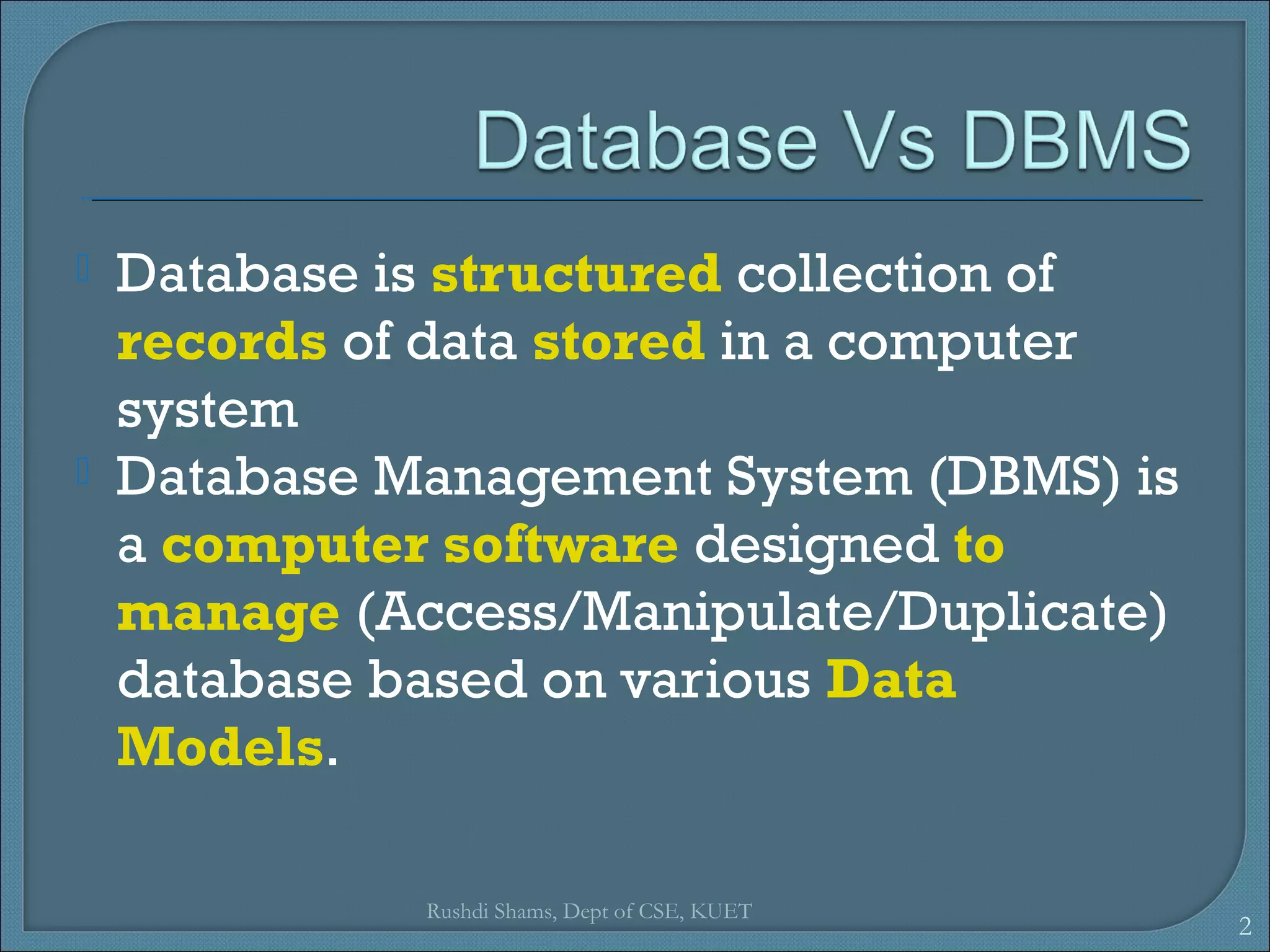
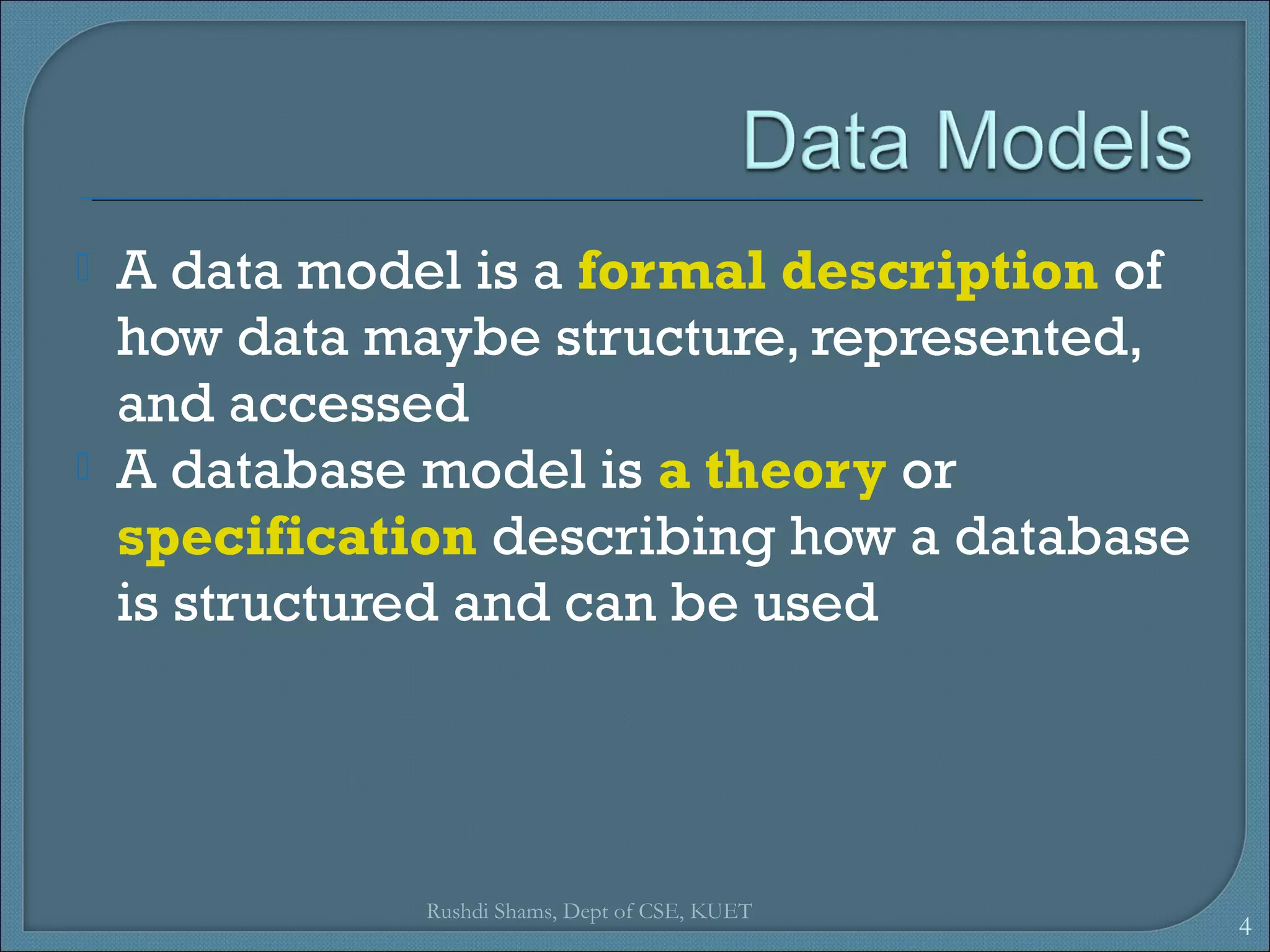
