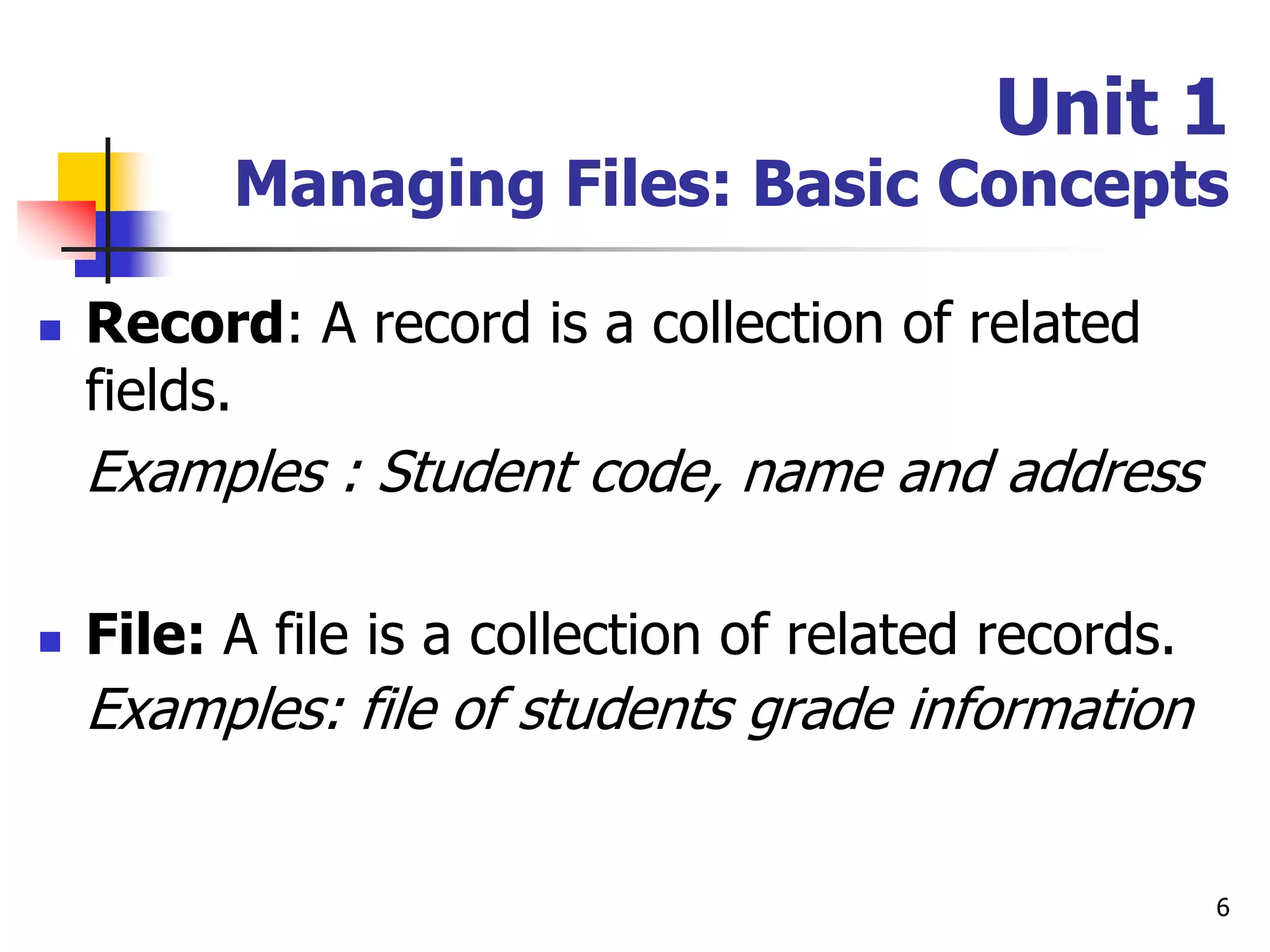
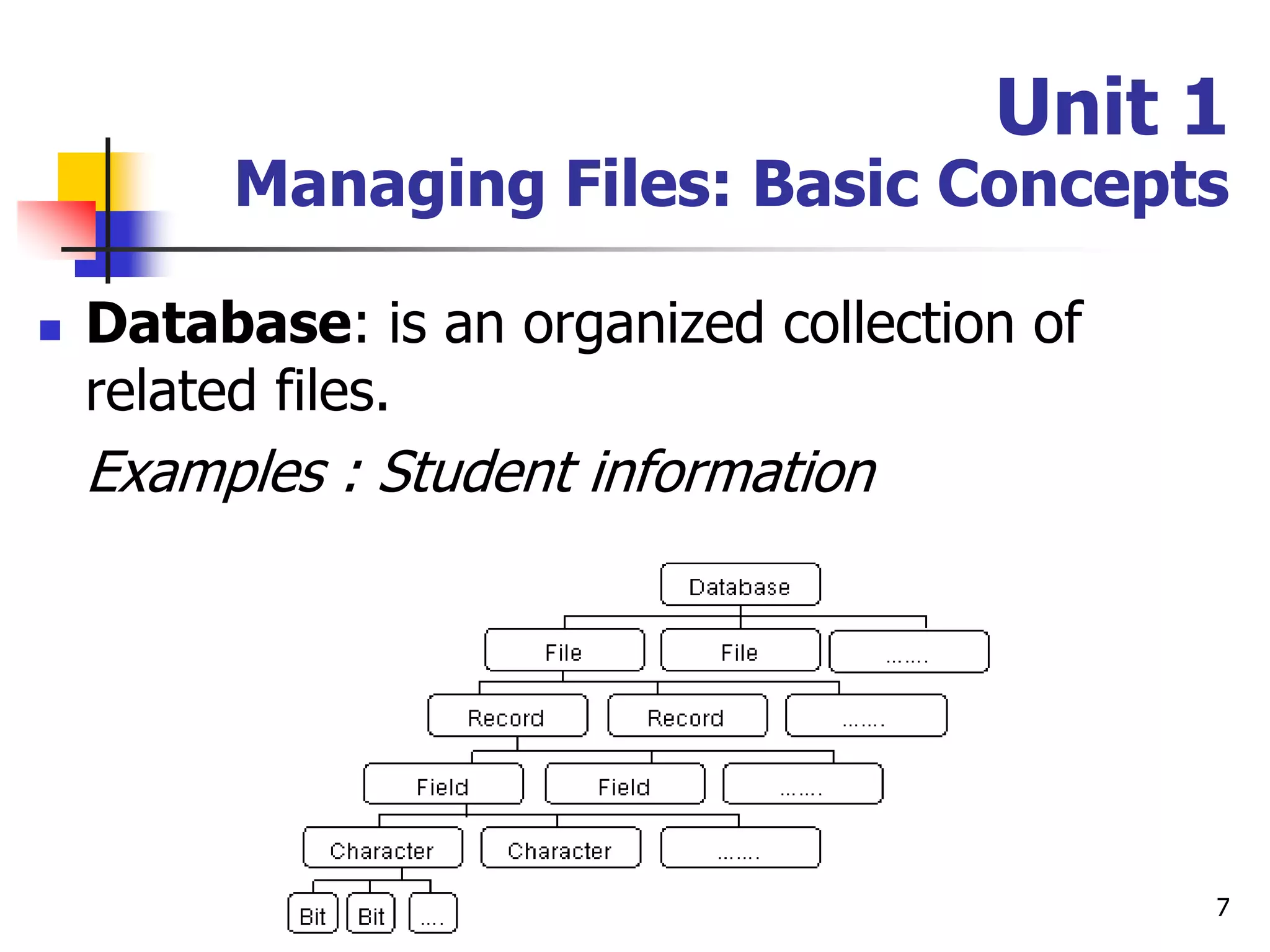
