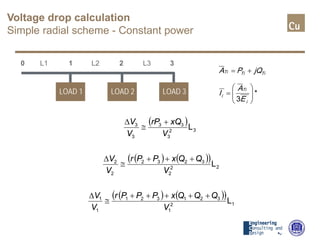
This document discusses voltage drop calculation in cable lines. It provides information on the data required to start calculations, including cable parameters, load characteristics, installation scheme, and maximum allowed voltage drop. It then covers calculations for simple radial lines under conditions of constant current and constant power. For constant current, the voltage drop is calculated based on cable resistance and reactance, line length, and load current. For constant power, an iterative method is used to calculate the voltage at the end of the line based on load power and reactive power. Sample calculations are shown for both cases.