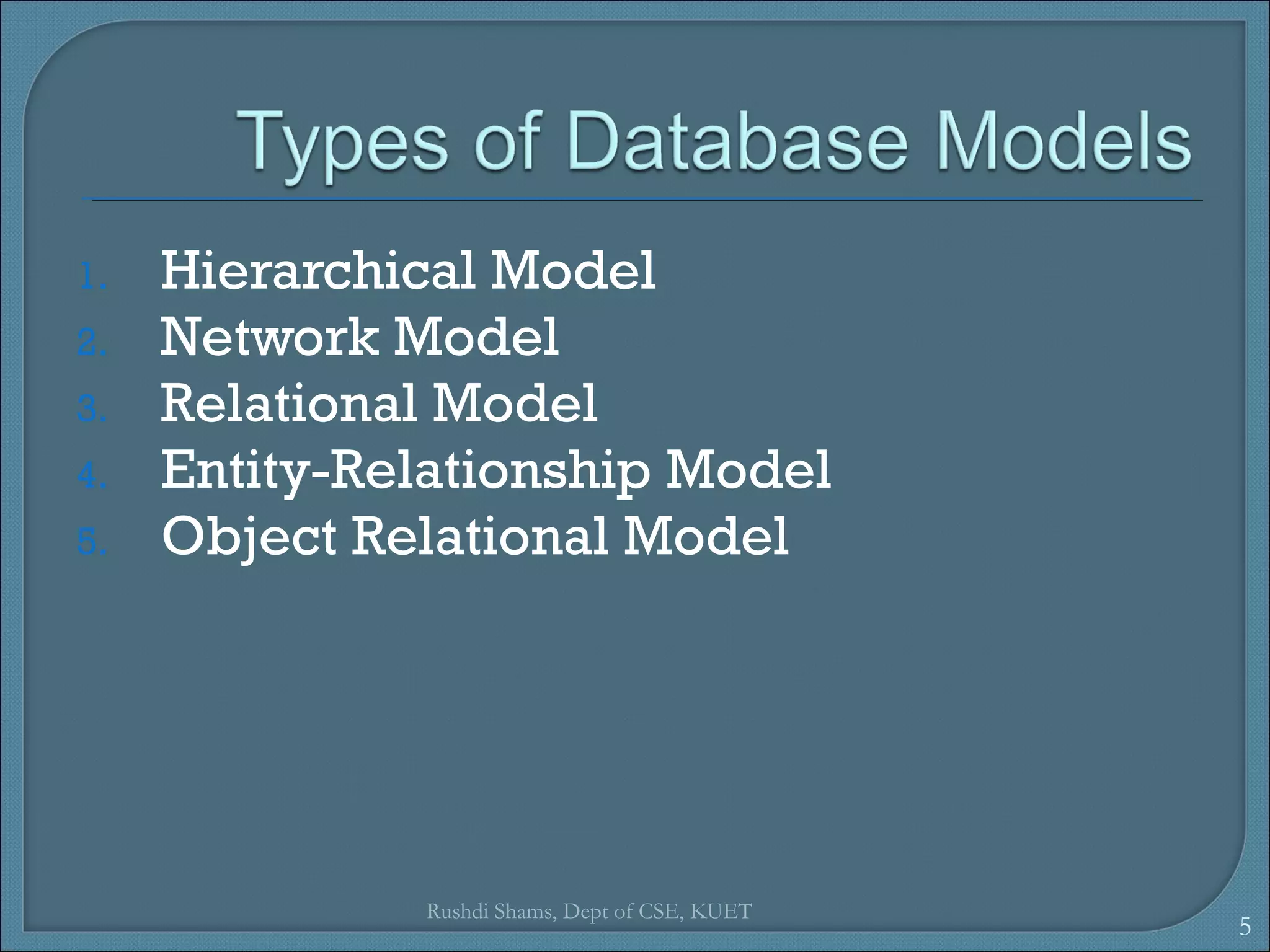
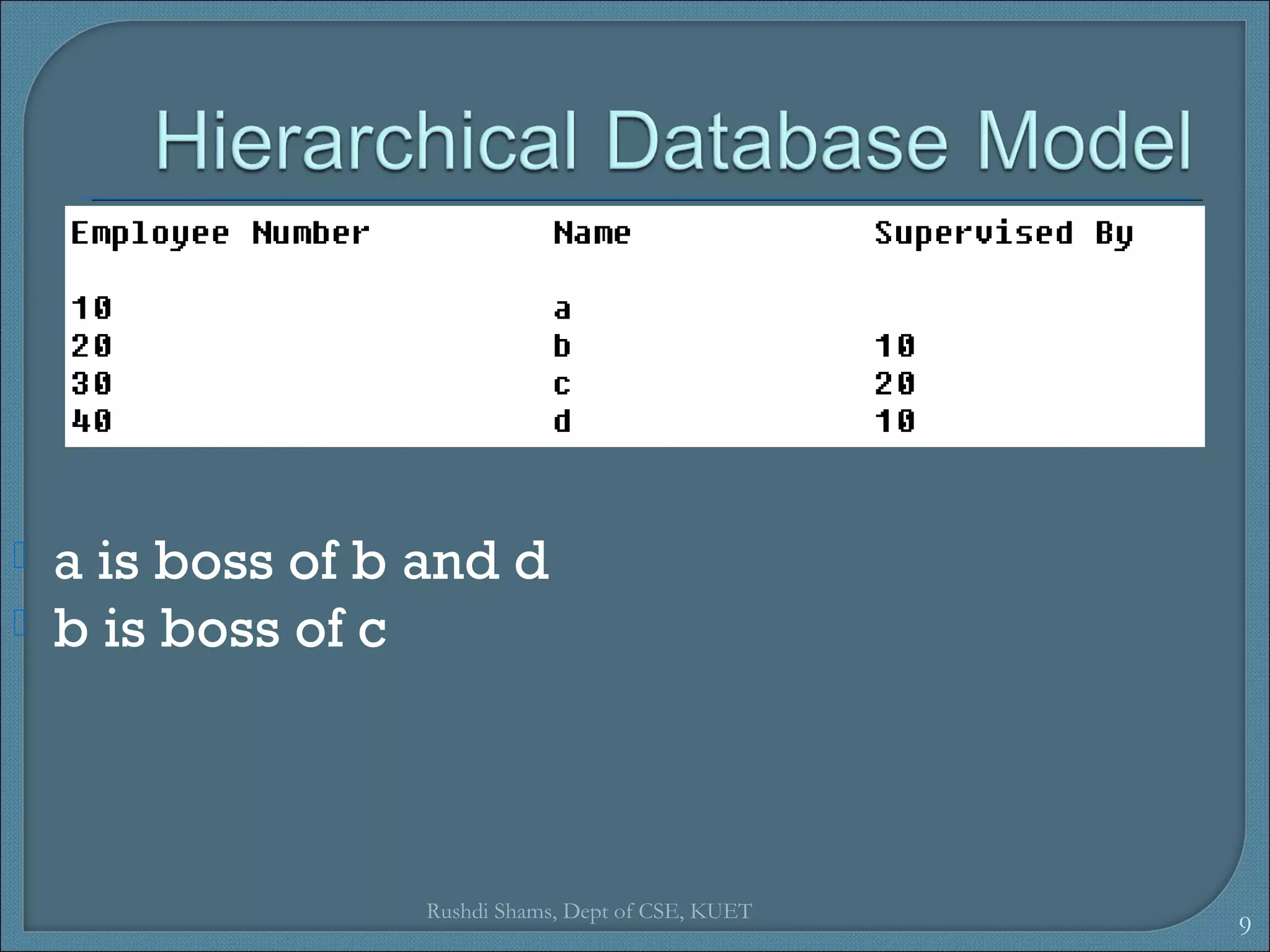
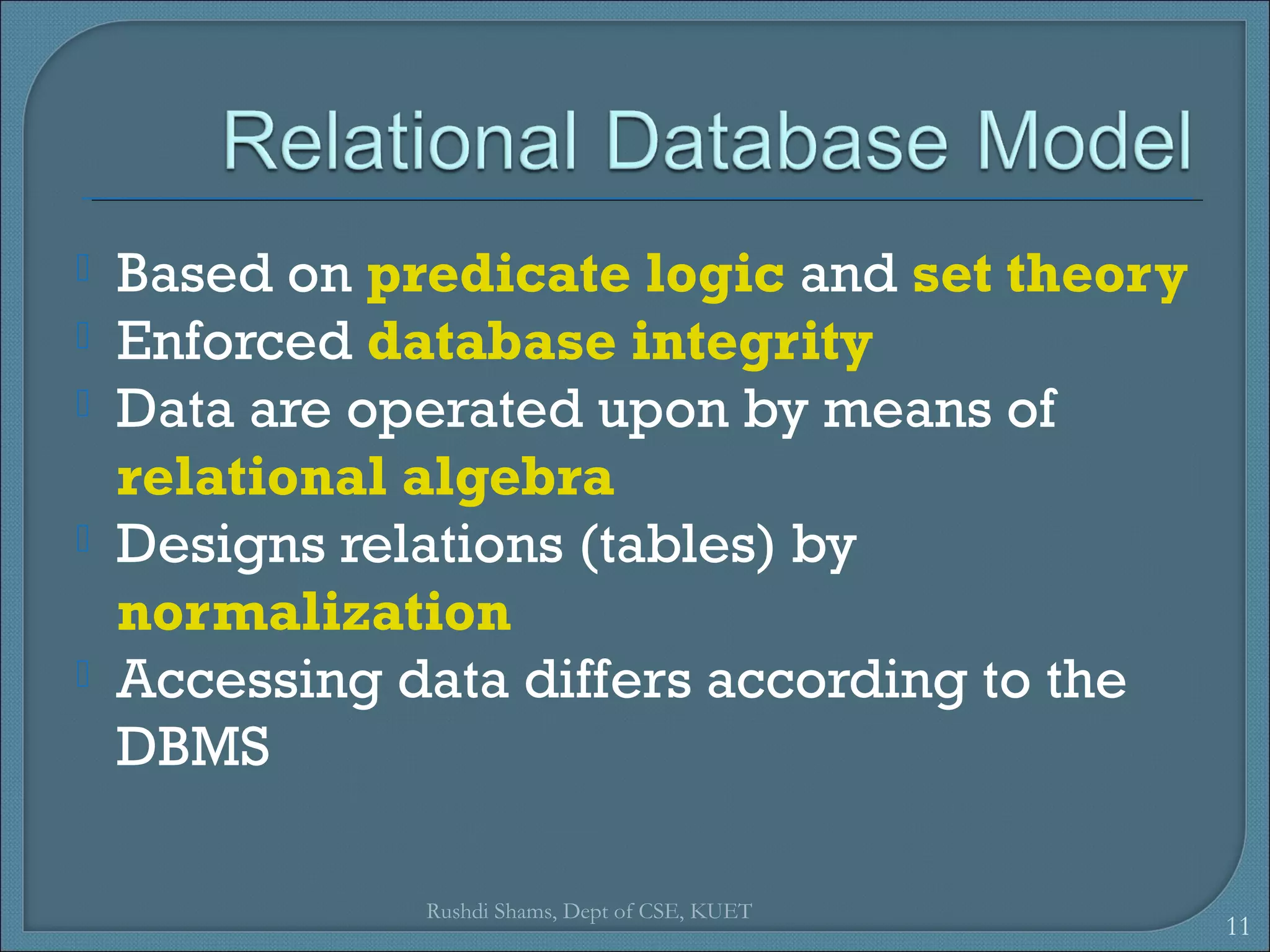
