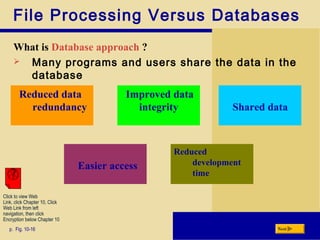
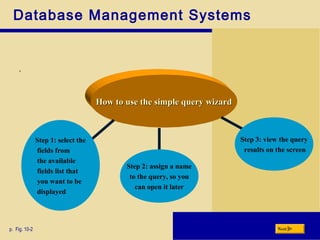
This chapter discusses database management and describes key concepts. It explains that data must be organized and processed to become useful information. Various techniques are presented for maintaining high quality data, including adding, changing, deleting records, and validating data. The chapter differentiates between a file processing system and database approach, describing how databases reduce redundancy and improve access. It also outlines the functions of database management systems and characteristics of different database types like relational, object-oriented and multidimensional. Finally, the roles of database analysts, administrators and users are discussed.