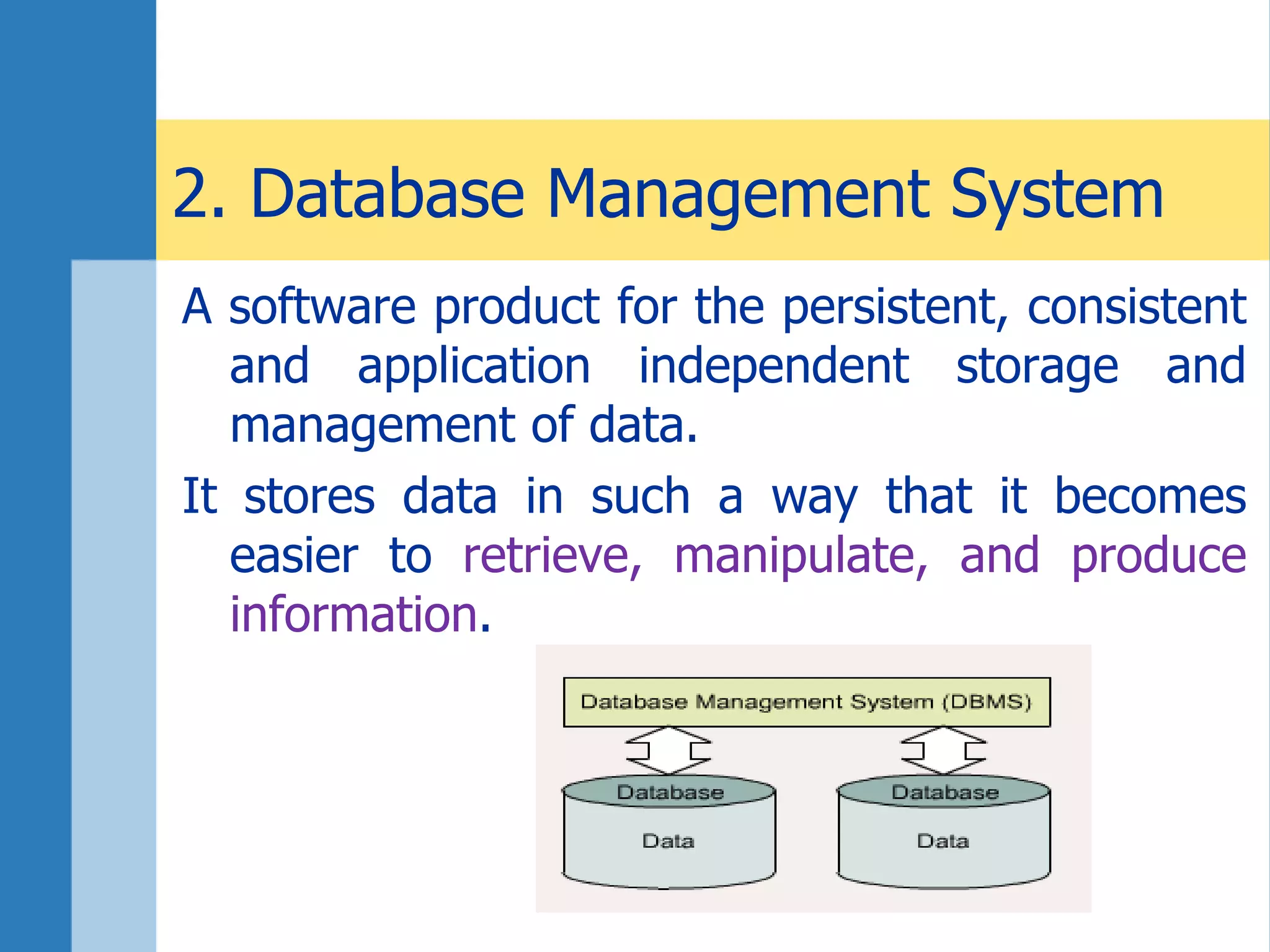
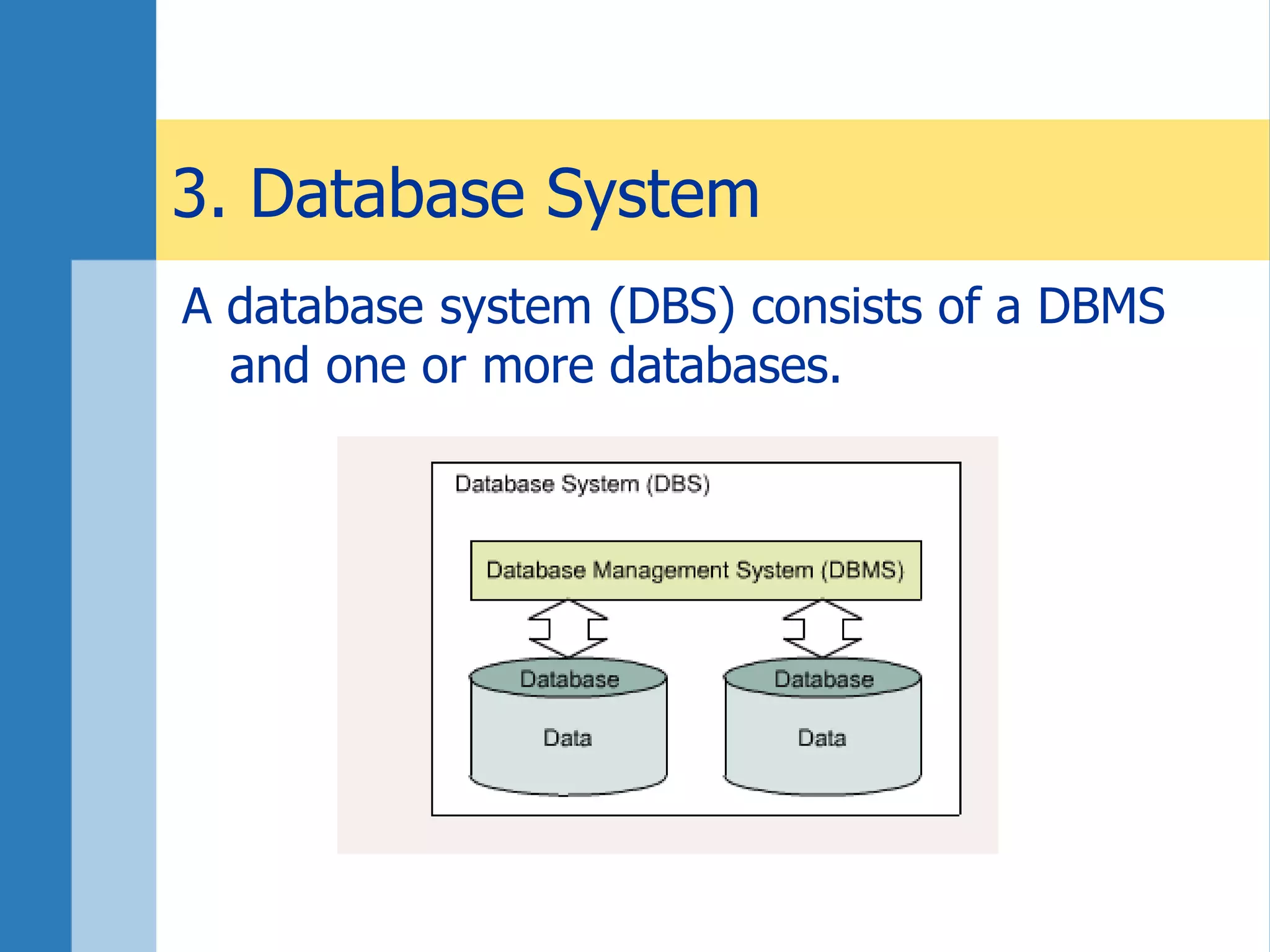
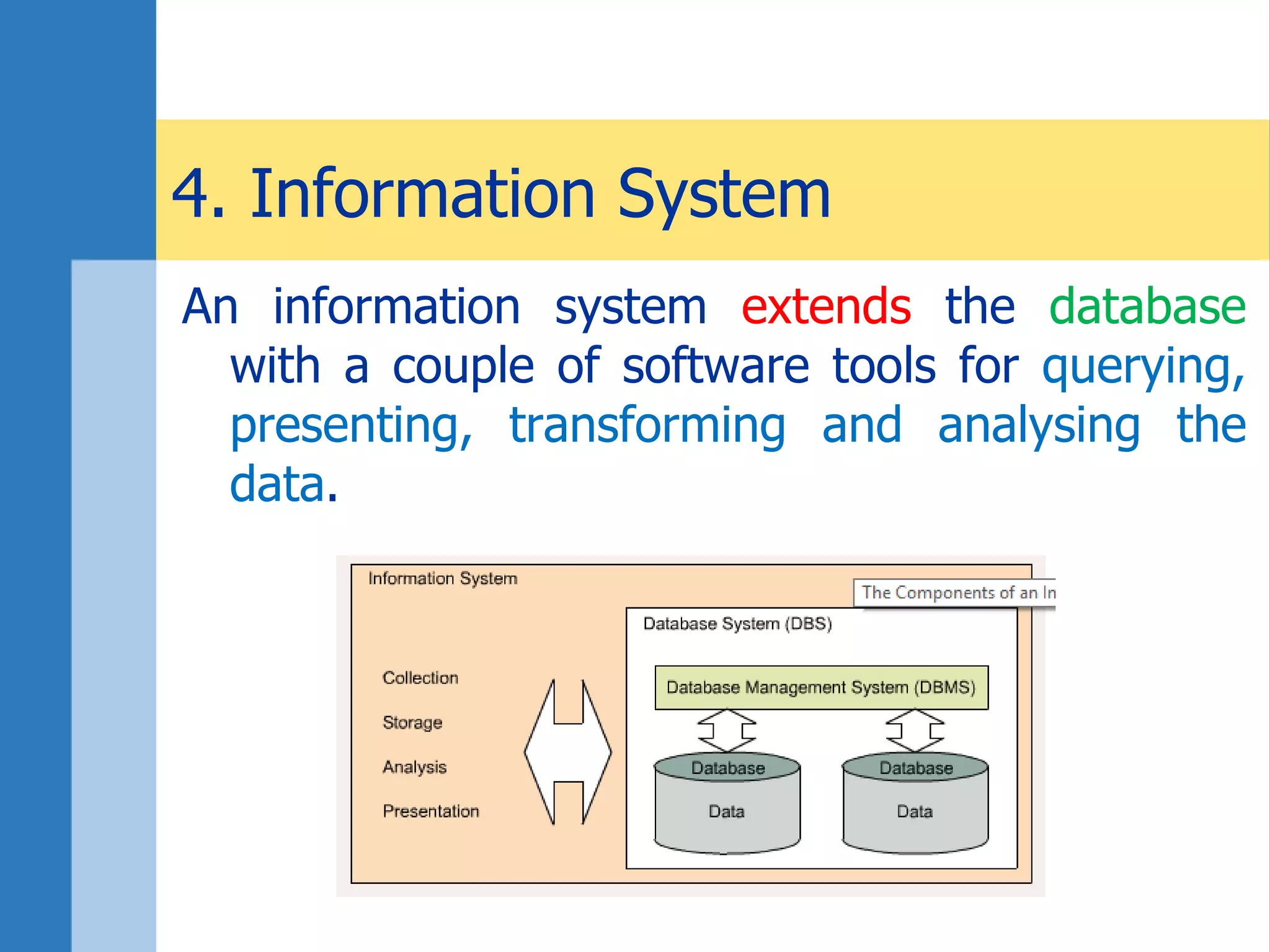