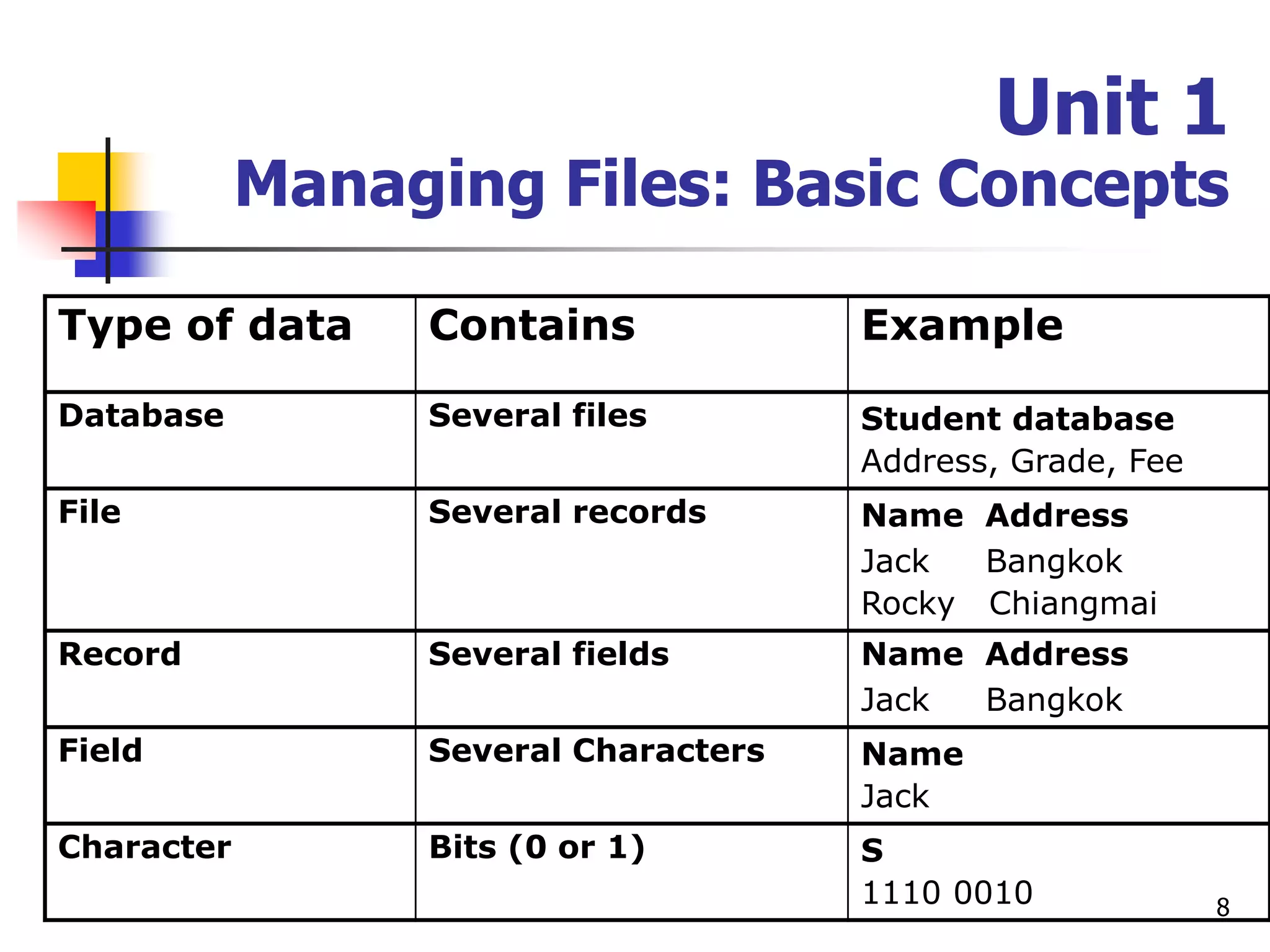
