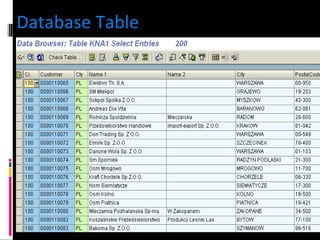
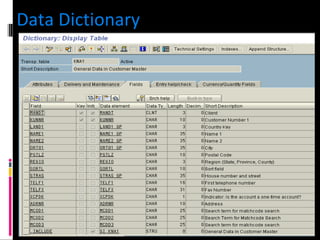
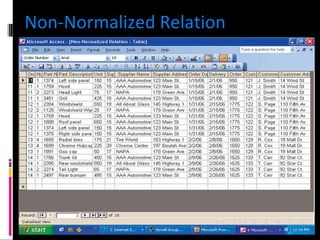
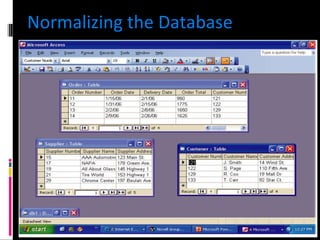
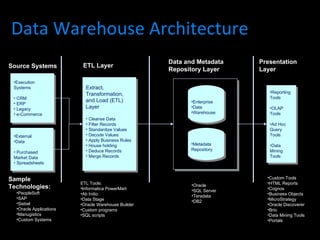
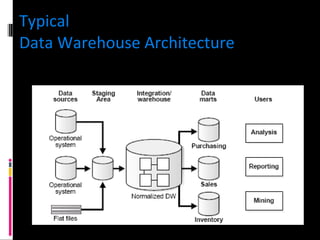
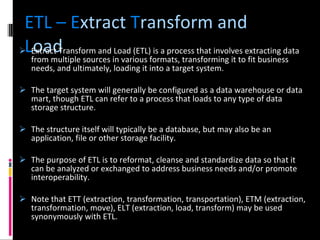
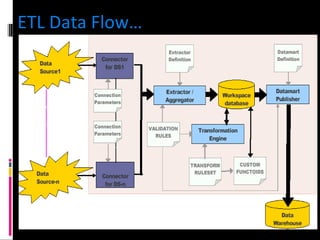
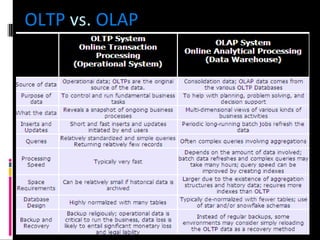
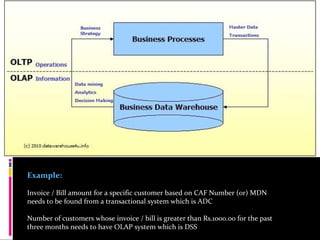
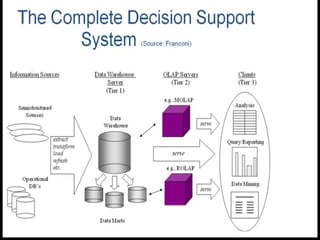
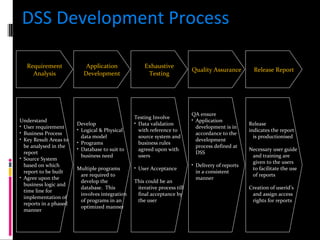
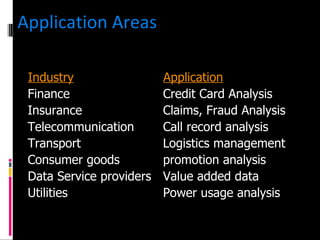
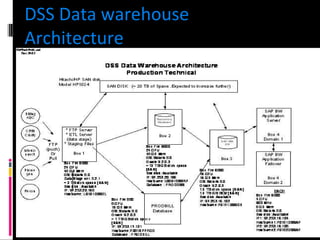
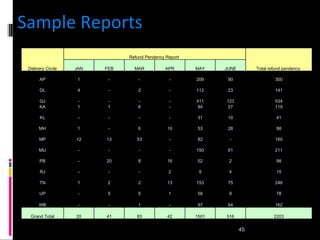
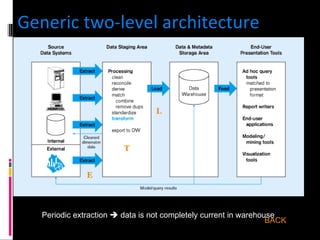
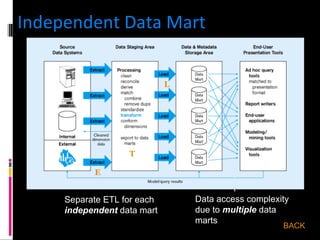
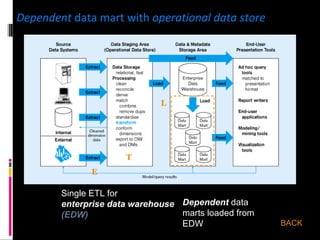
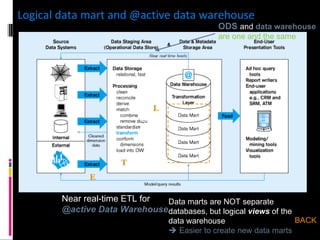
The document discusses various concepts related to database design and data warehousing. It describes how DBMS minimize problems like data redundancy, isolation, and inconsistency through techniques like normalization, indexing, and using data dictionaries. It then discusses data warehousing concepts like the need for data warehouses, their key characteristics of being subject-oriented, integrated, and time-variant. Common data warehouse architectures and components like the ETL process, OLAP, and decision support systems are also summarized.