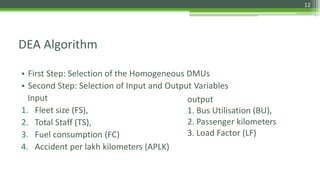
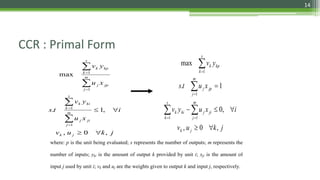
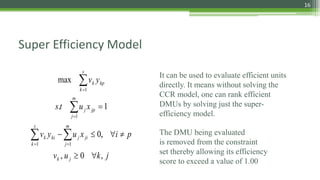
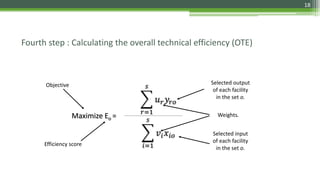
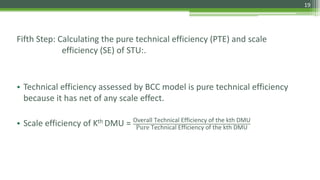
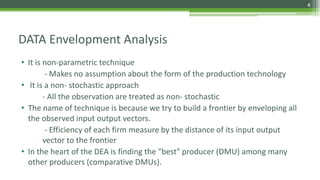
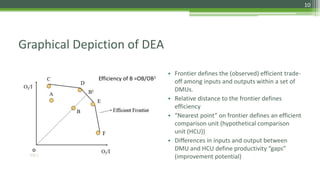
DEA is a non-parametric technique used to measure the relative efficiency of decision making units (DMUs) that use multiple inputs to produce multiple outputs. It works by constructing a production frontier boundary comprised of the most efficient DMUs to evaluate how efficiently other DMUs use inputs to produce outputs. The methodology was originally developed in 1978 and has since been applied in various industries to evaluate organizations, identify best practices, and determine potential efficiency improvements for inefficient units.







![Data envelopment analysis (DEA) Methodology
• DEA requires the multiple inputs and outputs for each DMU to be
specified.
• DEA defines efficiency score for each DMU as a weighted sum of
outputs [total output] divided by a weighted sum of inputs [total input].
• DEA restricts all efficiency scores to the range 0 to 1.
• DEA calculates the numerical value of the efficiency score for a
particular DMU by choosing input/output weights that maximize the
score, thereby presenting the DMU in the best possible light.
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataenvelopmentanalysis172ts016-180418064254/85/Data-envelopment-analysis-11-320.jpg)