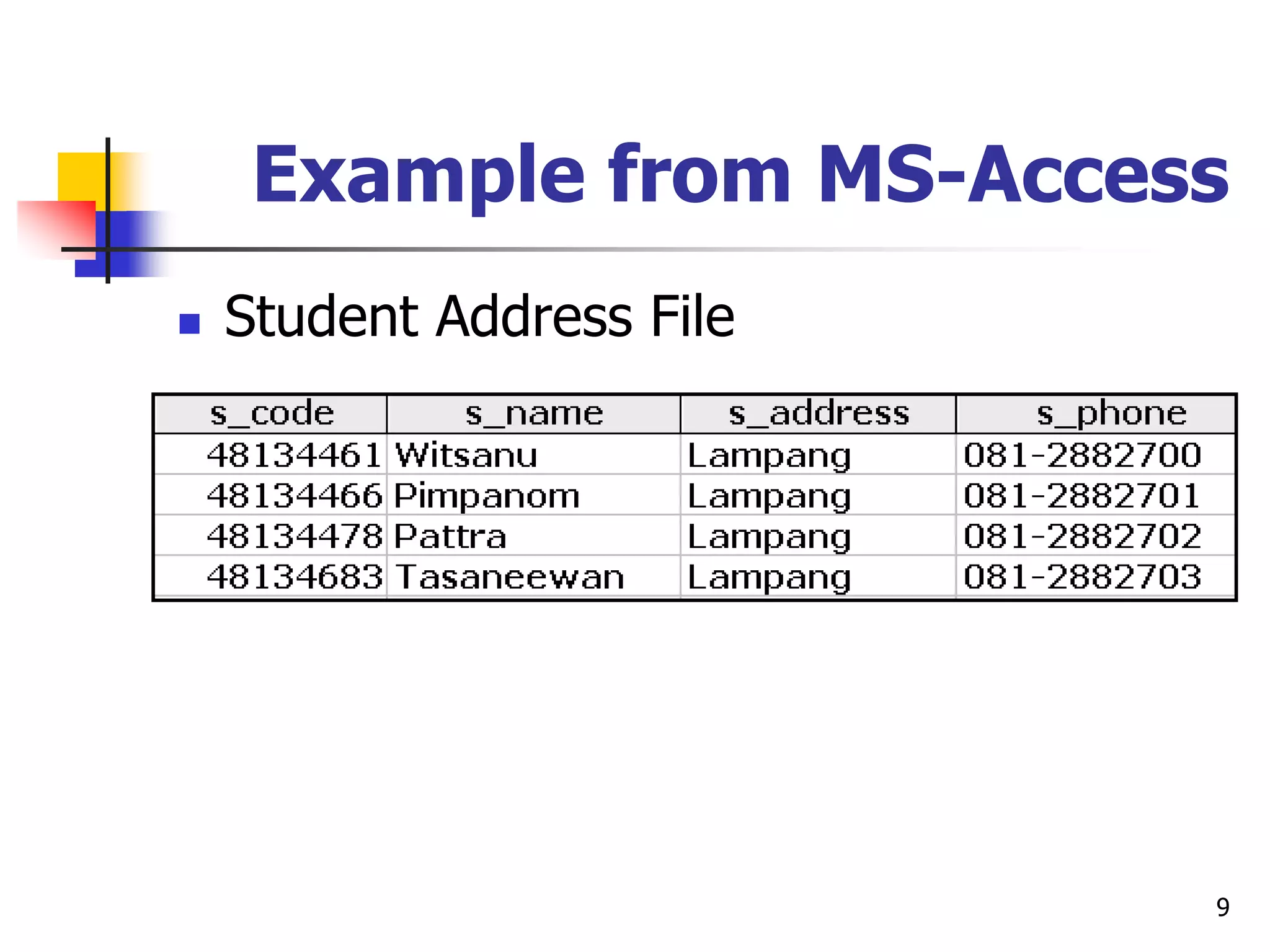
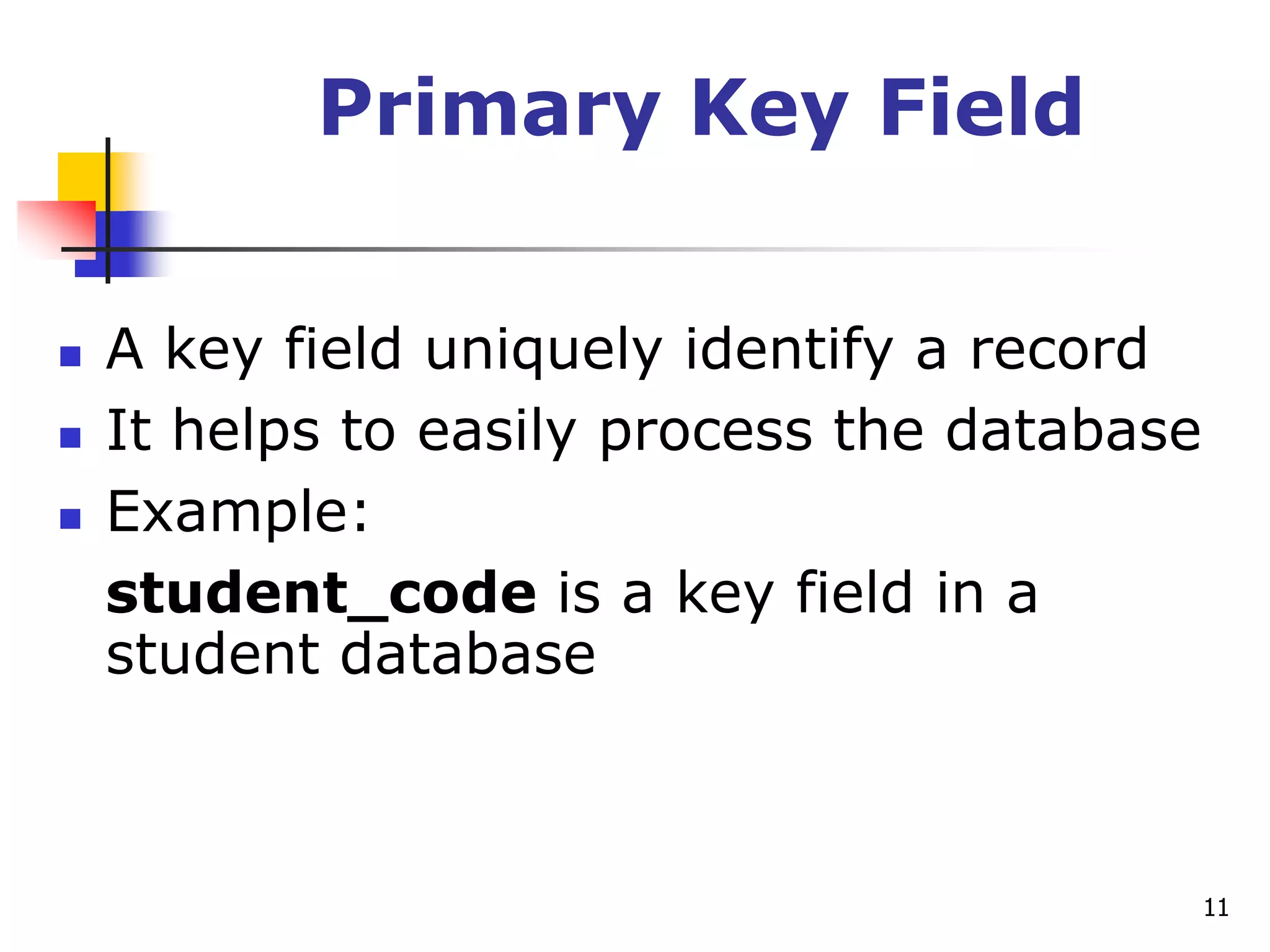