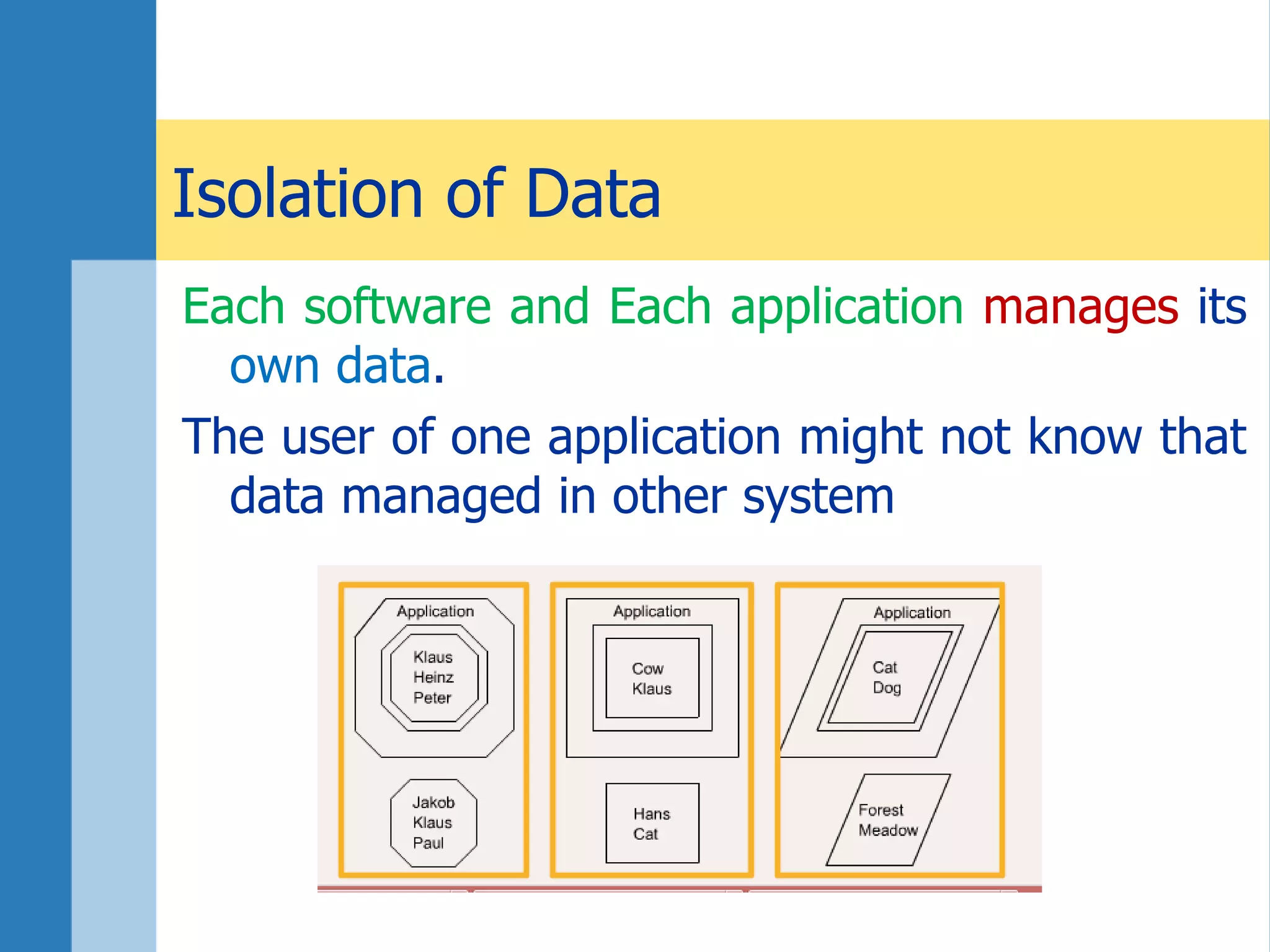
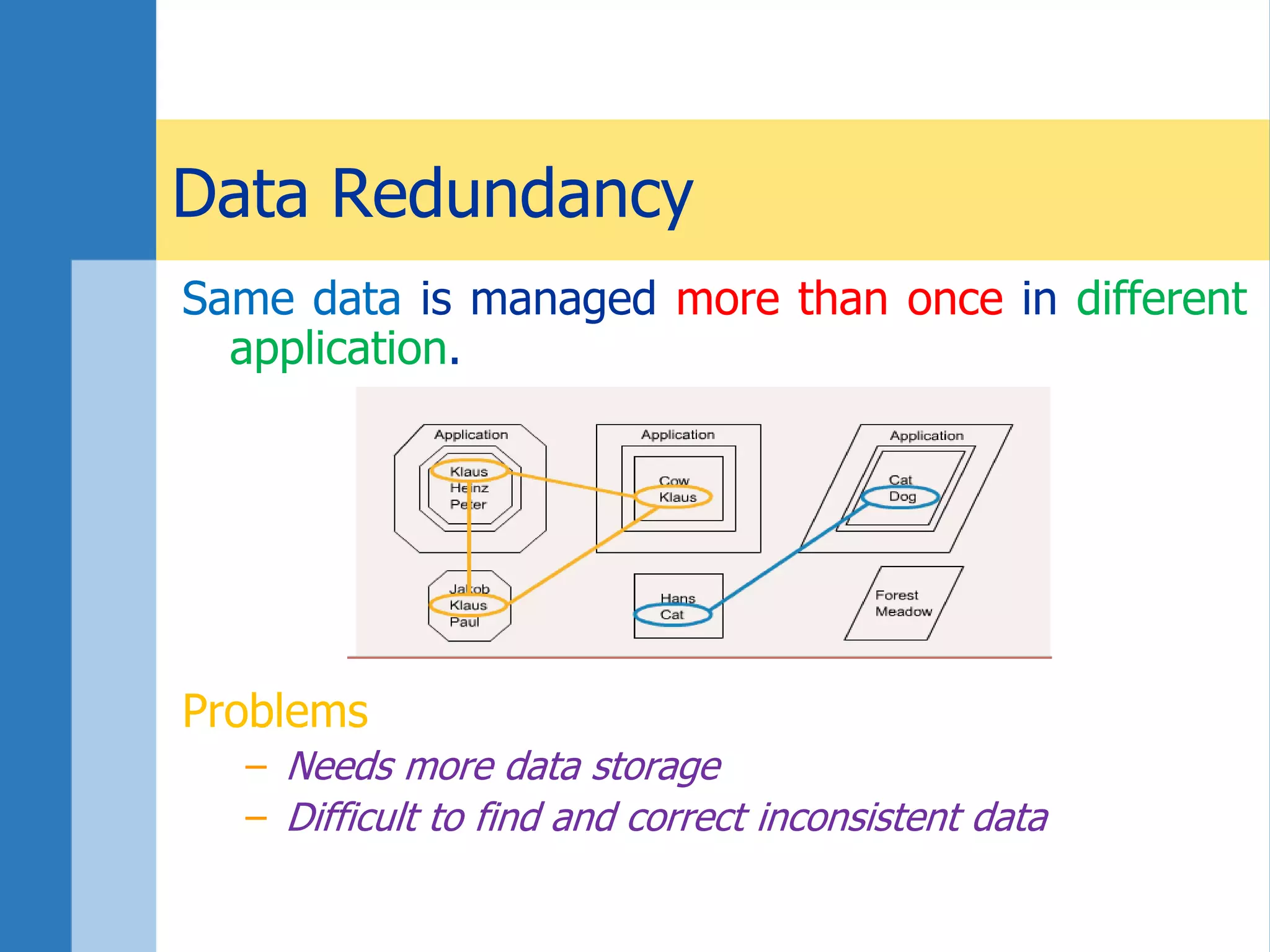
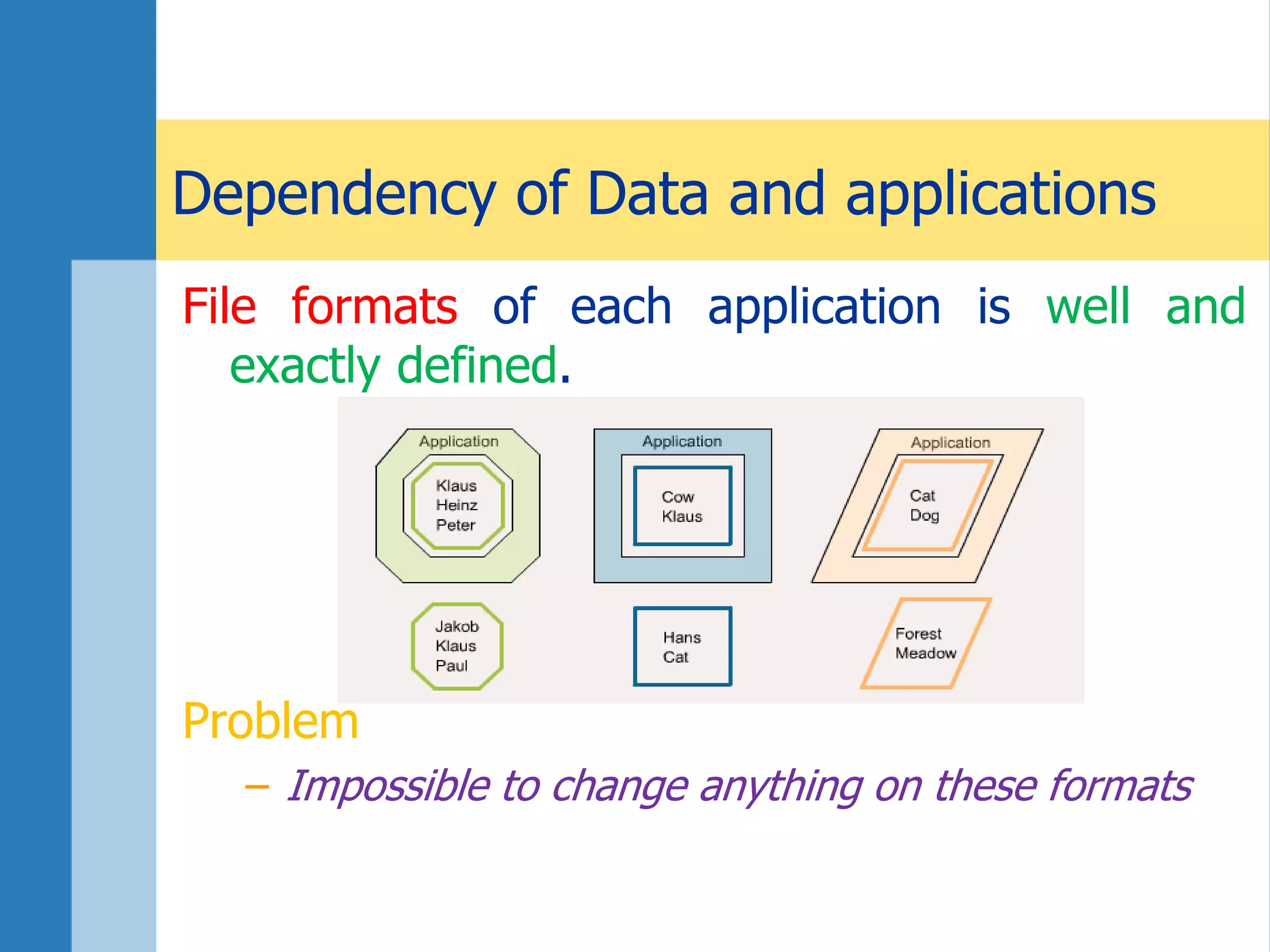
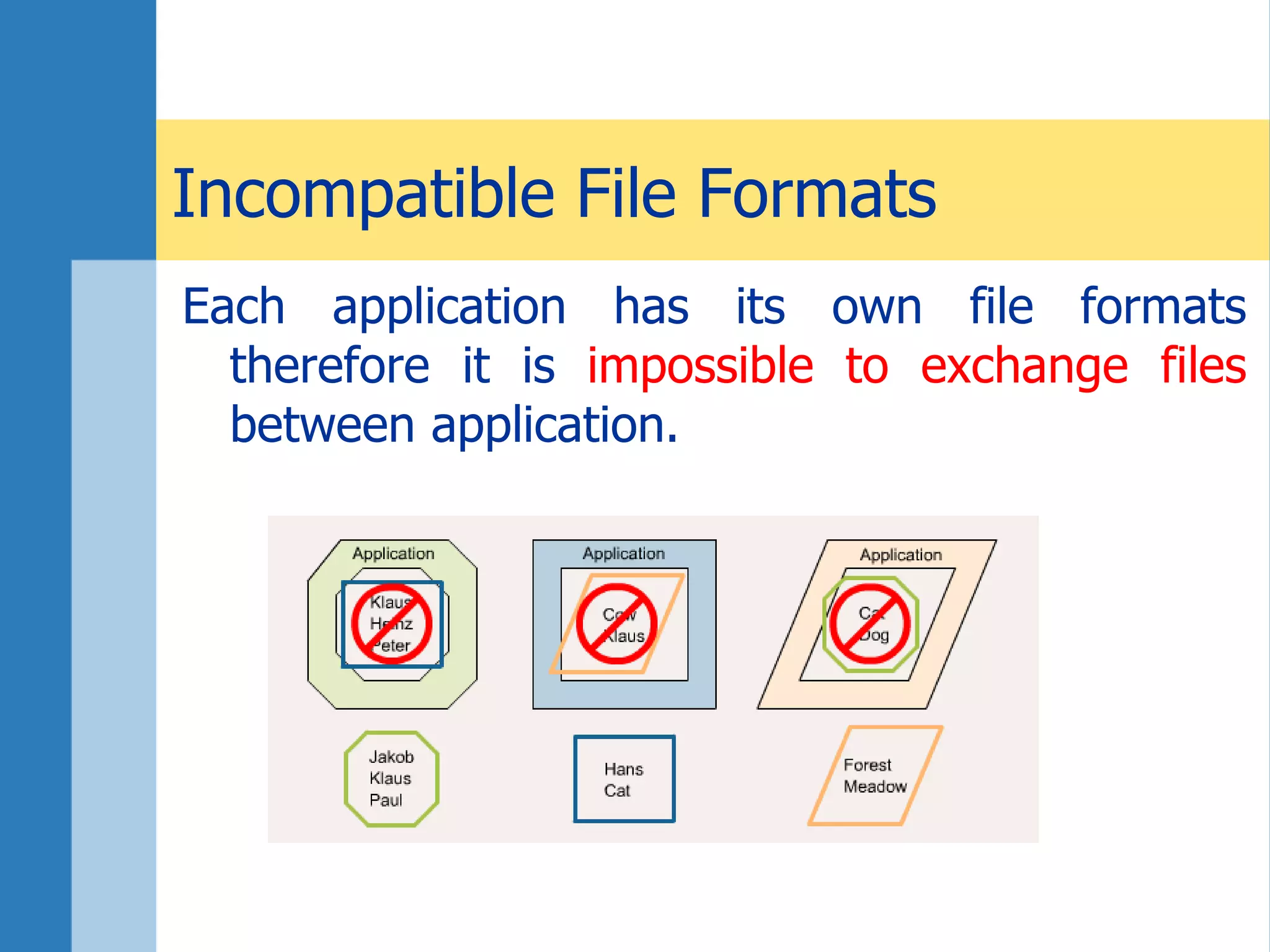
