1. The document discusses voltage drop calculations for DC distribution lines under different loading and feeding conditions. It provides formulas to calculate the voltage drop and power loss for lines fed at one end or both ends.
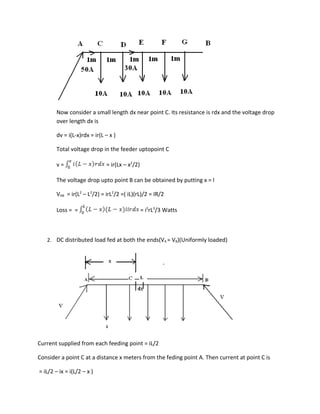
2. Examples are given for calculating the voltage drop and maximum voltage drop for a 200m line fed at one end and loaded uniformly with 2A/m. Also for a 1000m line fed at both ends with 220V and loaded with 0.5A/m, it shows how to find the maximum and minimum voltages.
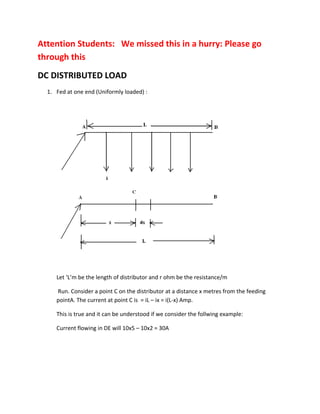
3. Key formulas introduced are for voltage drop up to a point x on a line fed at one end as V=ir(Lx-x^2/2)

![Solution:
Current loading: i = 0.5A/m
r = 2x0.05x1000 = 0.1x10-3 ohm
L = 1000m
I = iL = 500A
R = rL = 0.1 ohm]
Maximum voltage drop = IR/8 = 500x0.1/8 = 6.25V
Minimum voltage occurs at the mid point and its value is = V –IR/8 = 220 – 6.25 =
213.75V](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dcdistributedload-091209231903-phpapp01/85/Dc-Distributed-Load-4-320.jpg)