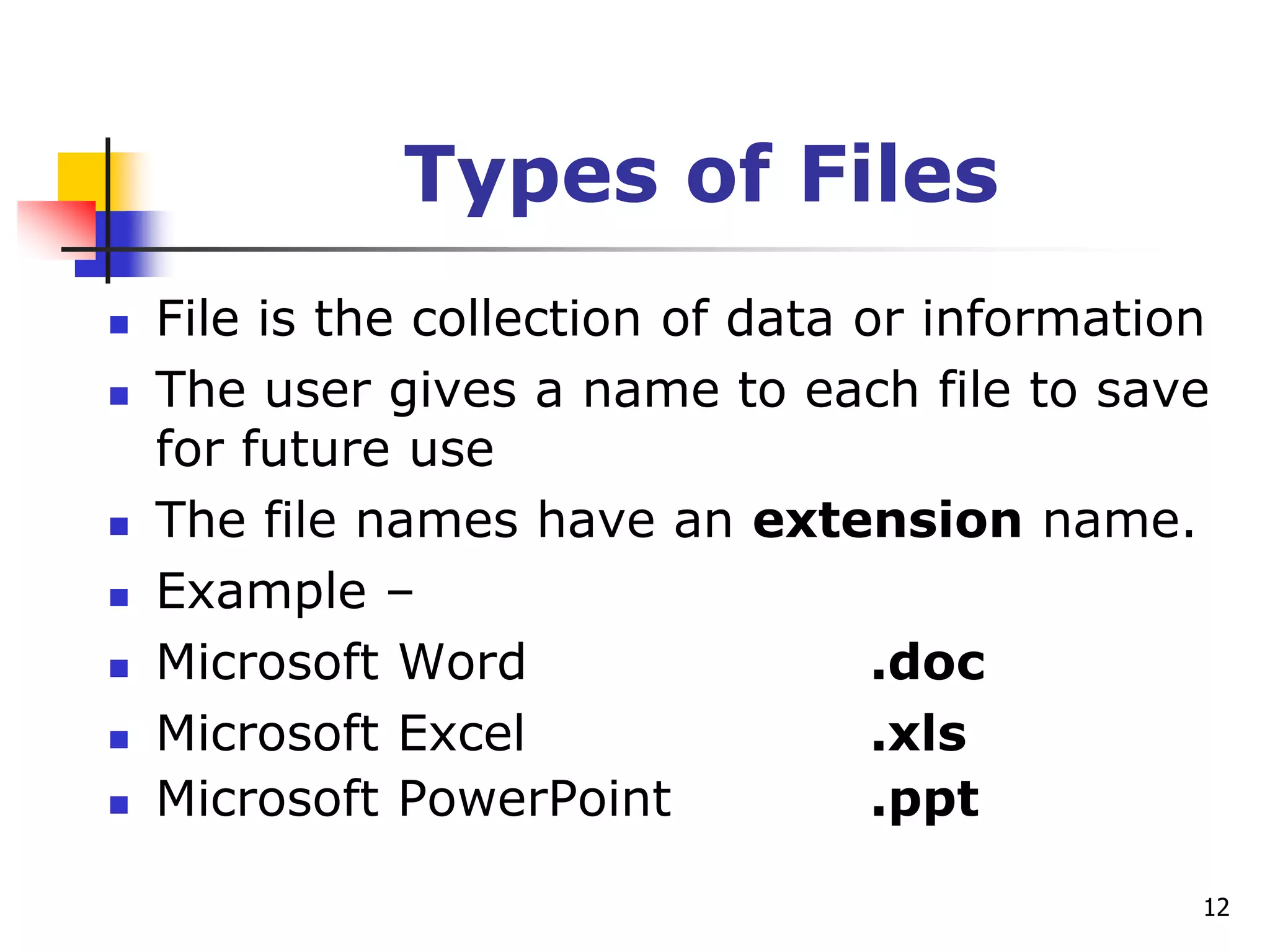
