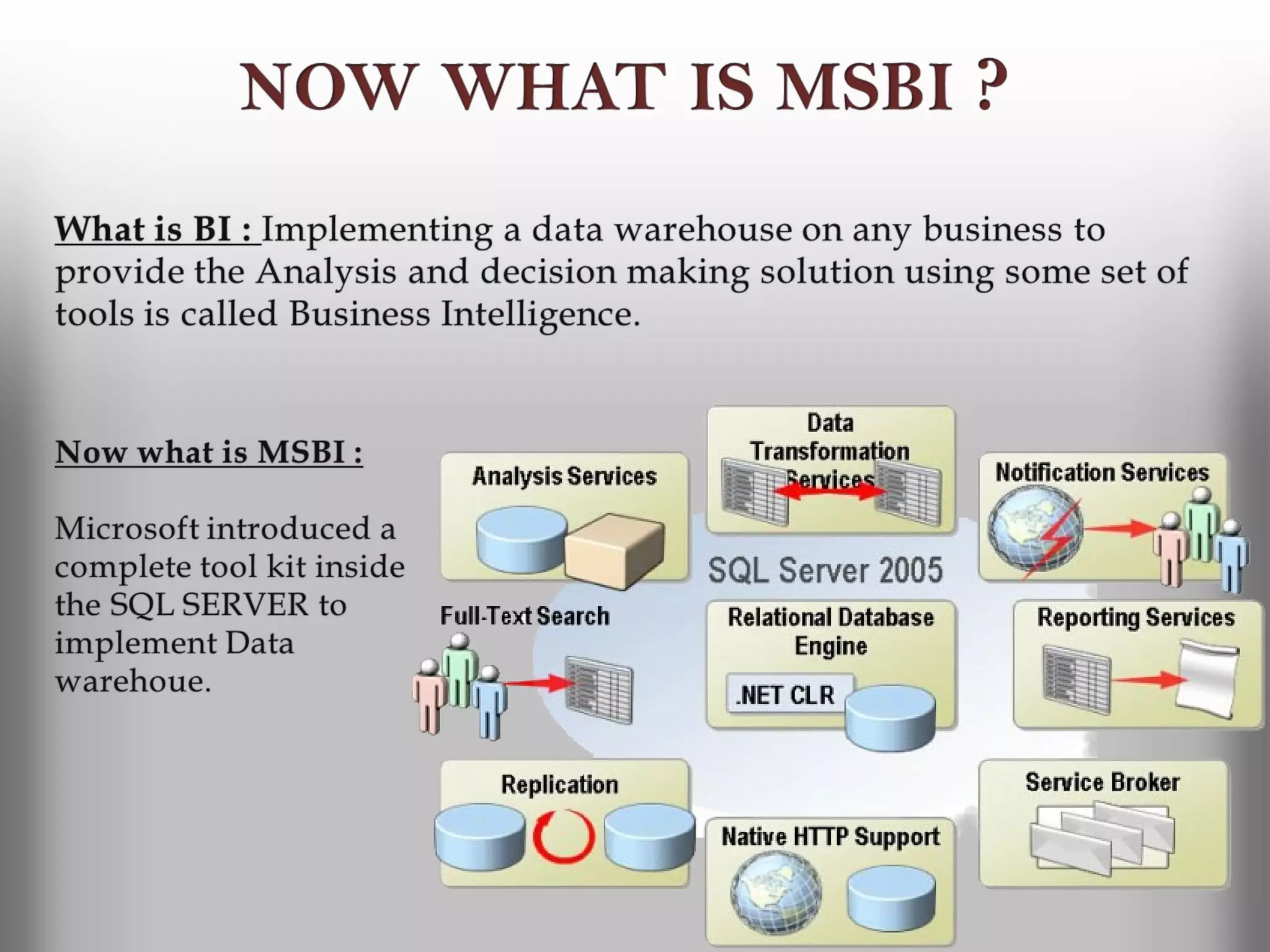
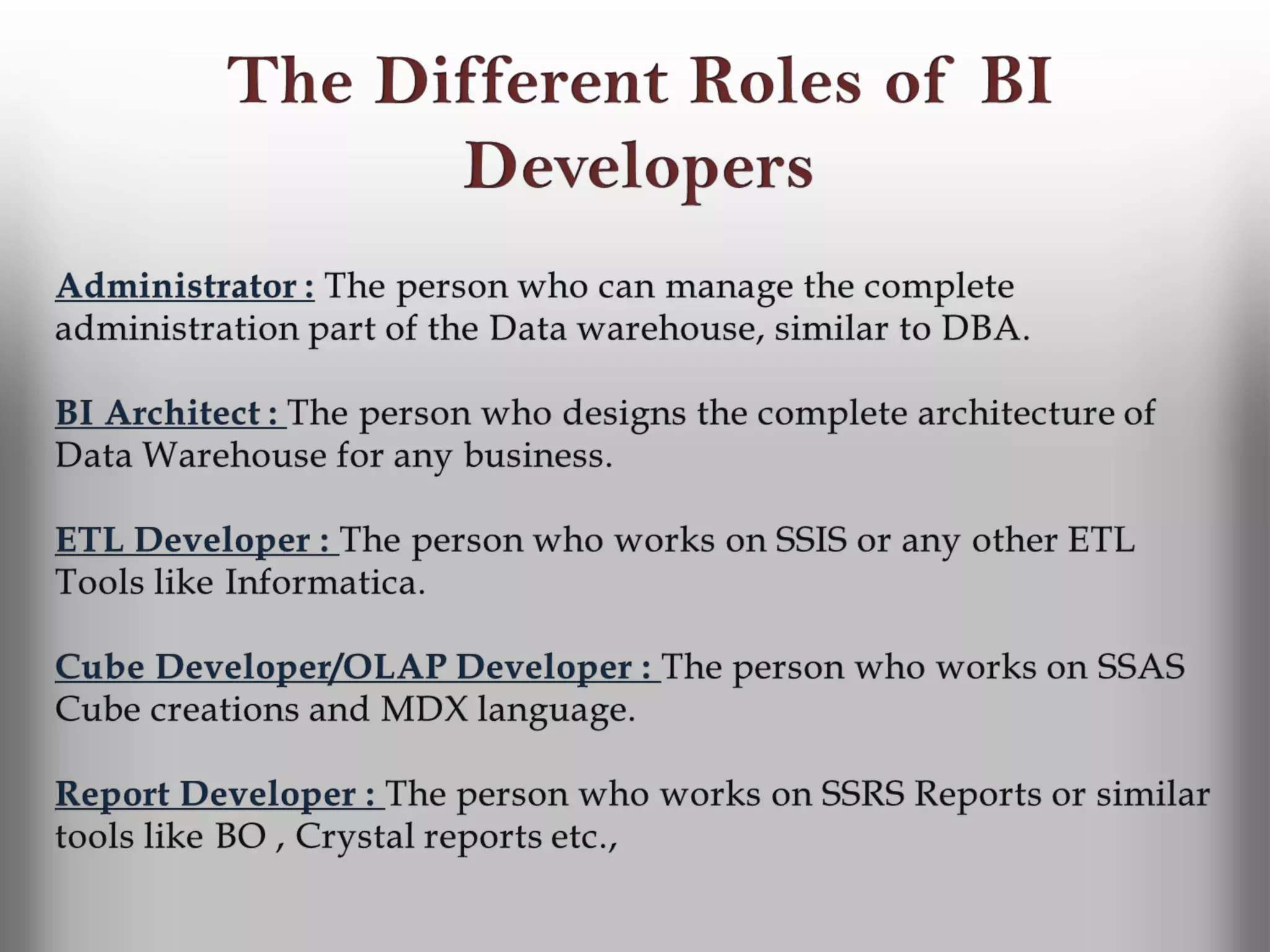
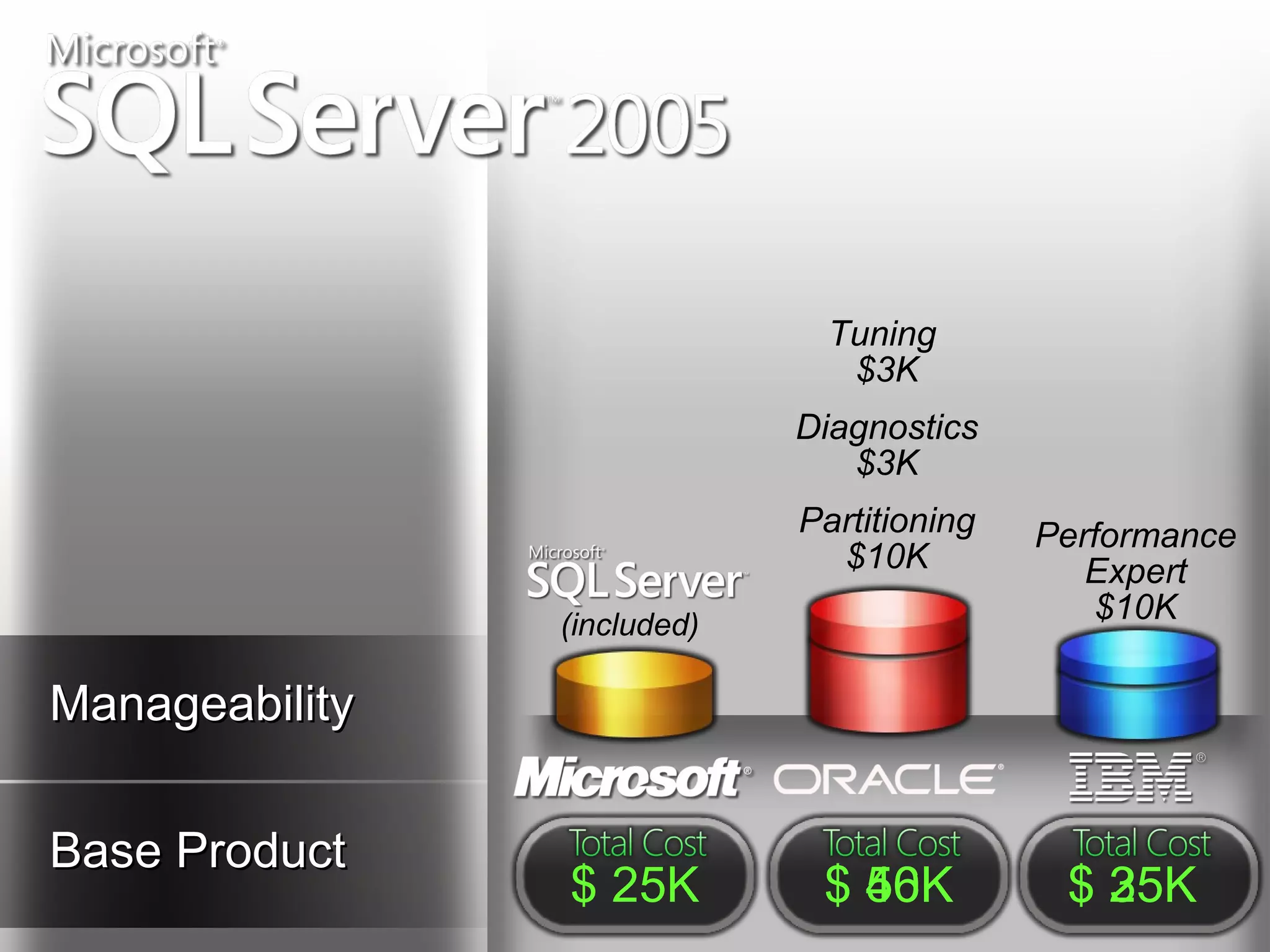
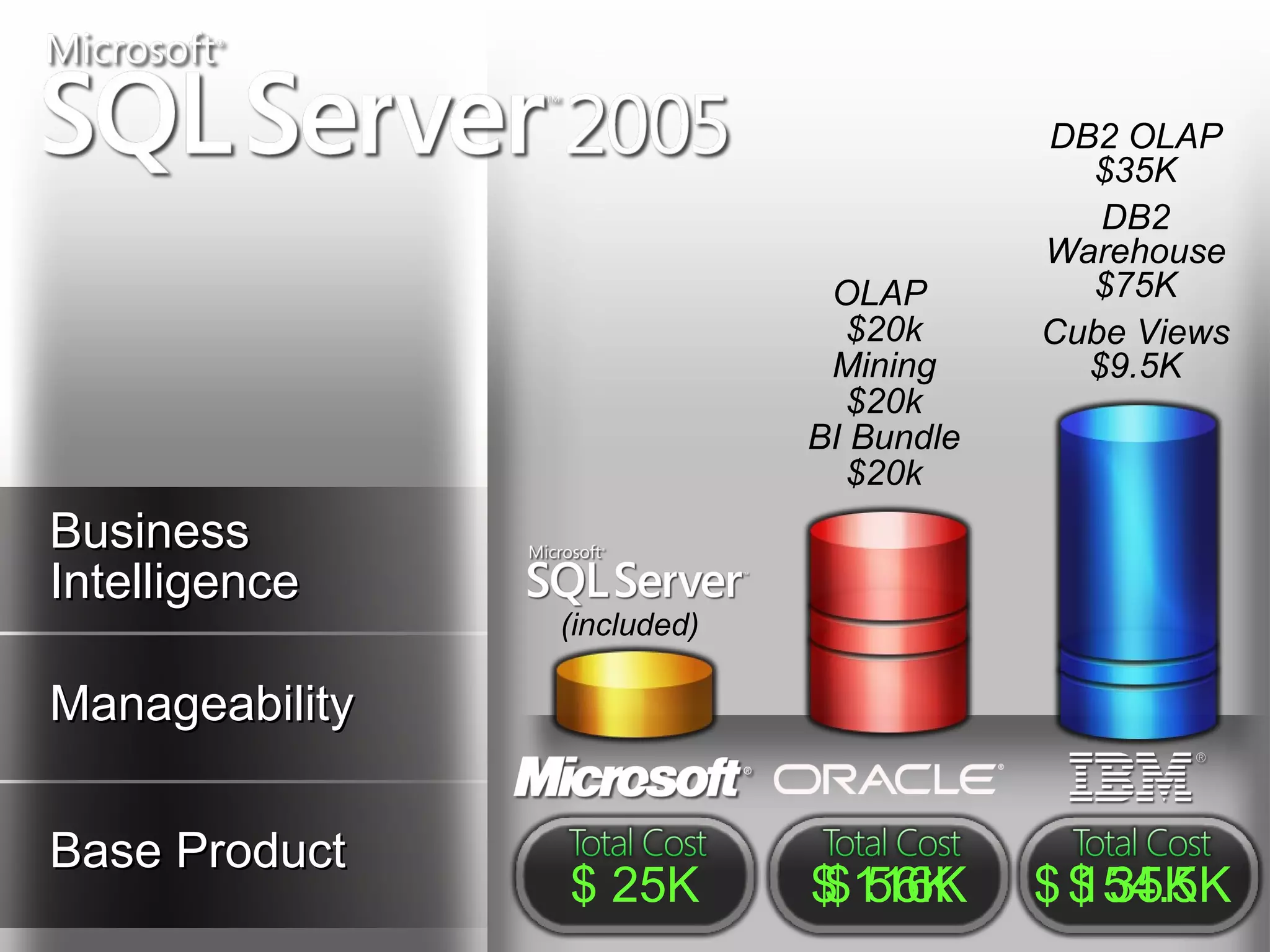
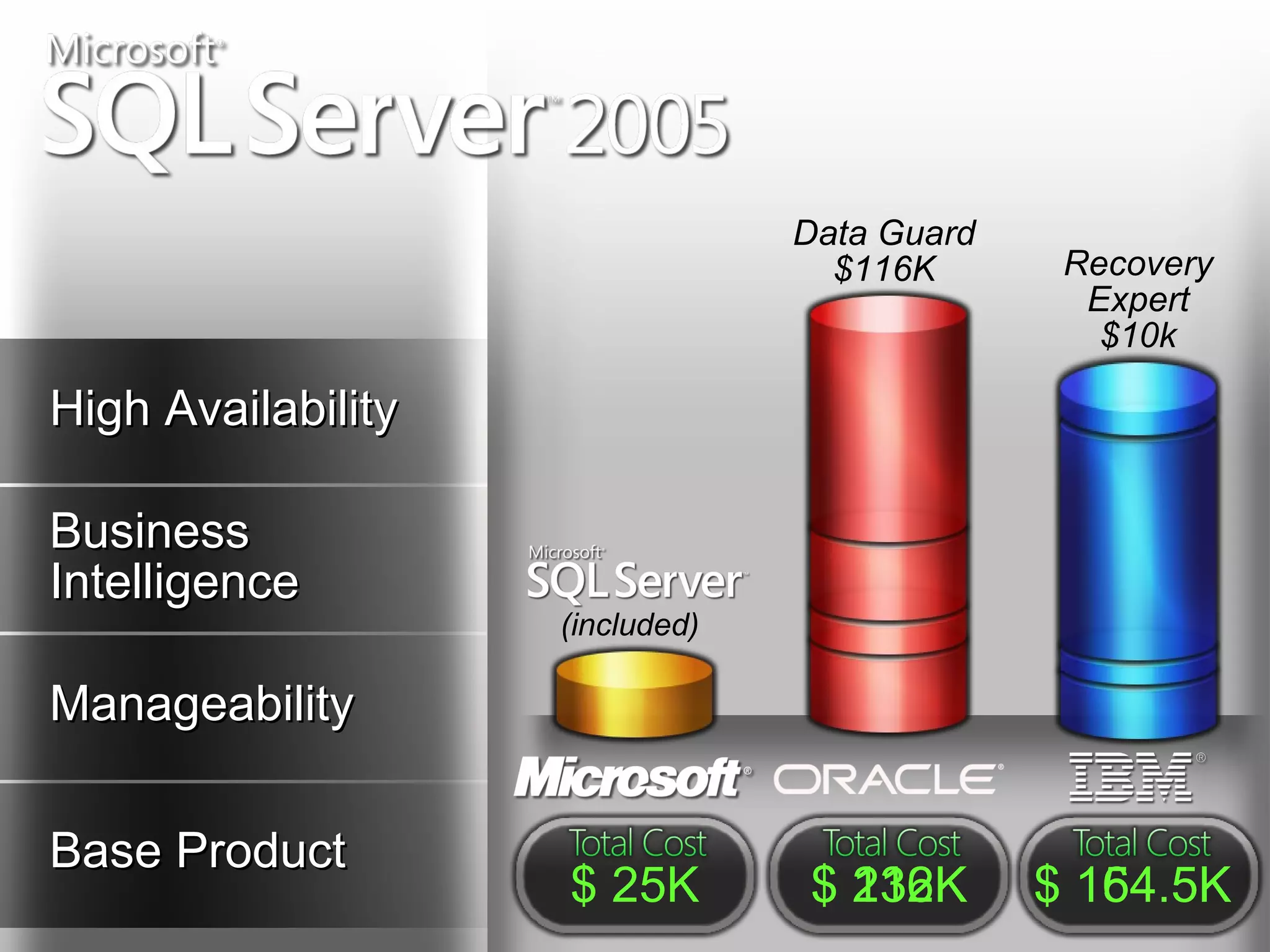
