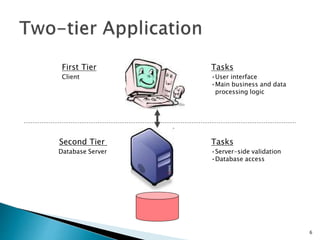
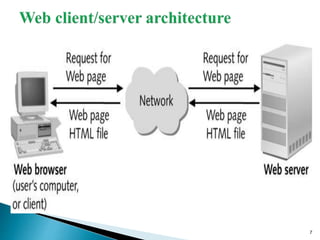
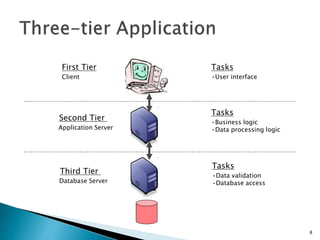
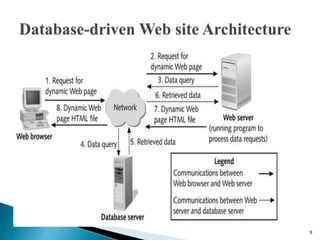
A web database allows storing and accessing data via the internet. It uses a client-server architecture with a web interface to connect to backend database servers. Large businesses rely on web databases to store customer information and make it accessible online. Web databases provide platform independence and standardization through their use of web technologies like HTML. Their future involves new technologies like NoSQL, Hadoop, universal memory and blockchain.