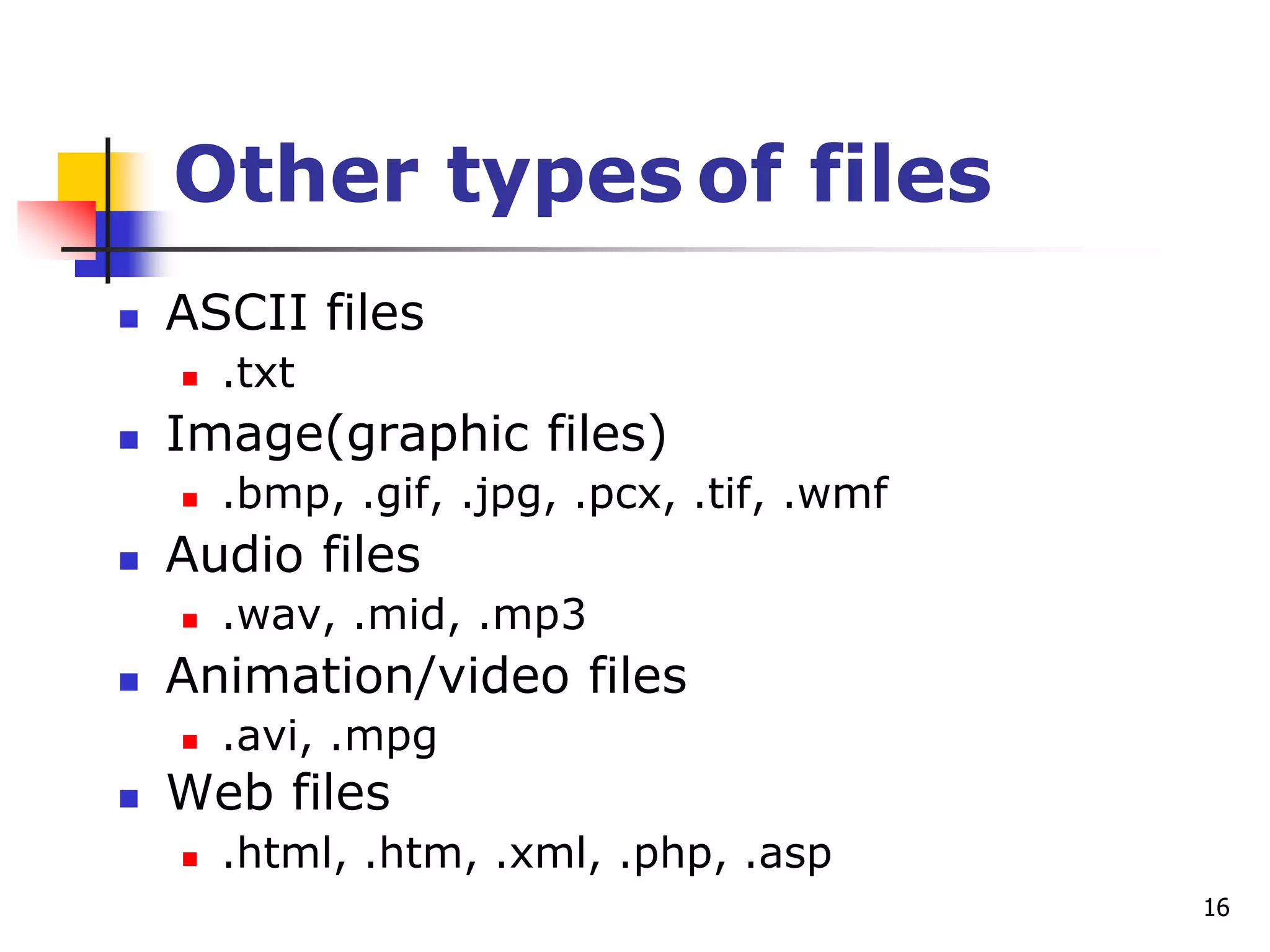
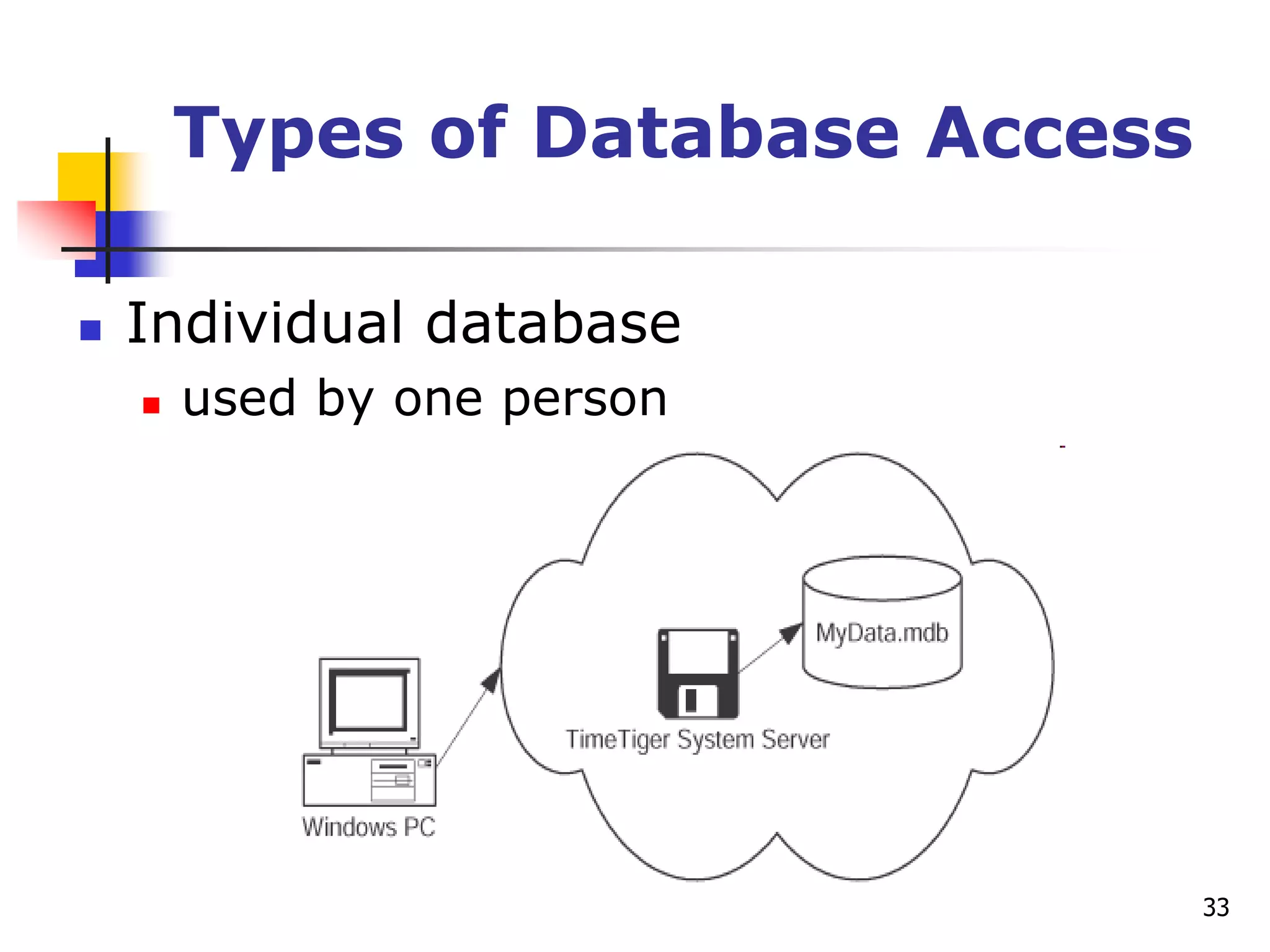
