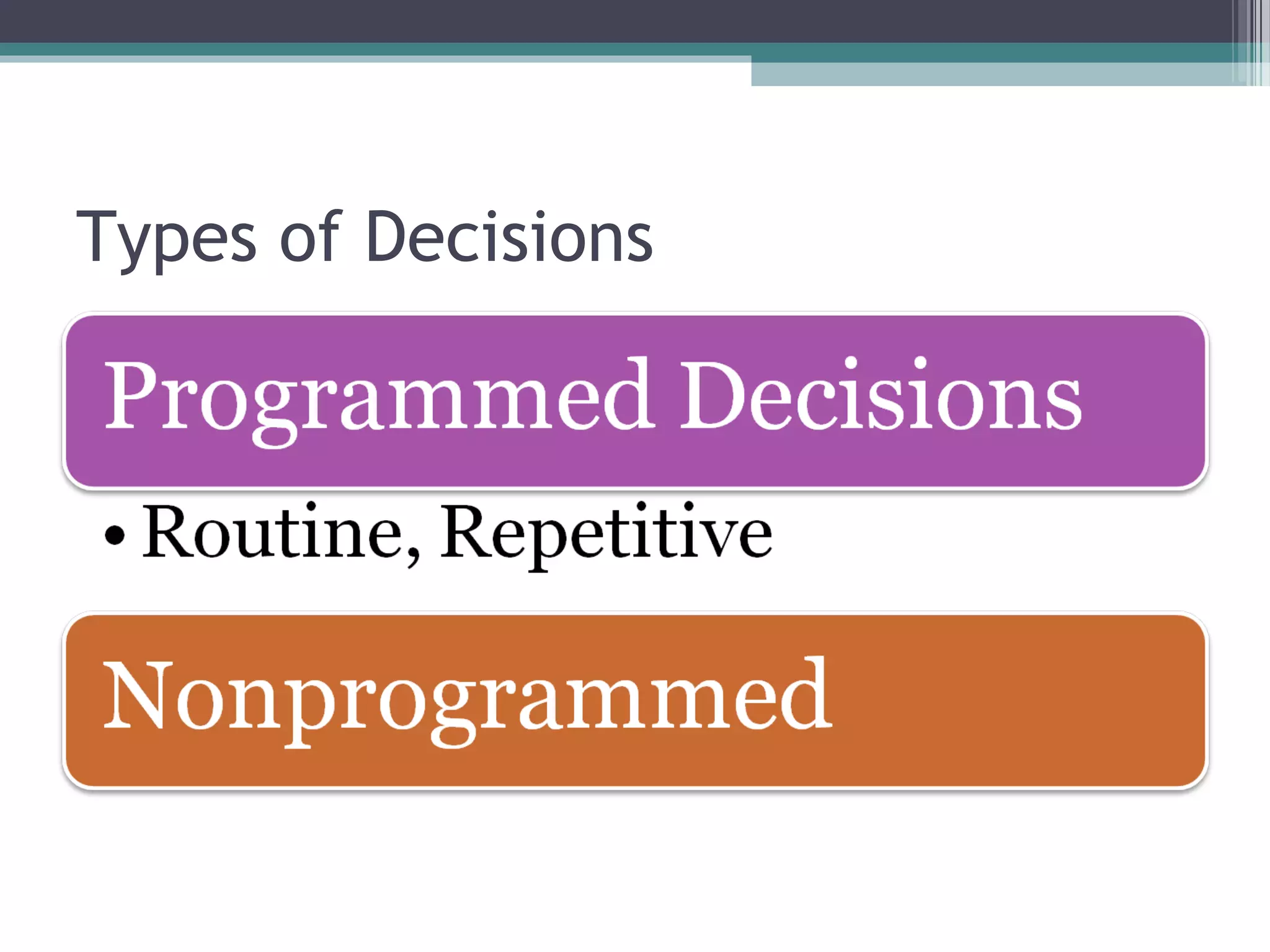










This document discusses managerial decision making and the rational decision making process. It describes how managers are evaluated based on their decisions and the importance of results. The rational decision making process is similar to strategic planning and helps managers evaluate alternatives systematically. While rational decision making aims to find the best solution, it has limitations like not considering all alternatives due to constraints of time, information and uncertainty. The document also outlines the typical steps in a managerial decision making process and how to make a business plan.