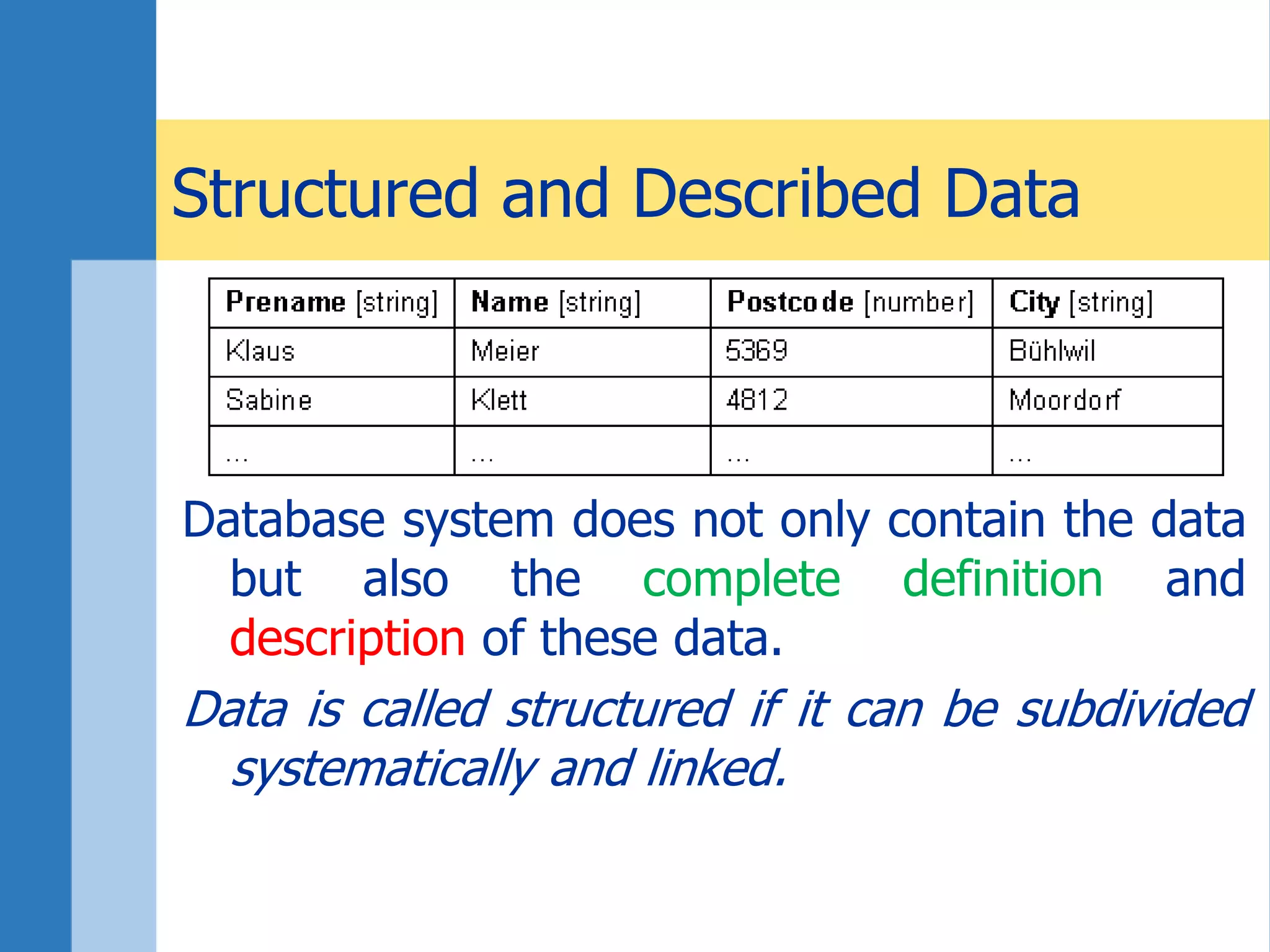
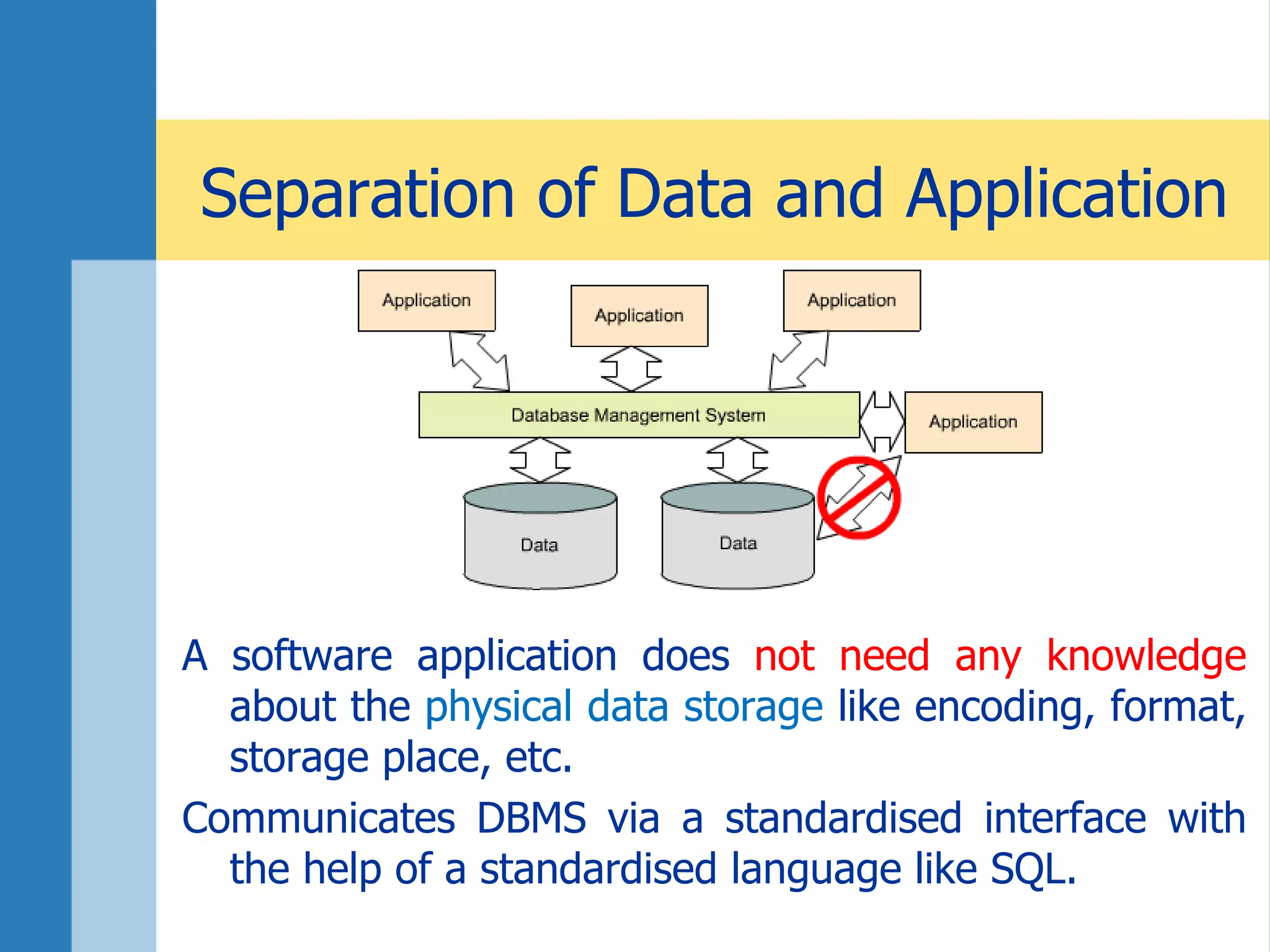
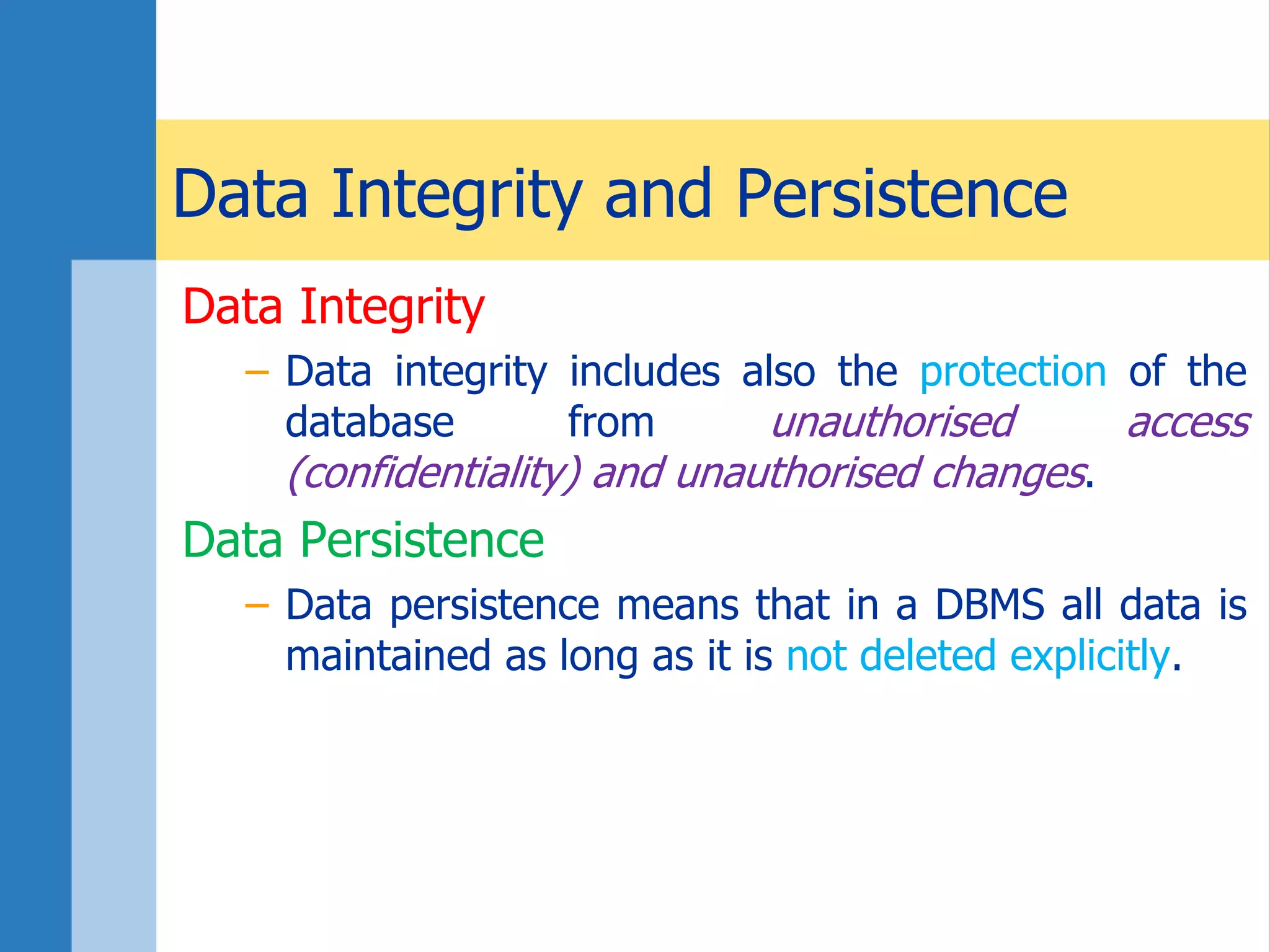