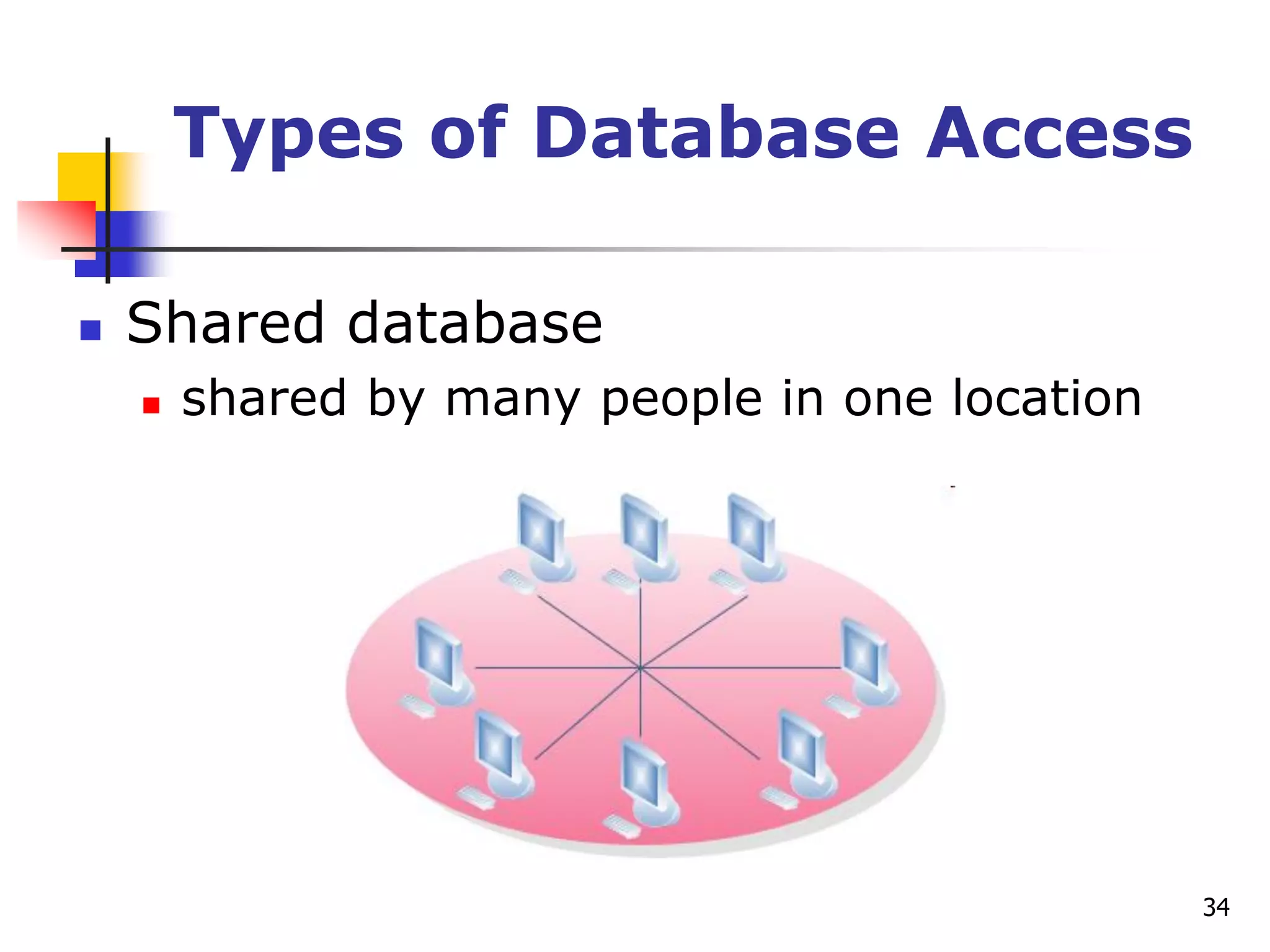
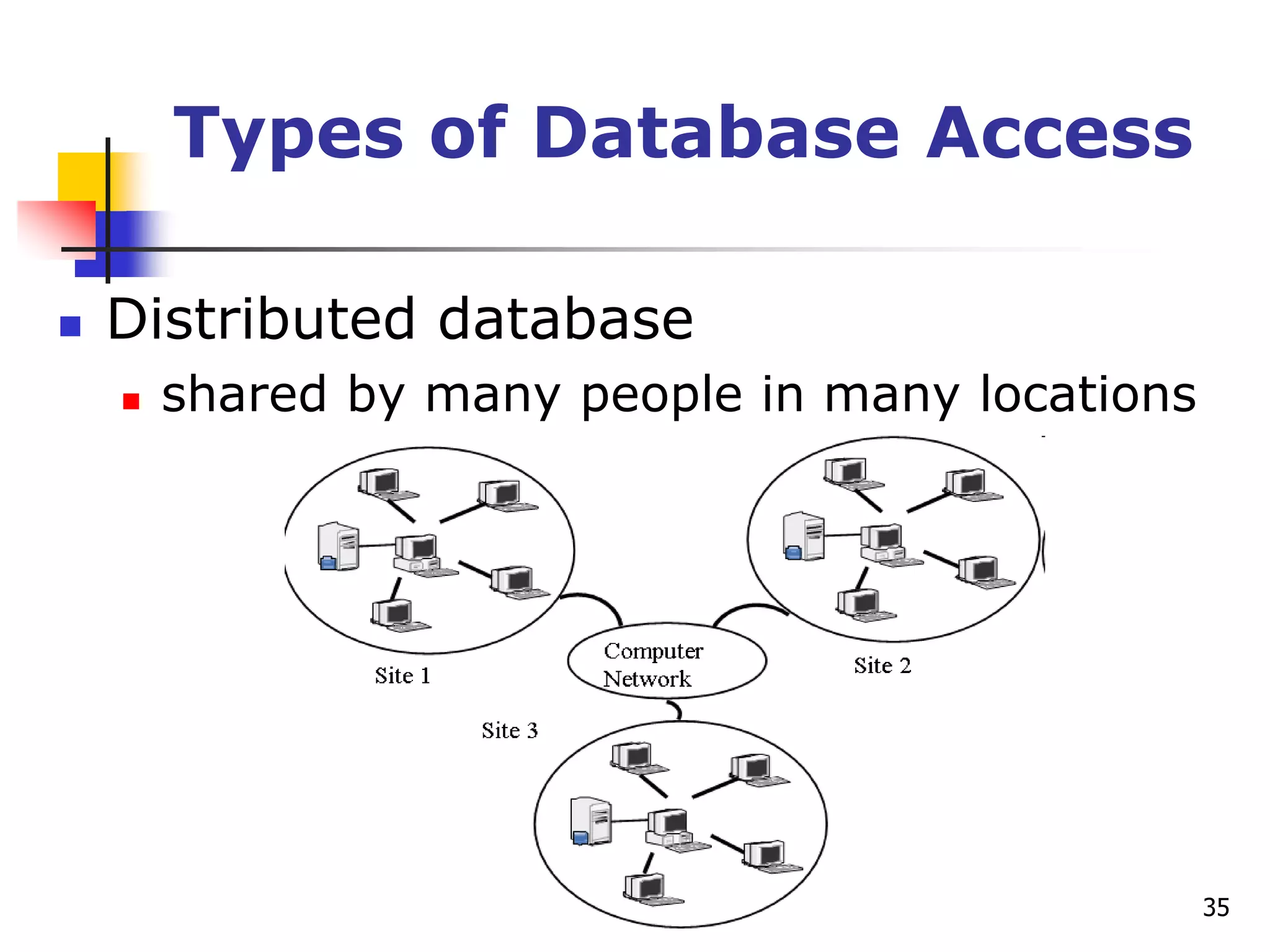