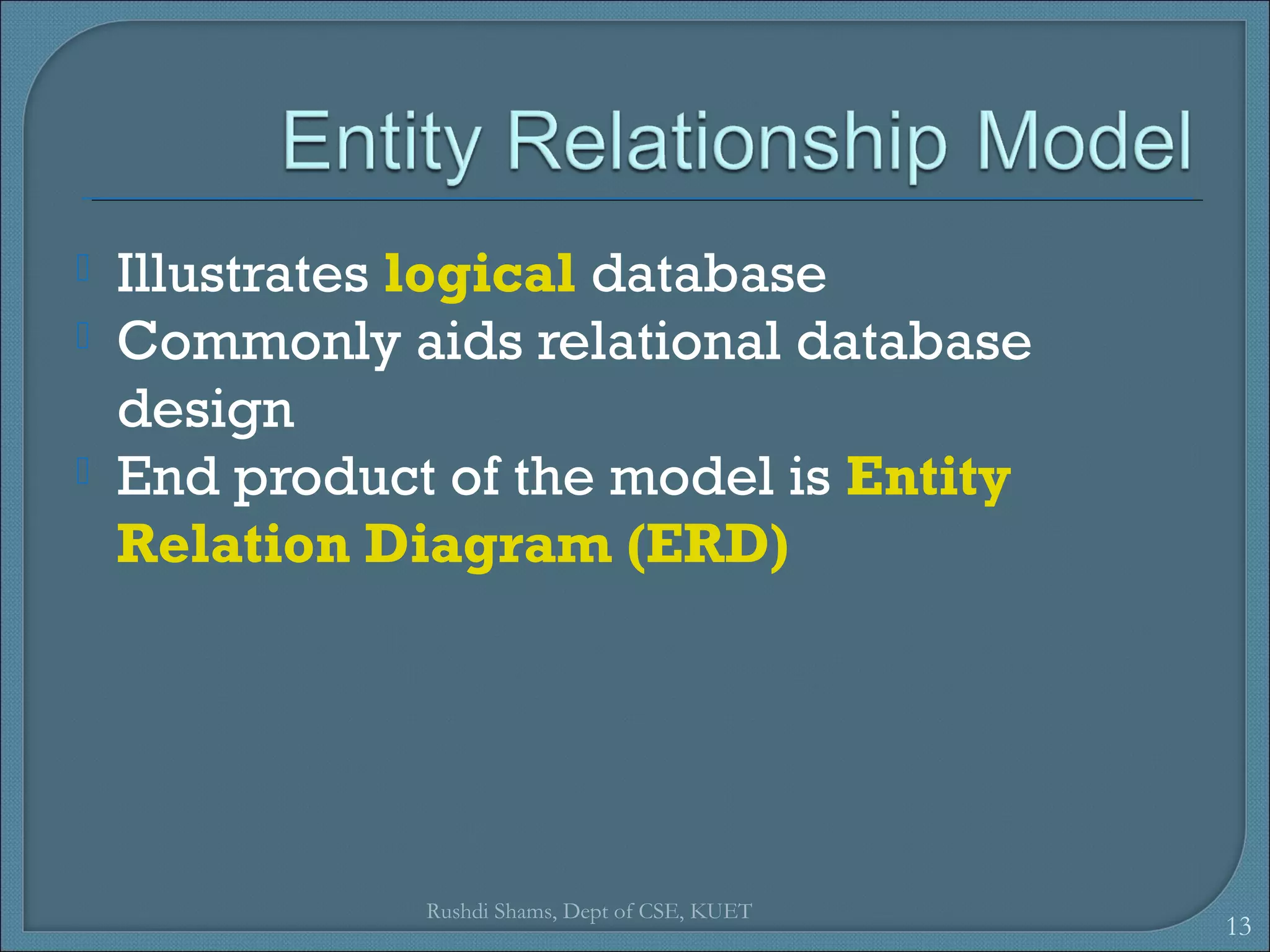
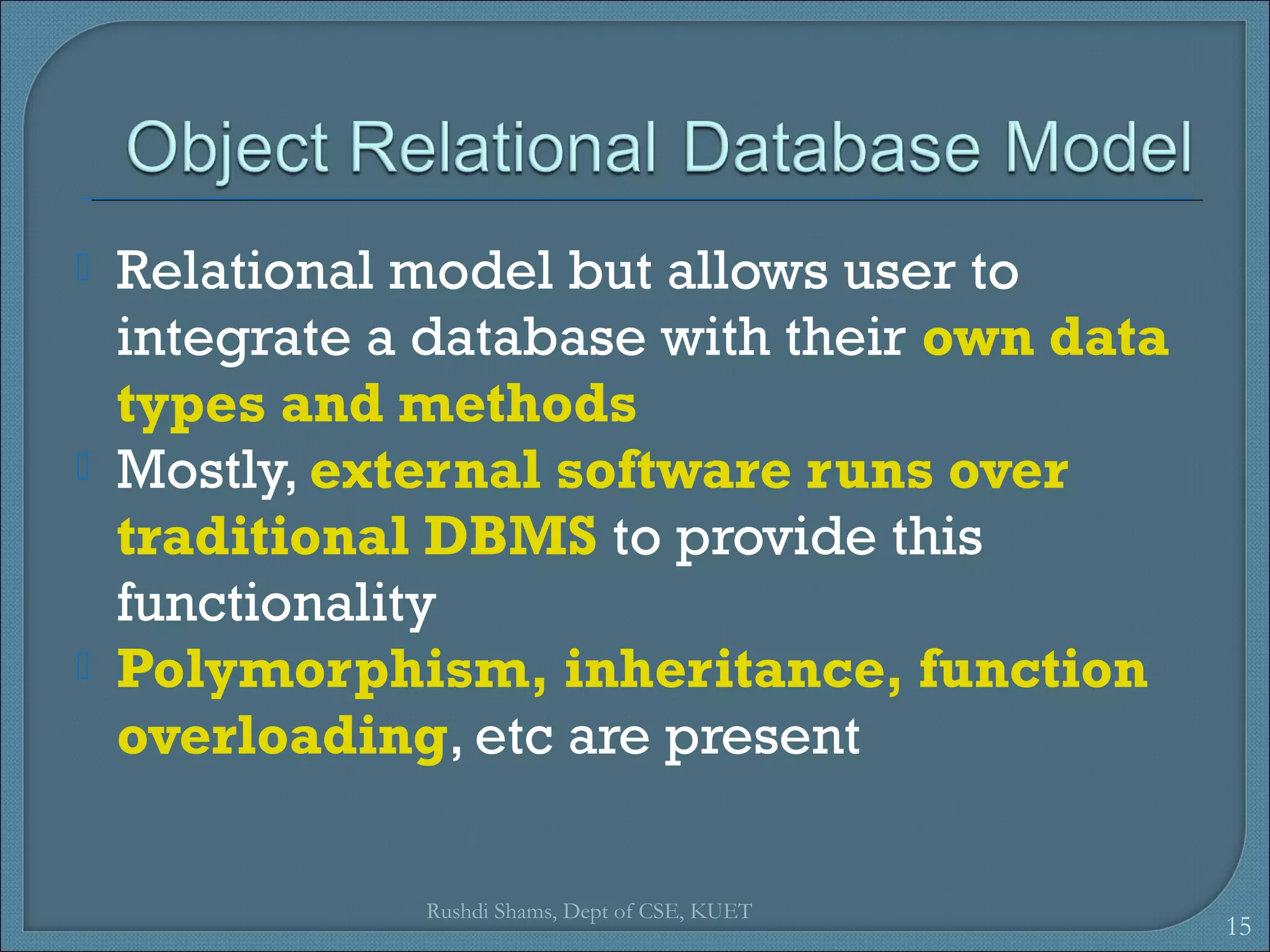