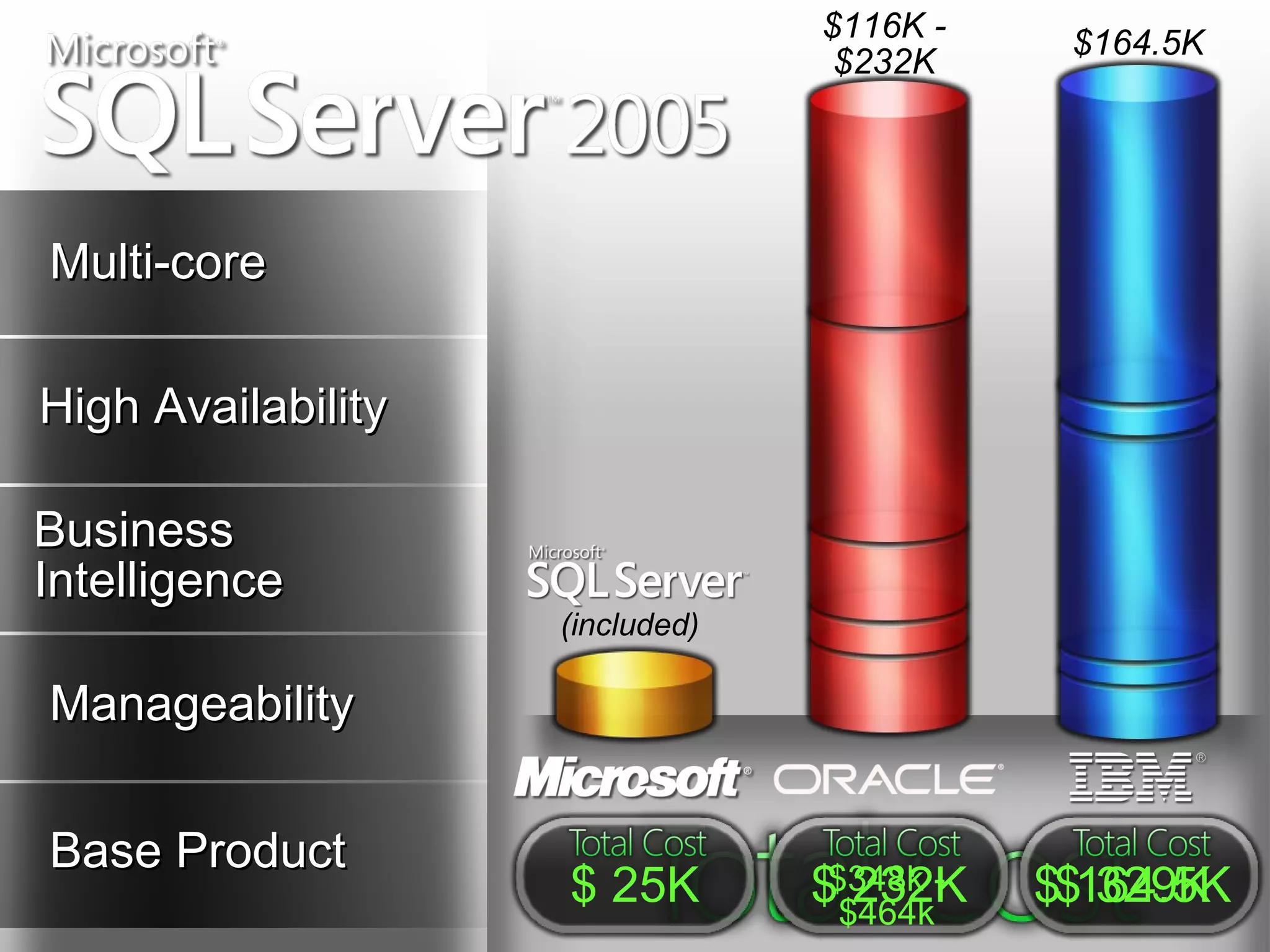
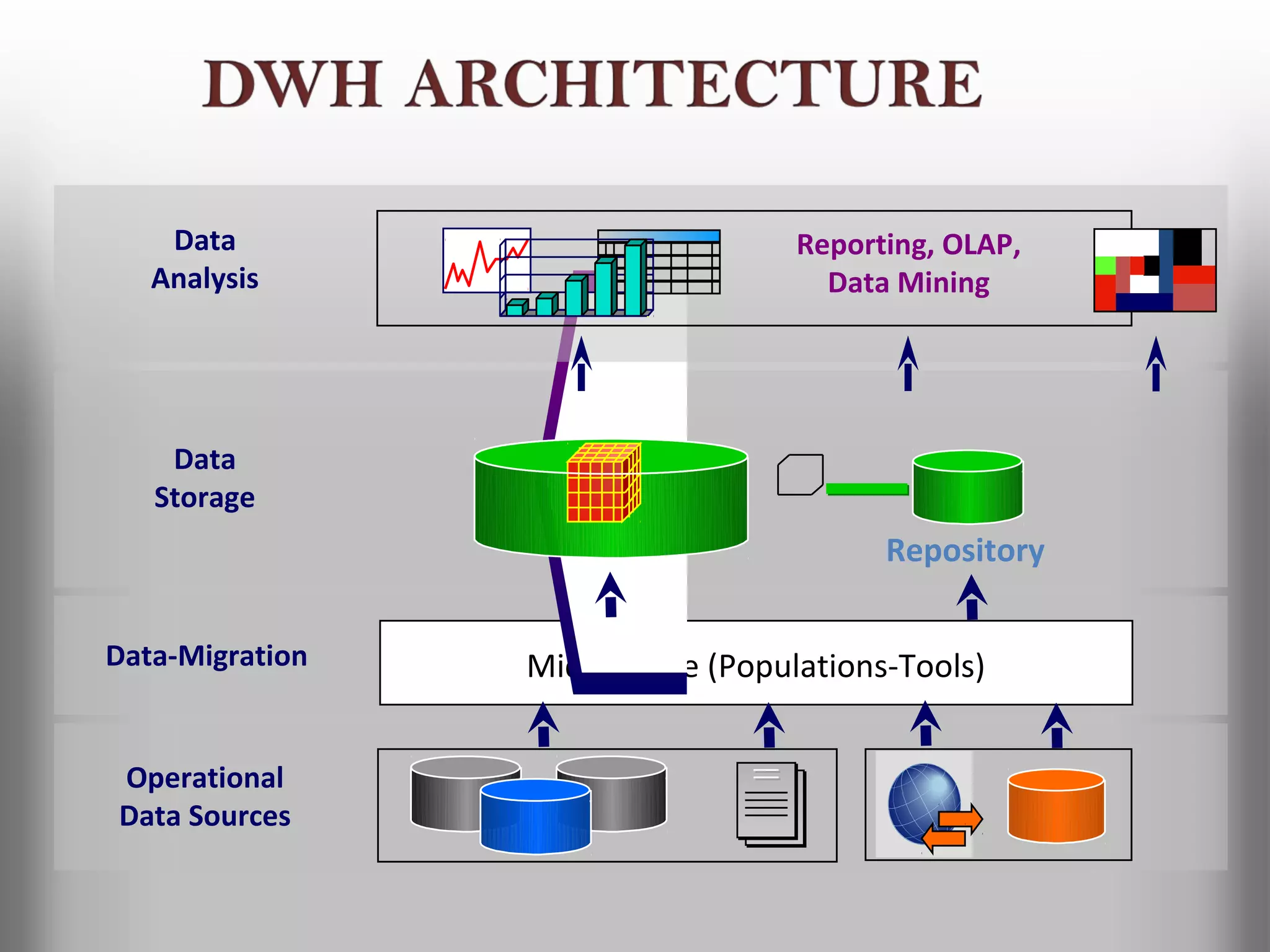
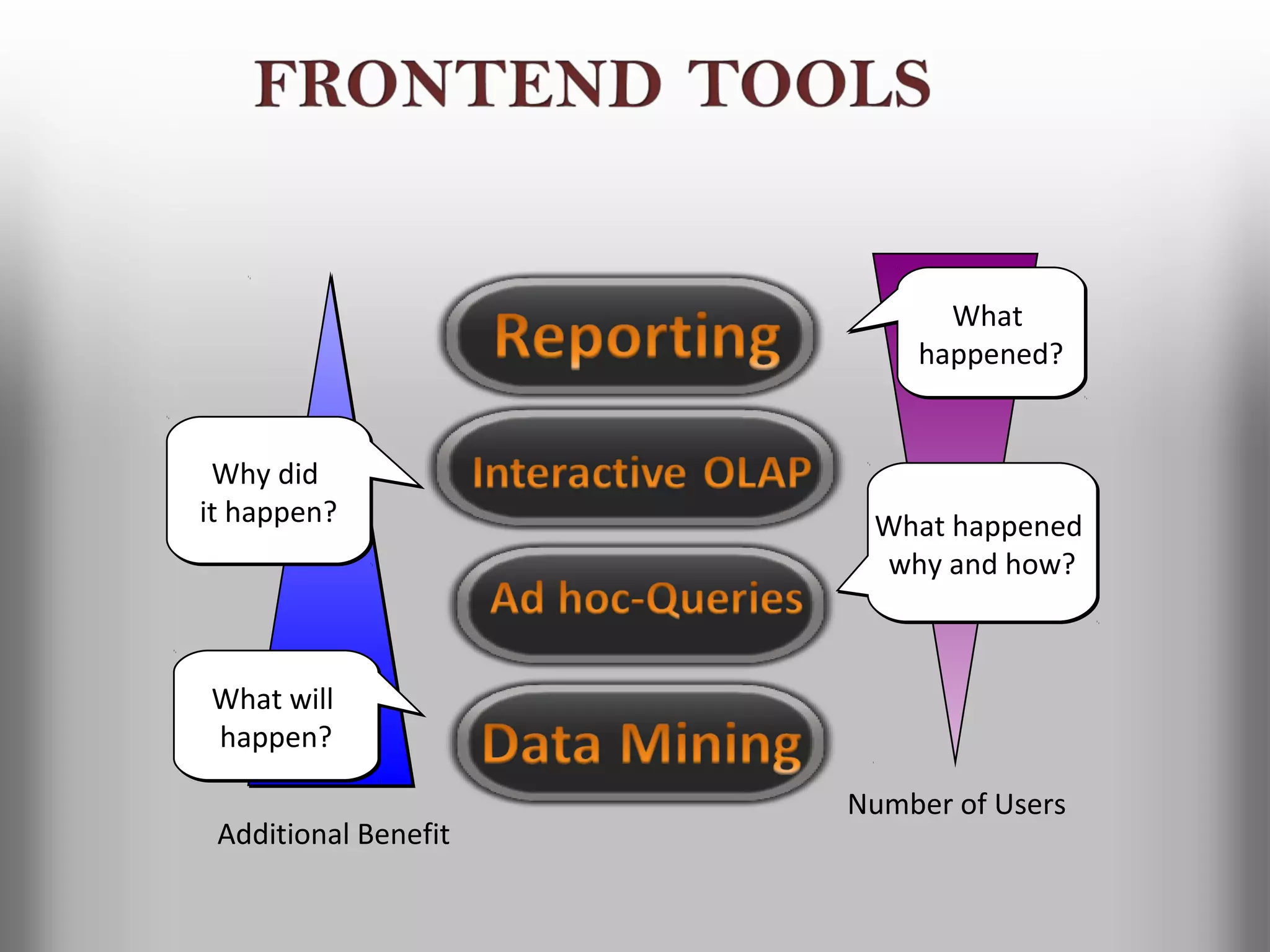
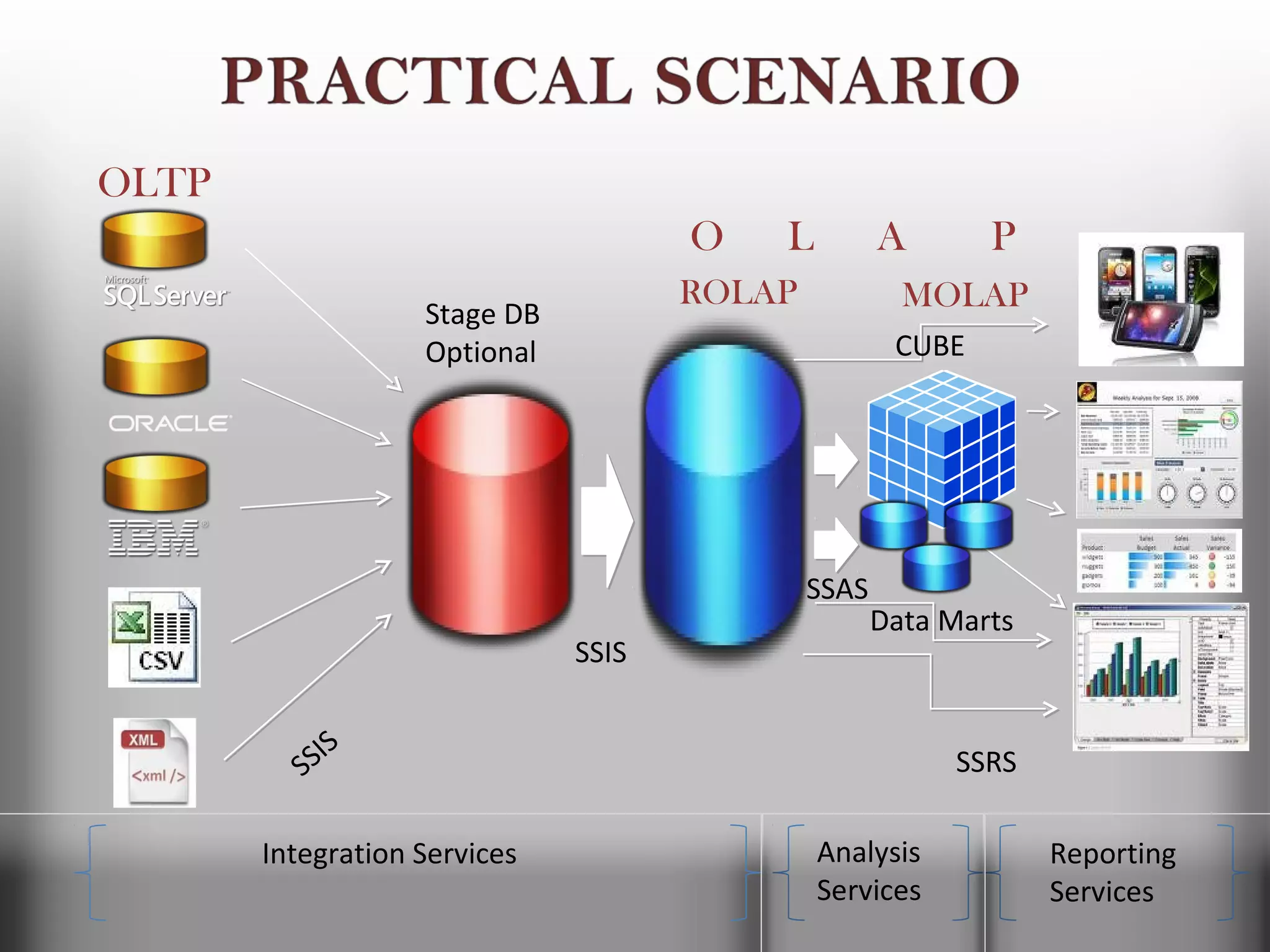
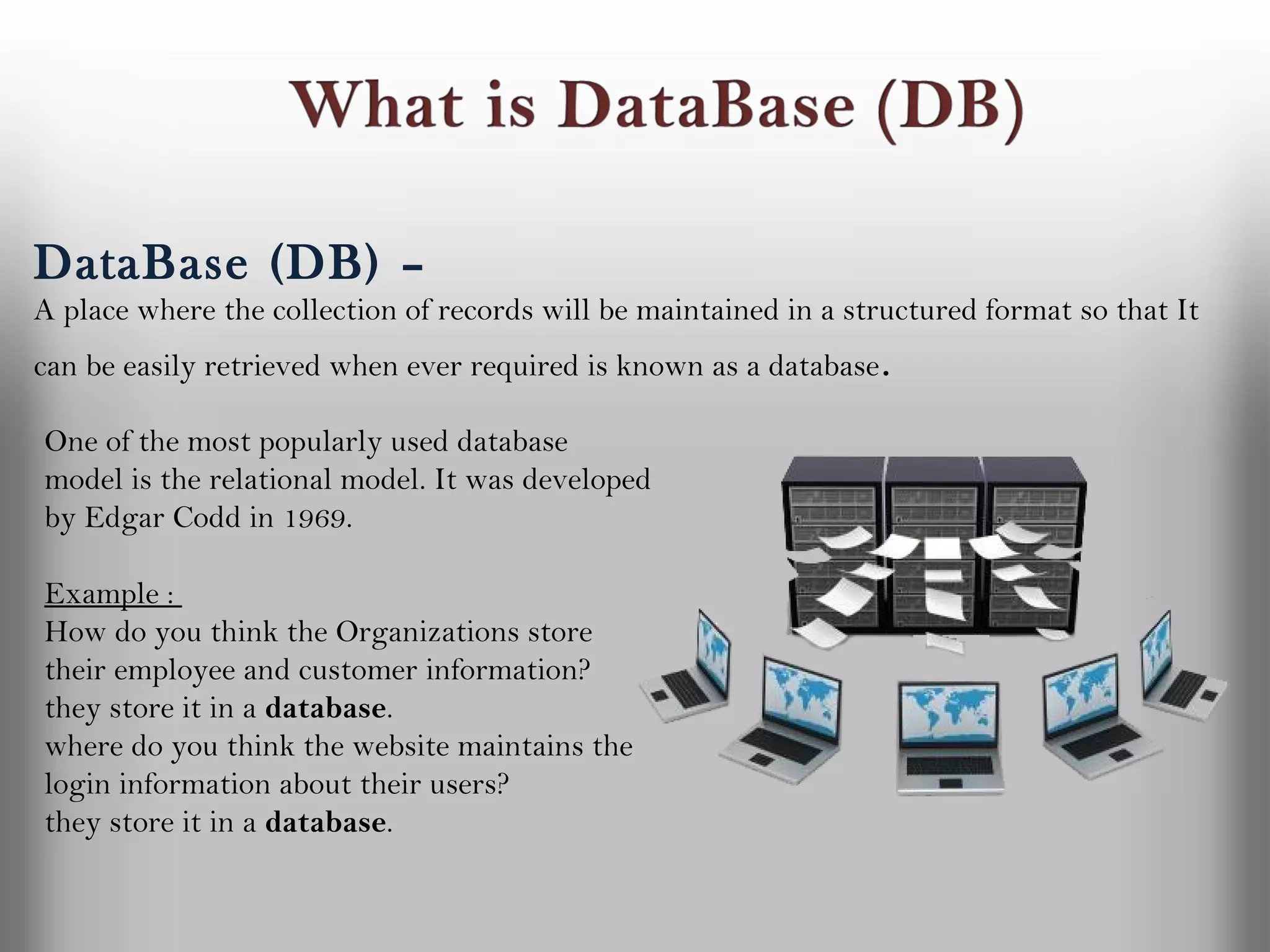
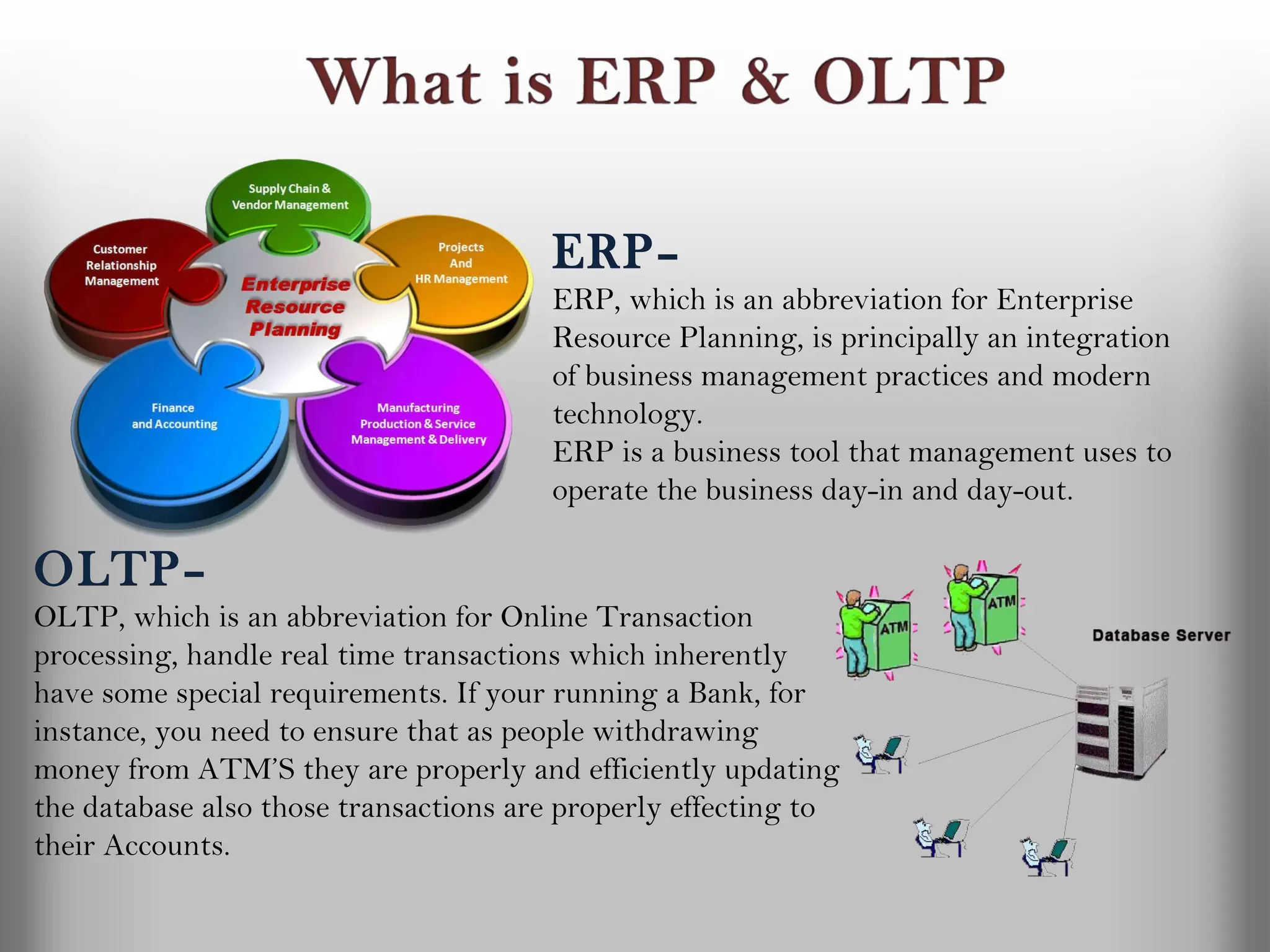