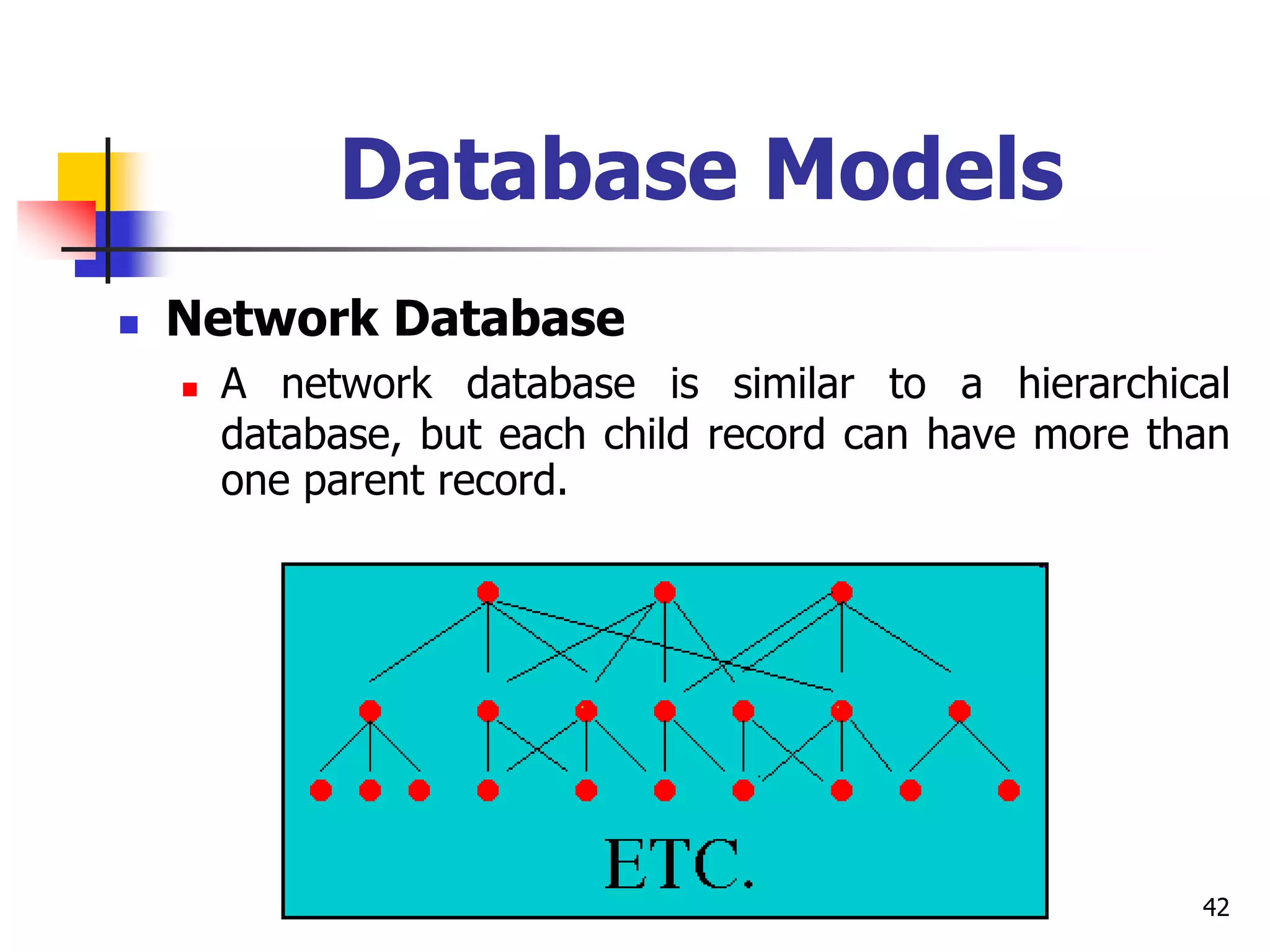