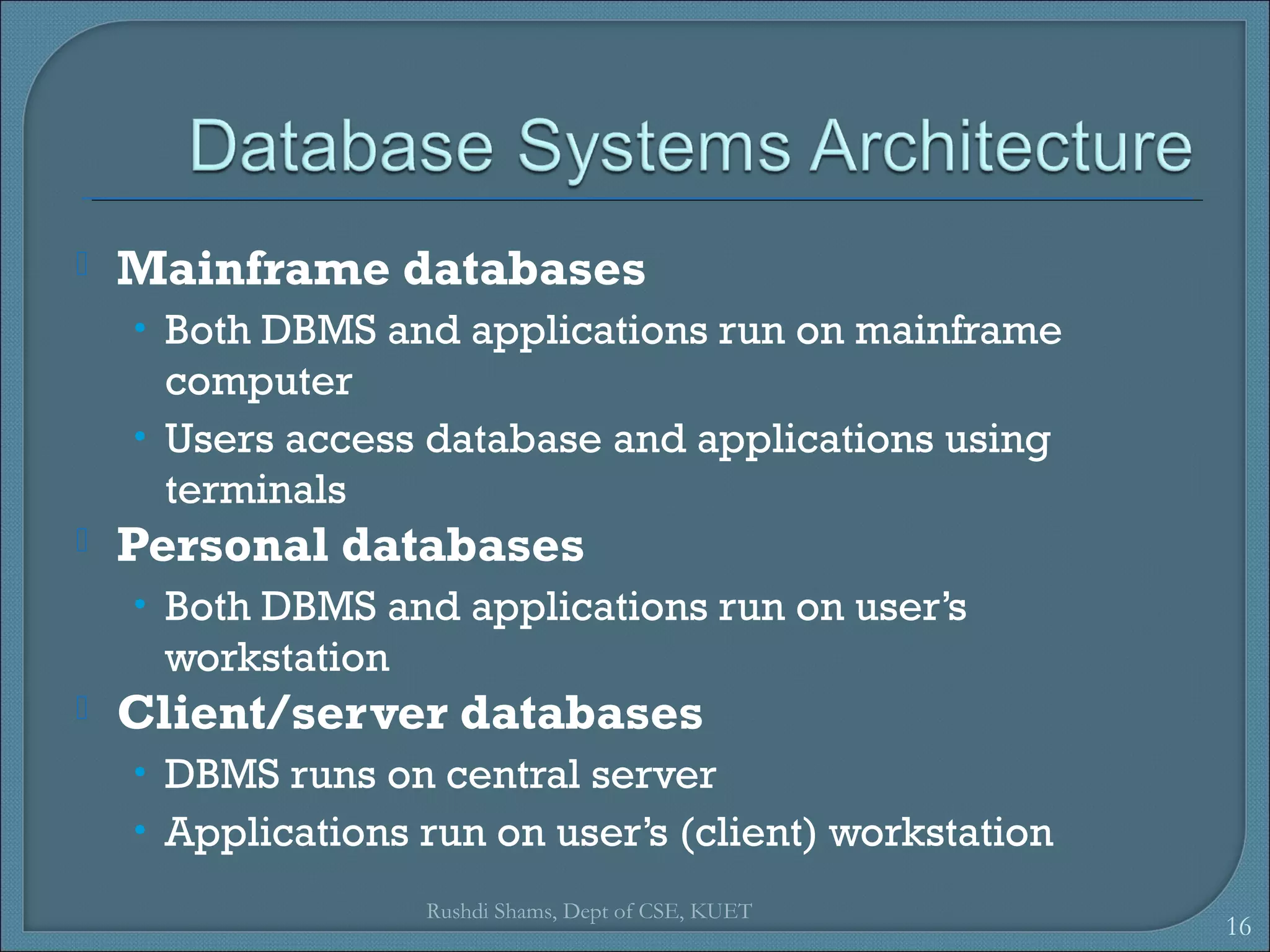
This document discusses database models and database systems architecture. It describes hierarchical, network, relational, entity-relationship, and object-relational database models. It also discusses database management systems, how they are used to access and manipulate databases based on different data models, and how database systems are typically architected in mainframe, personal, and client-server configurations.