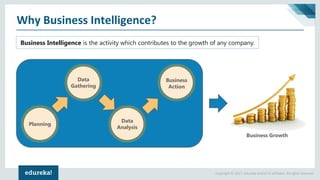
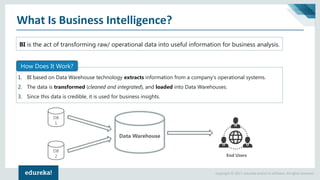
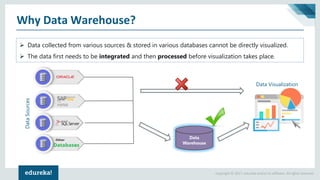
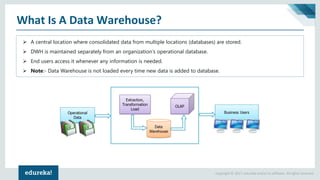
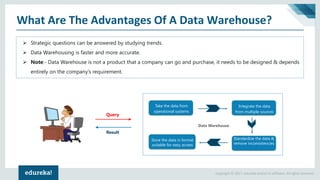
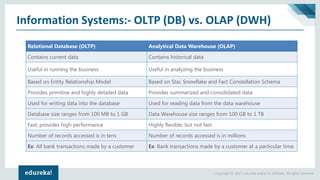
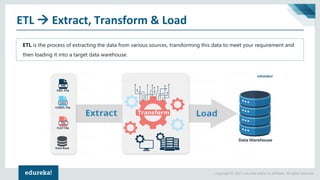
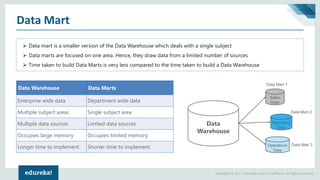
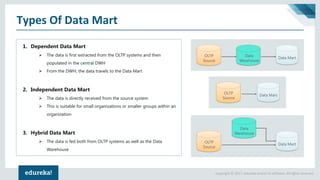
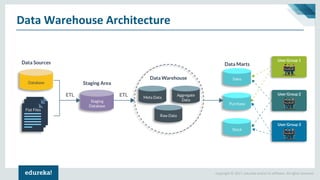
The document discusses the concepts of artificial intelligence, machine learning, business intelligence (BI), and data warehousing, outlining their importance and functionalities. It explains the process of transforming raw data into useful business insights through data warehouses, and highlights the differences between OLTP and OLAP systems. Further, it covers key terminologies, ETL processes, and provides an overview of data warehousing architecture.