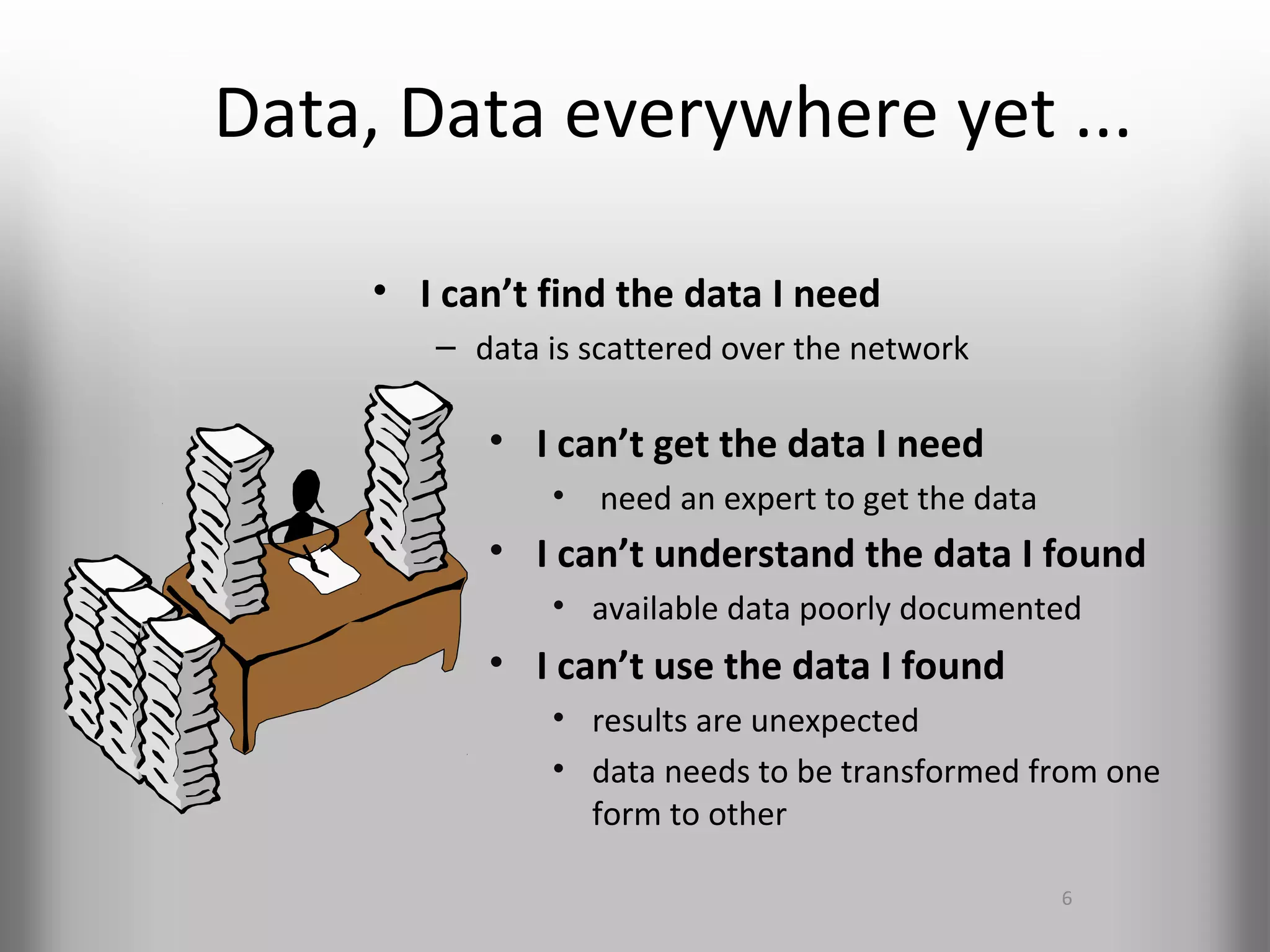
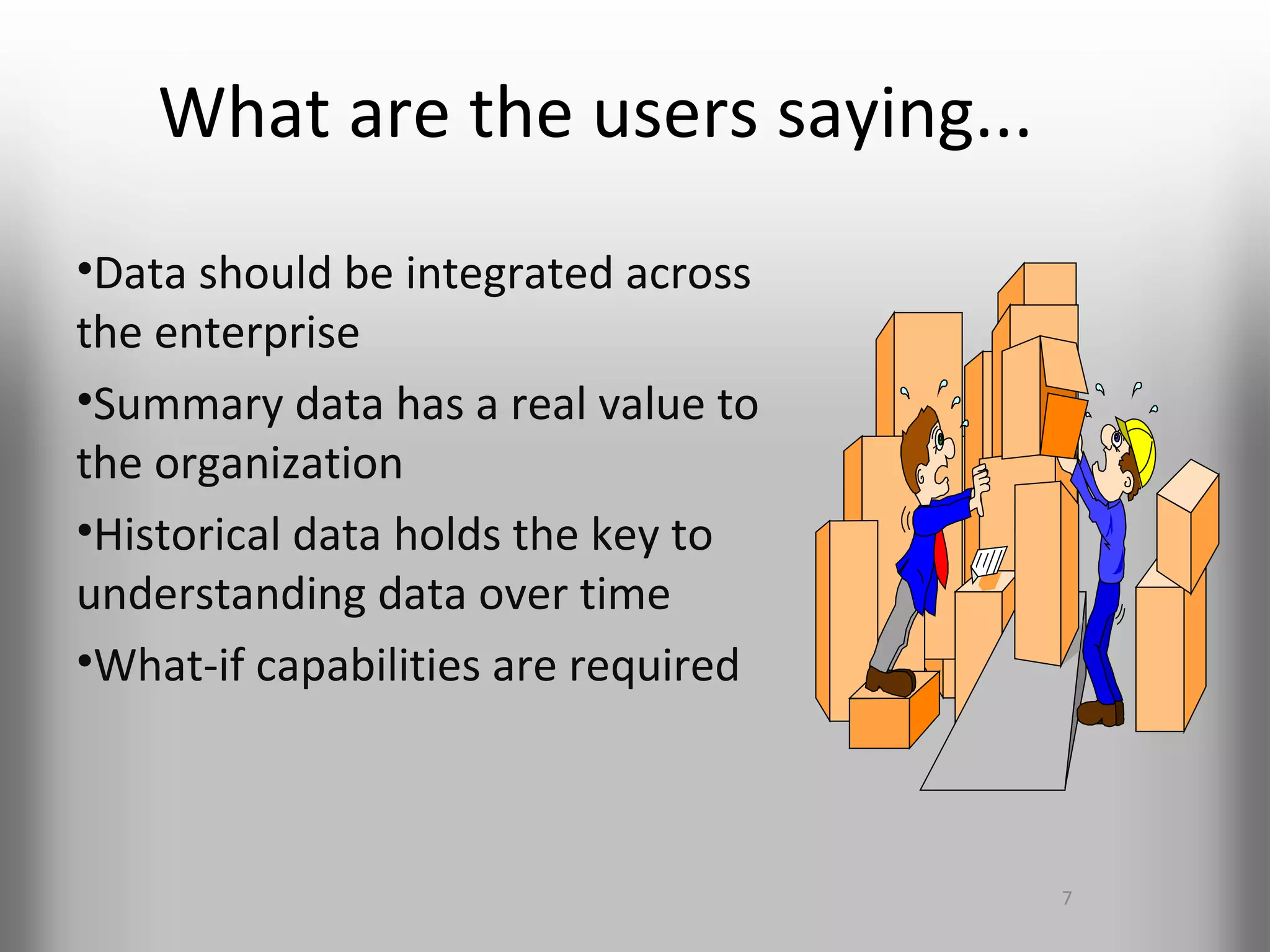
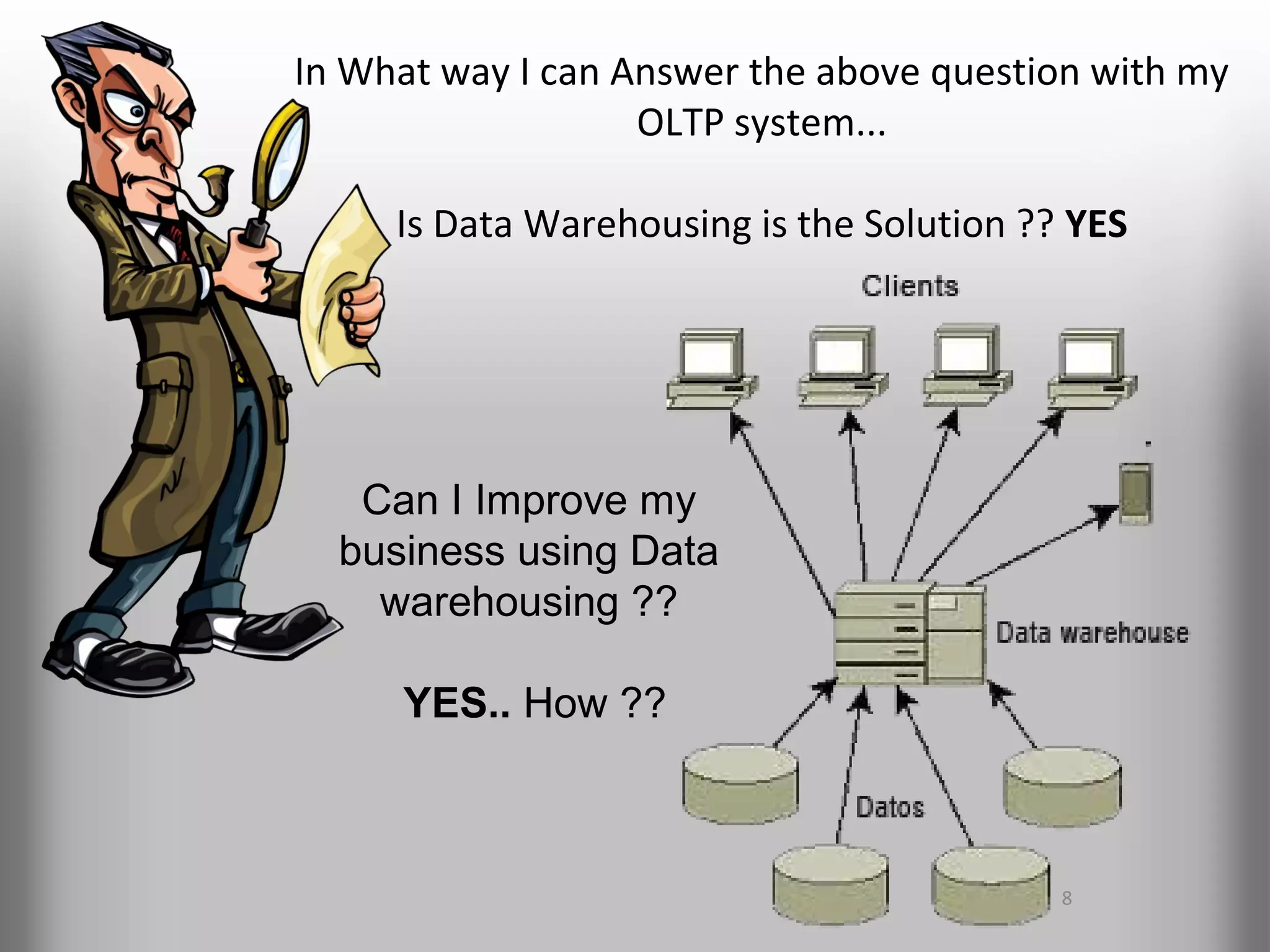
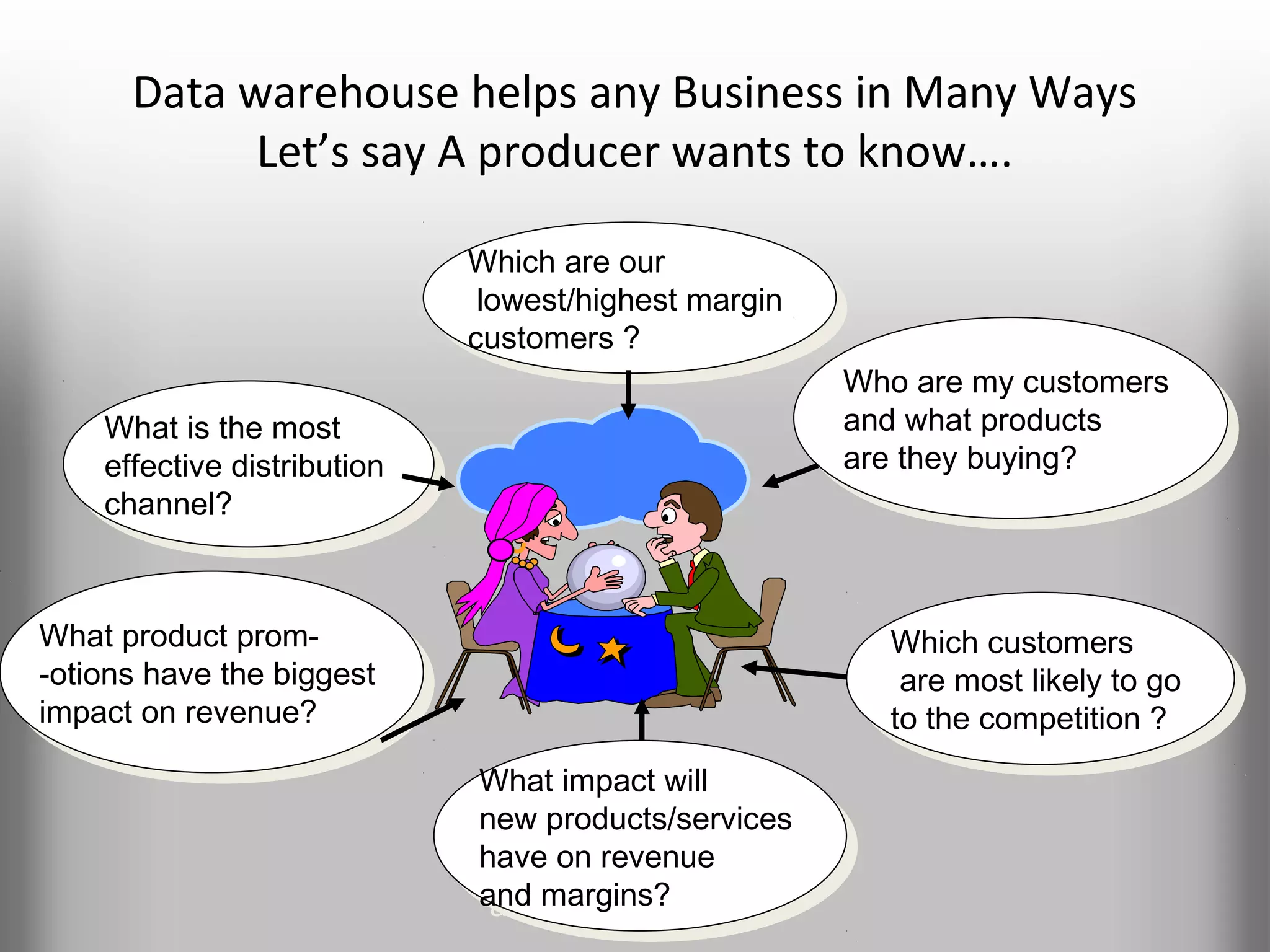
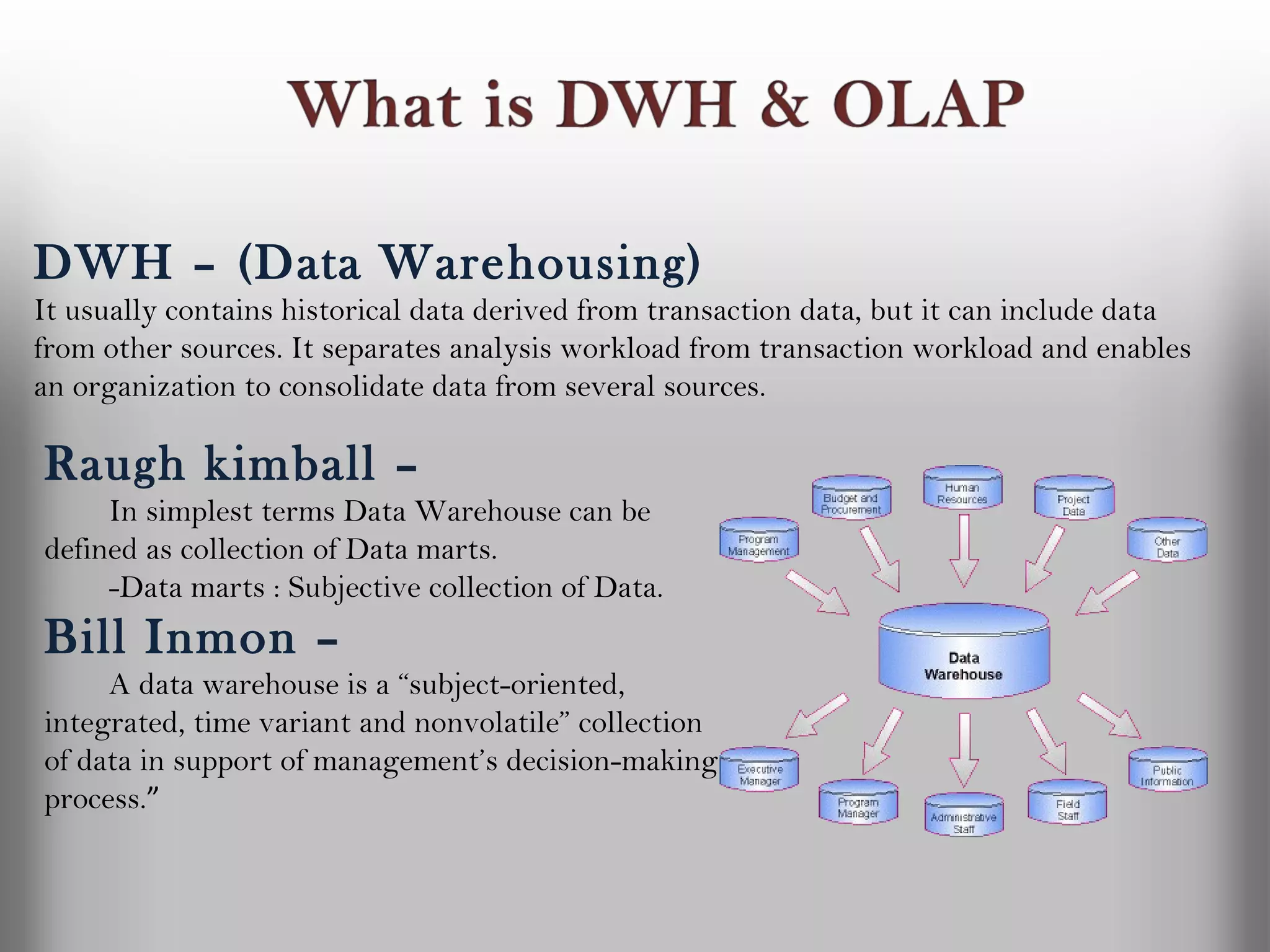