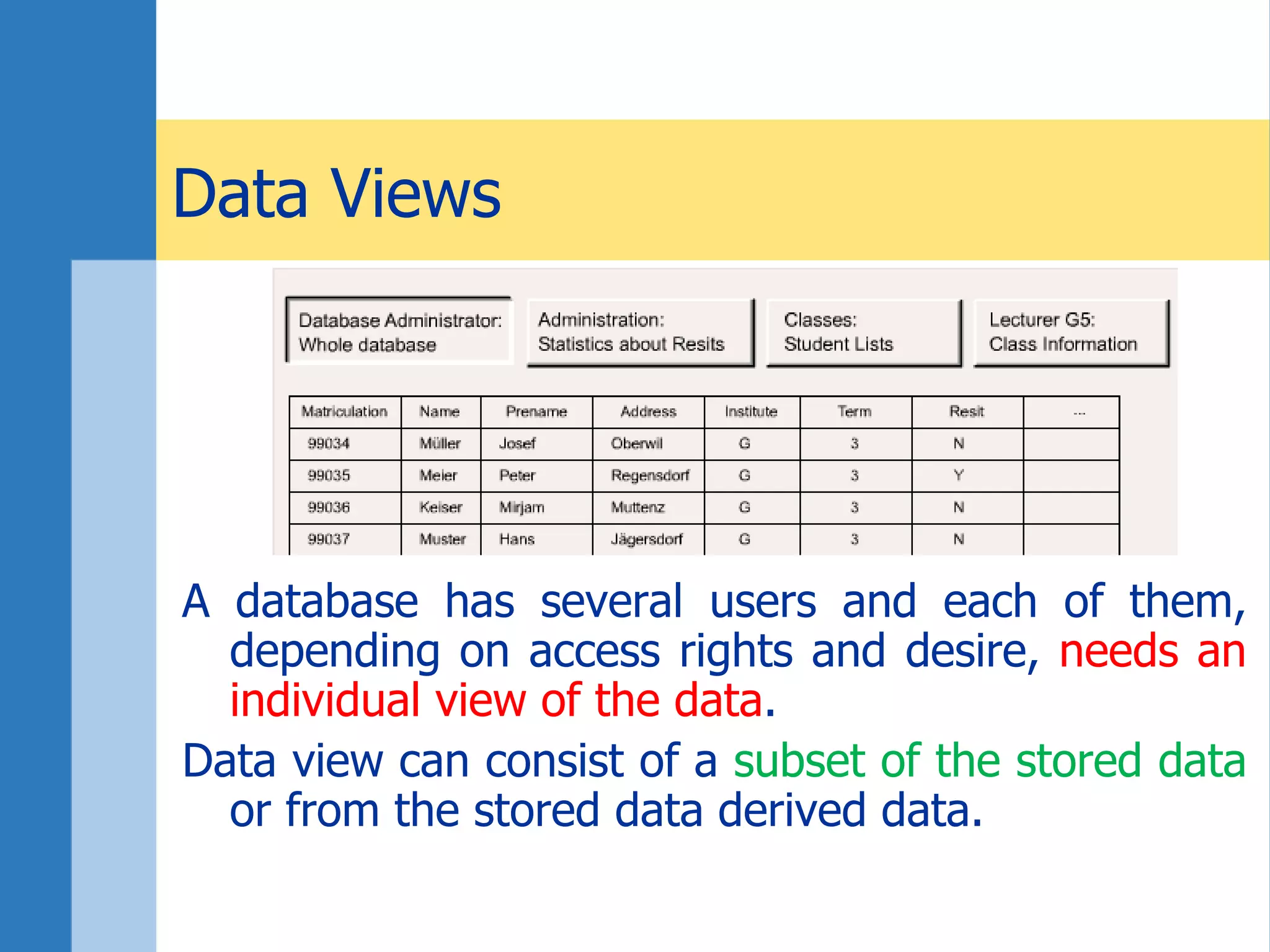
This document discusses key concepts related to databases and information systems. It defines data, information, and databases. It explains that a database management system (DBMS) stores data in a structured way to facilitate retrieval and use. An information system combines a DBMS with tools for querying, analyzing, and presenting the data. The document outlines advantages of database systems like concurrent access, structured storage, separation of data and applications, and data integrity and persistence. Examples of database applications discussed include banking transactions, timetables, and library catalogs.