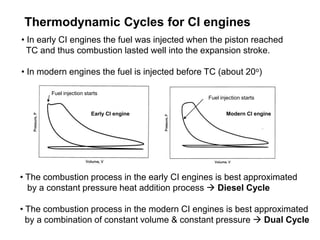
Thermodynamic Cycles for CI engines
- Early CI engines injected fuel at top dead center, resulting in combustion during the expansion stroke. Modern engines inject fuel before top dead center, around 20 degrees.
- The combustion process in early CI engines approximates a constant pressure heat addition process, known as the Diesel cycle. Modern CI engines' combustion approximates a combination of constant volume and constant pressure processes, known as the Dual cycle.
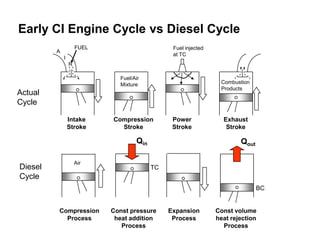
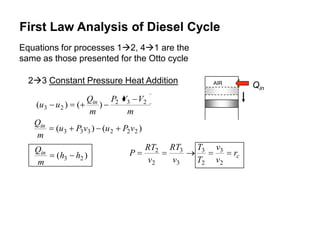
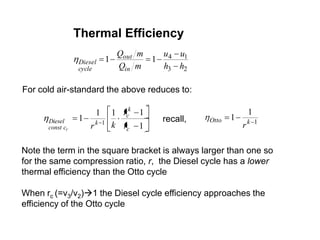
- The air-standard Diesel cycle consists of four processes: isentropic compression, constant pressure heat addition, isentropic expansion, and constant volume heat rejection. Its thermal efficiency is lower than the Otto cycle for the same compression ratio due to the later fuel injection