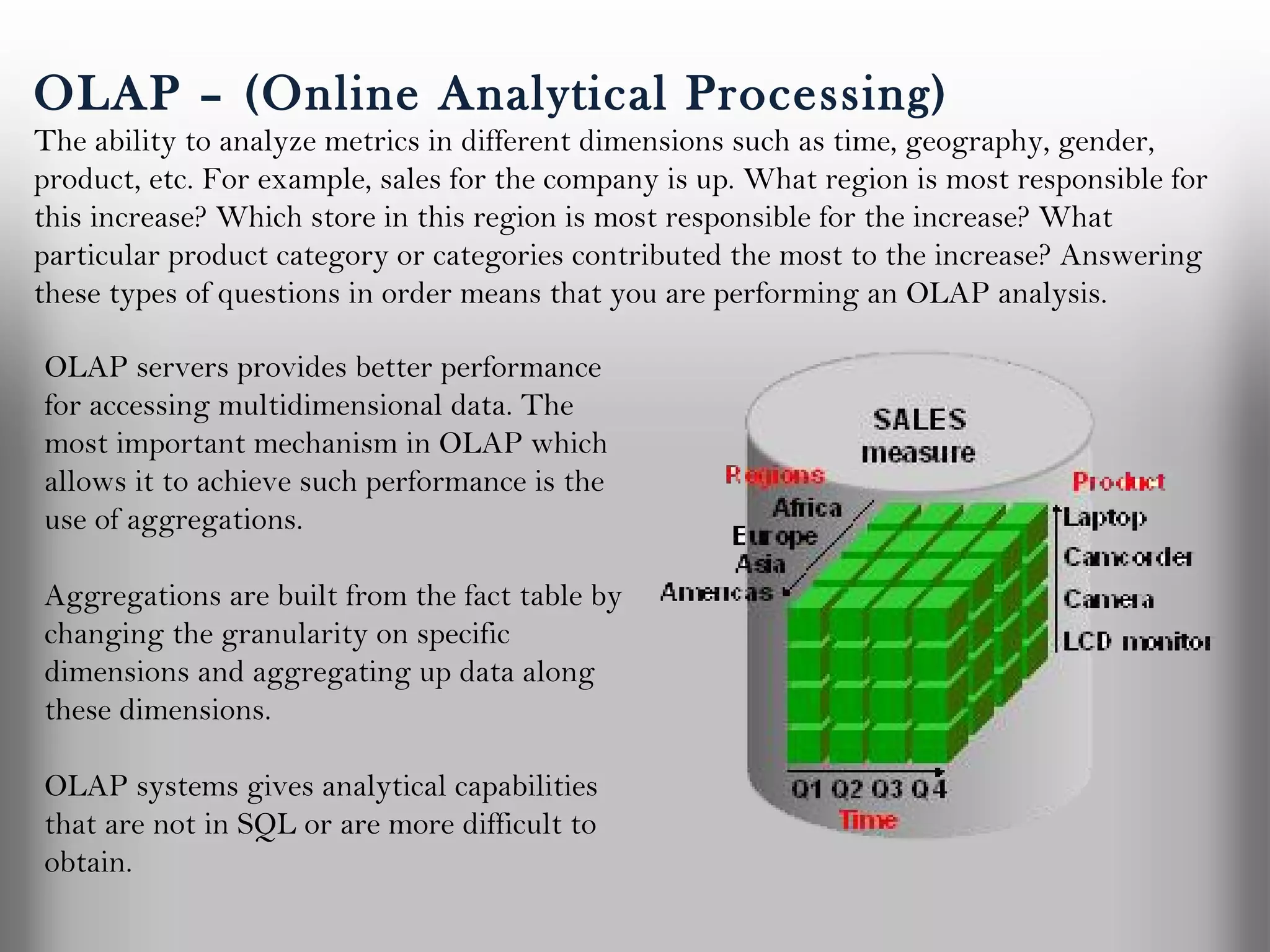
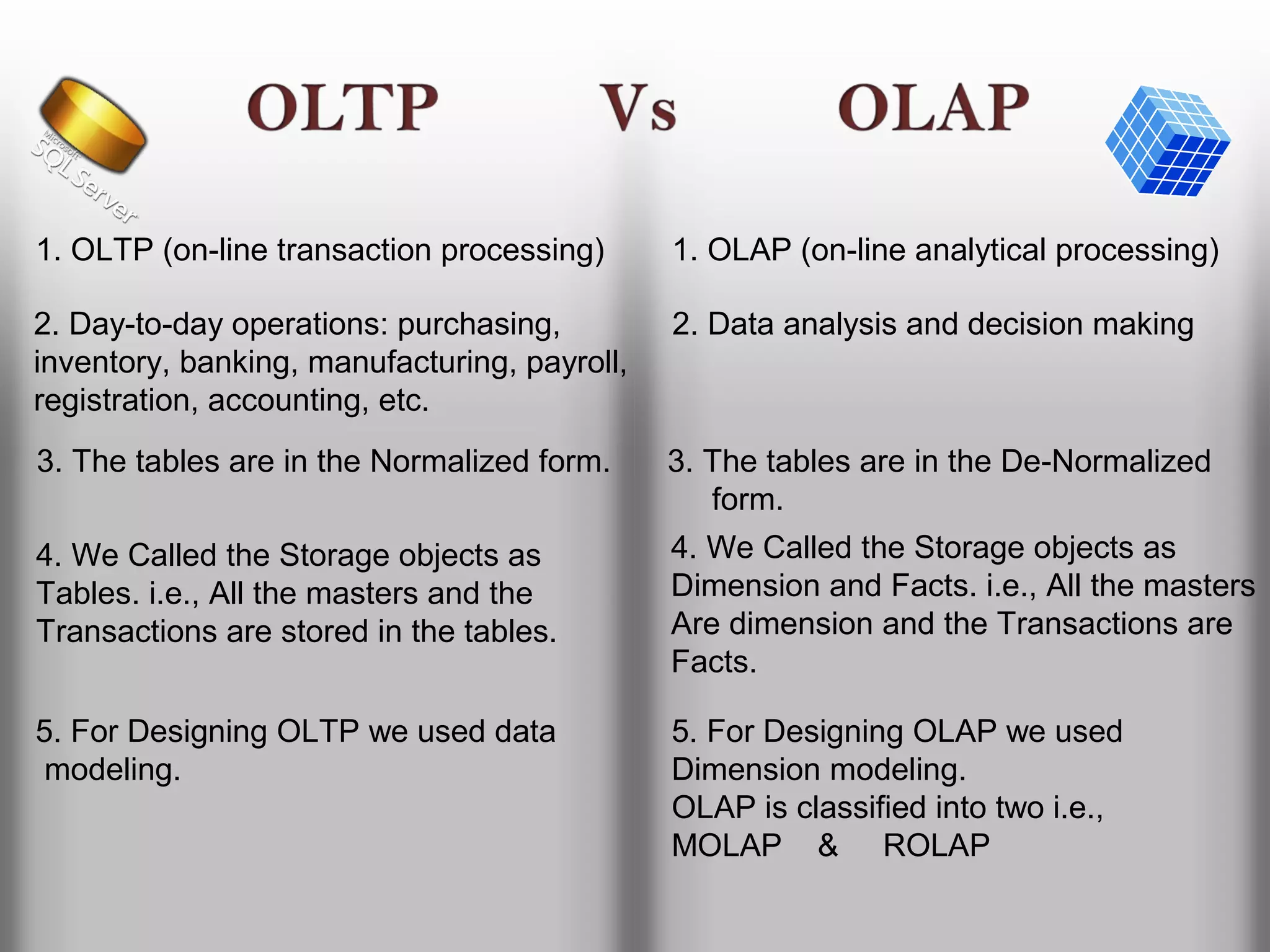
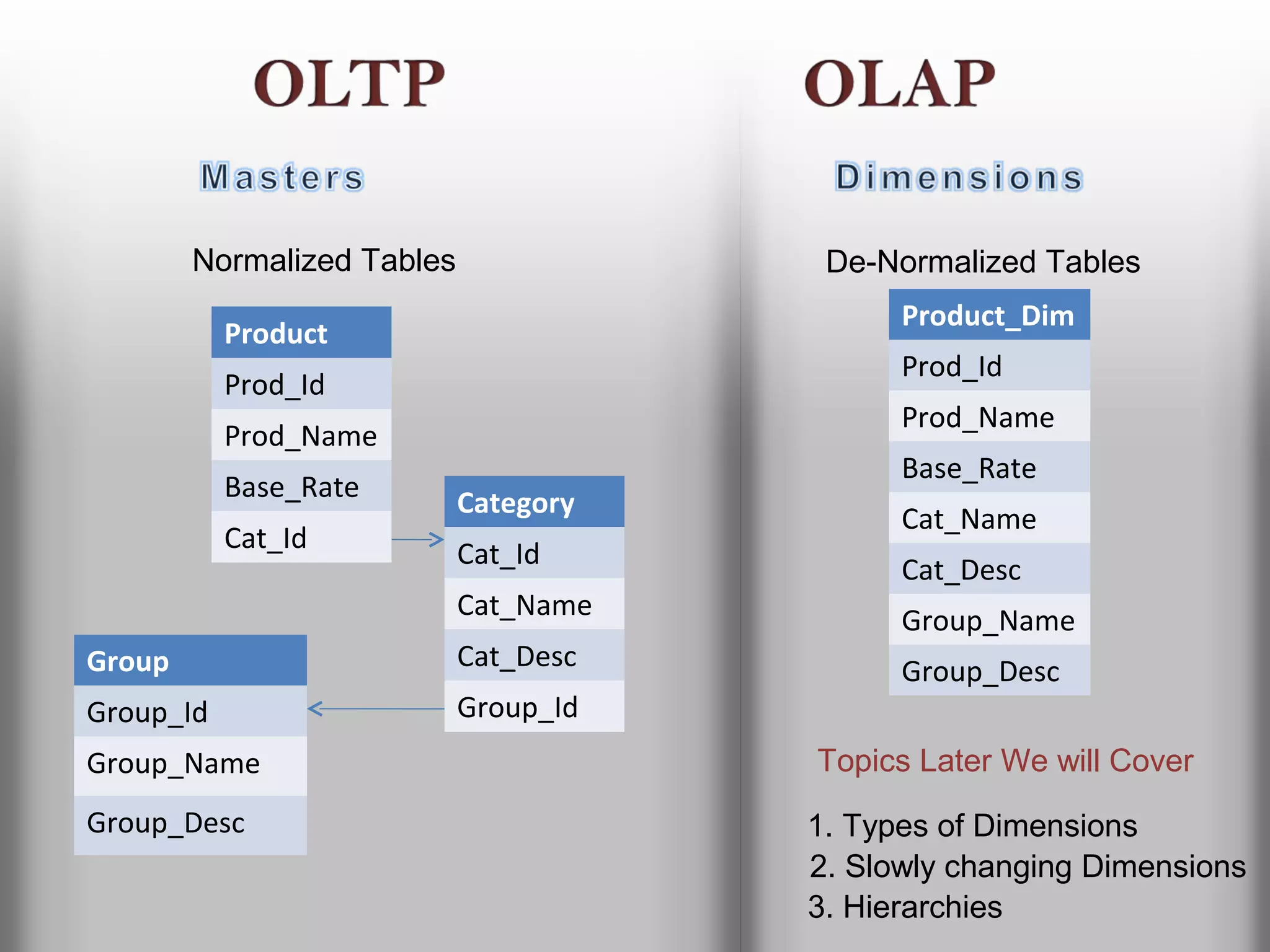
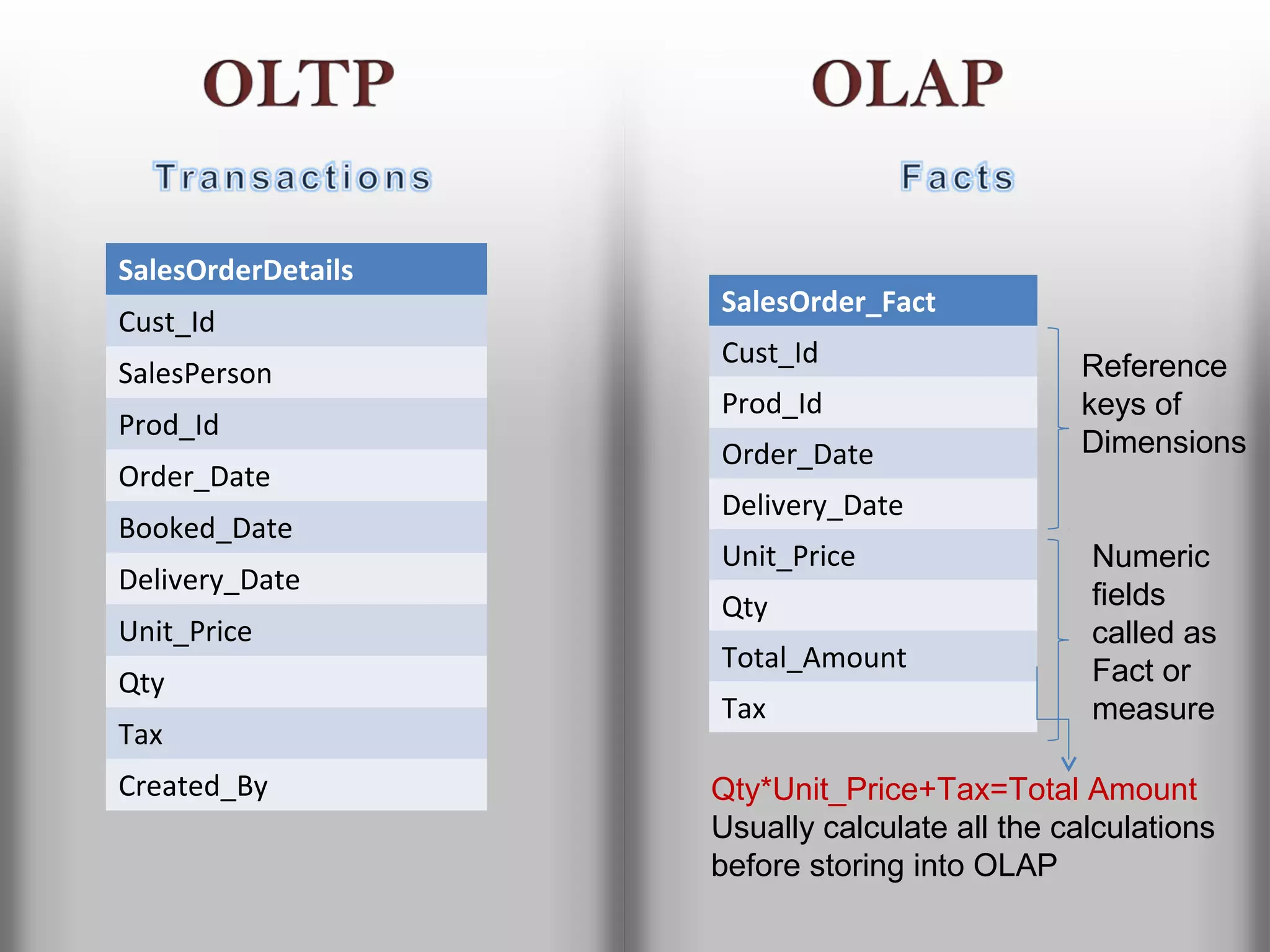
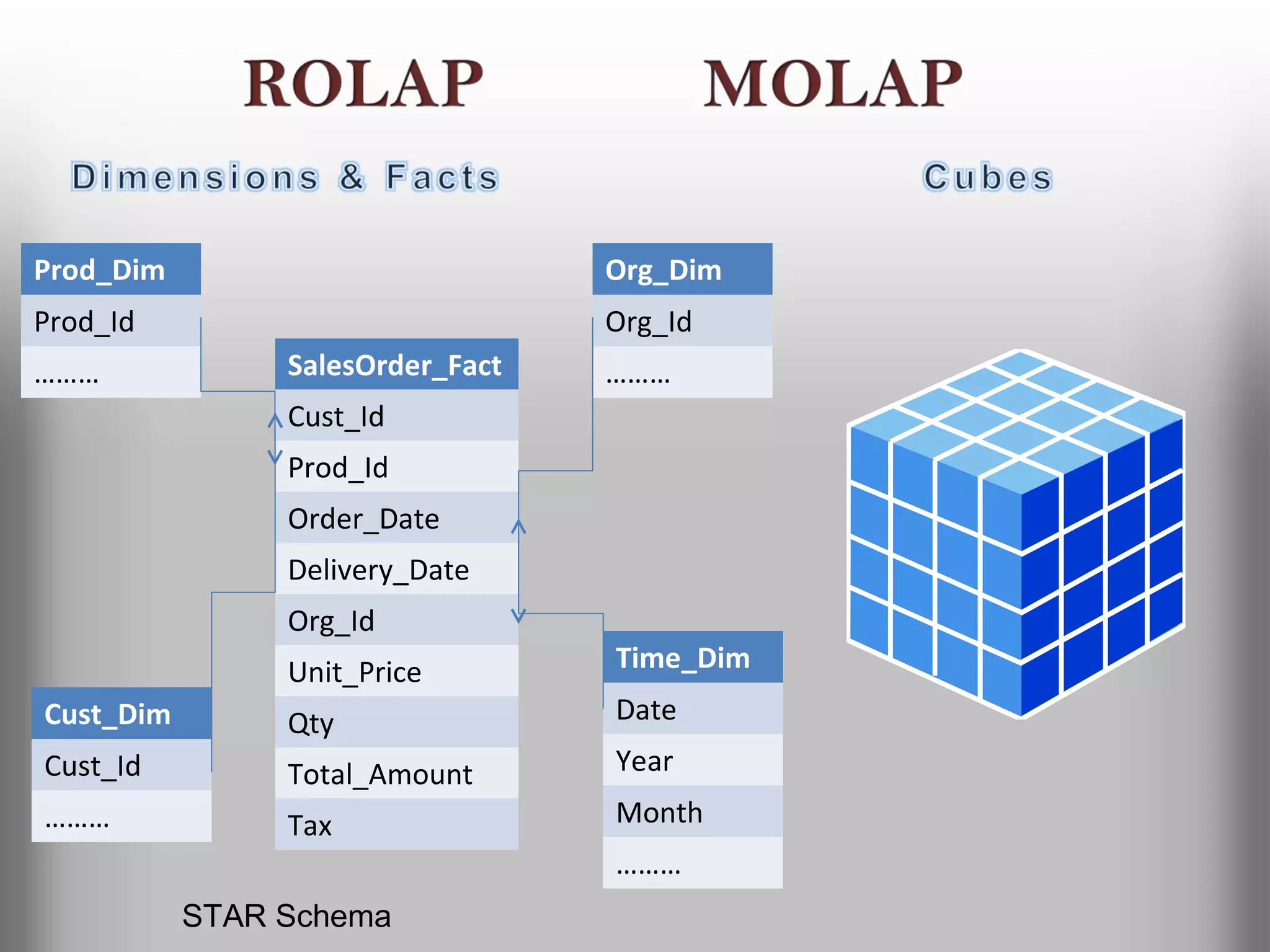
A database is a structured collection of records that can be easily retrieved. The relational model, developed by Edgar Codd in 1969, is one of the most popular database models. Organizations store employee and customer information in databases, and websites store user login information in databases. Data warehousing involves integrating data from different sources into a single database to facilitate reporting and analysis. It allows organizations to consolidate data to better understand business metrics and make strategic decisions.


![A single, complete and
consistent store of data
obtained from a variety of
different sources made
available to end users in a what
they can understand and use in
a business context.
[Barry Devlin]
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontomsbibyyasir-091011020822-phpapp01/75/Introduction-To-Msbi-By-Yasir-18-2048.jpg)