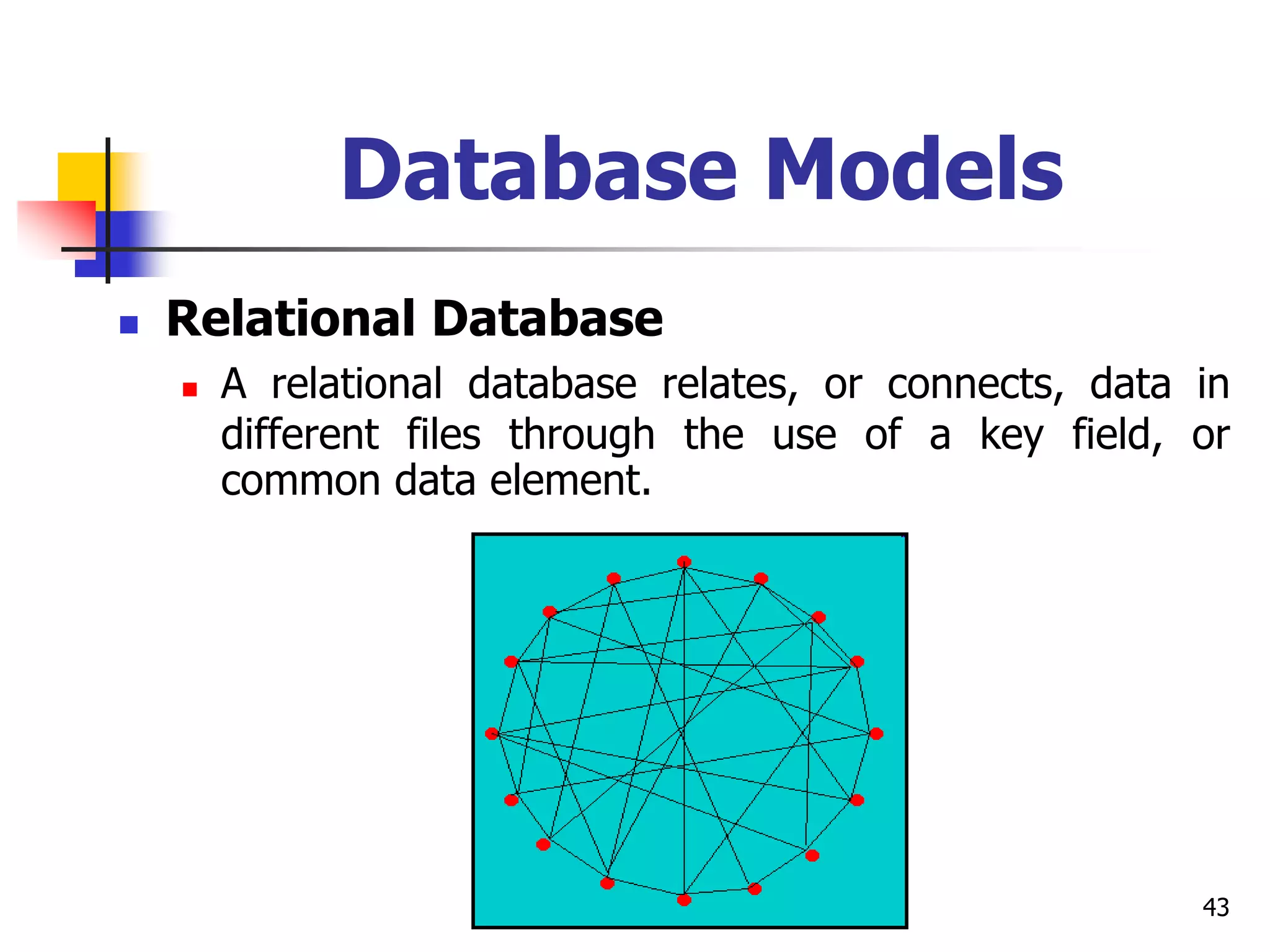
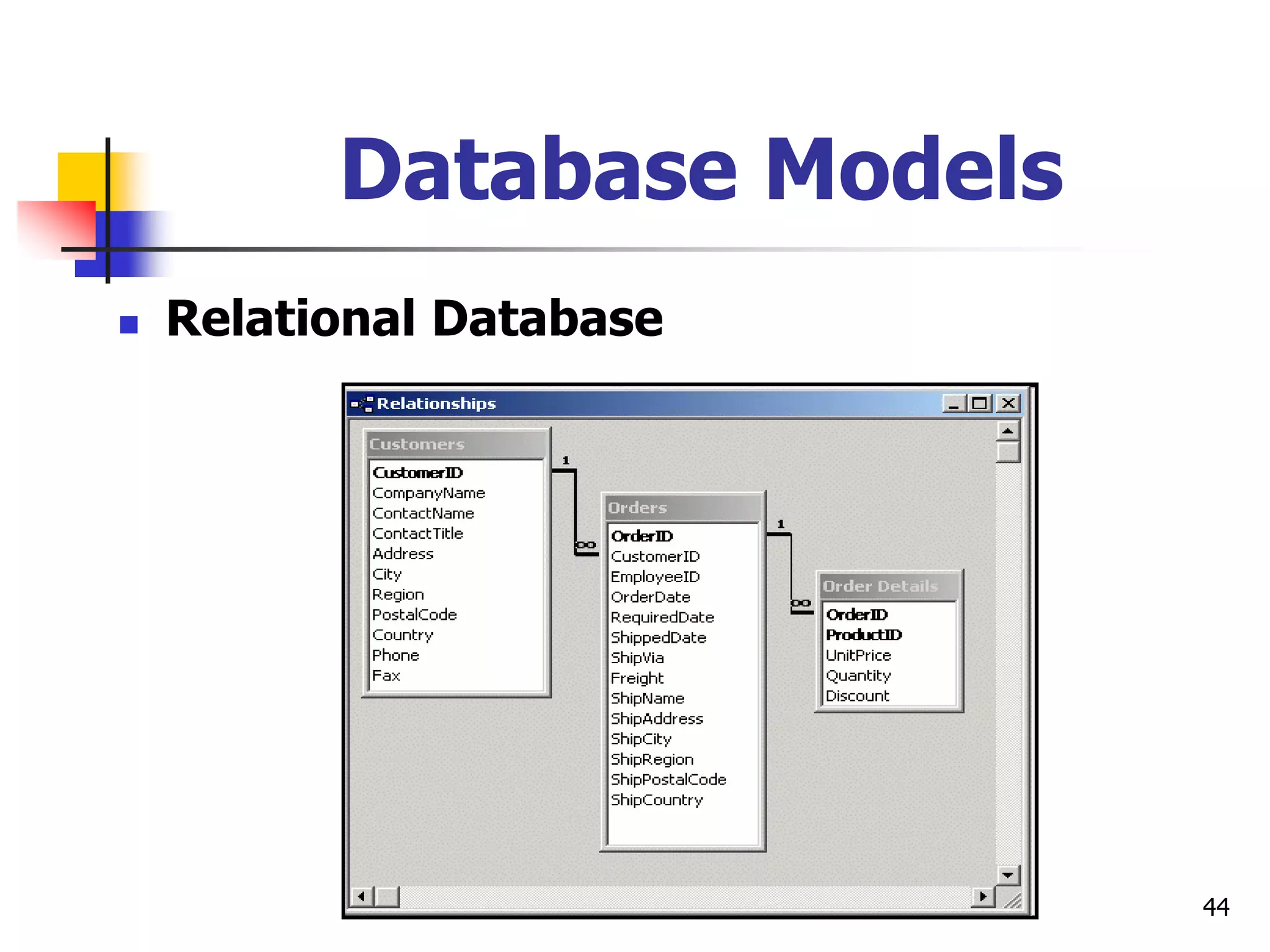
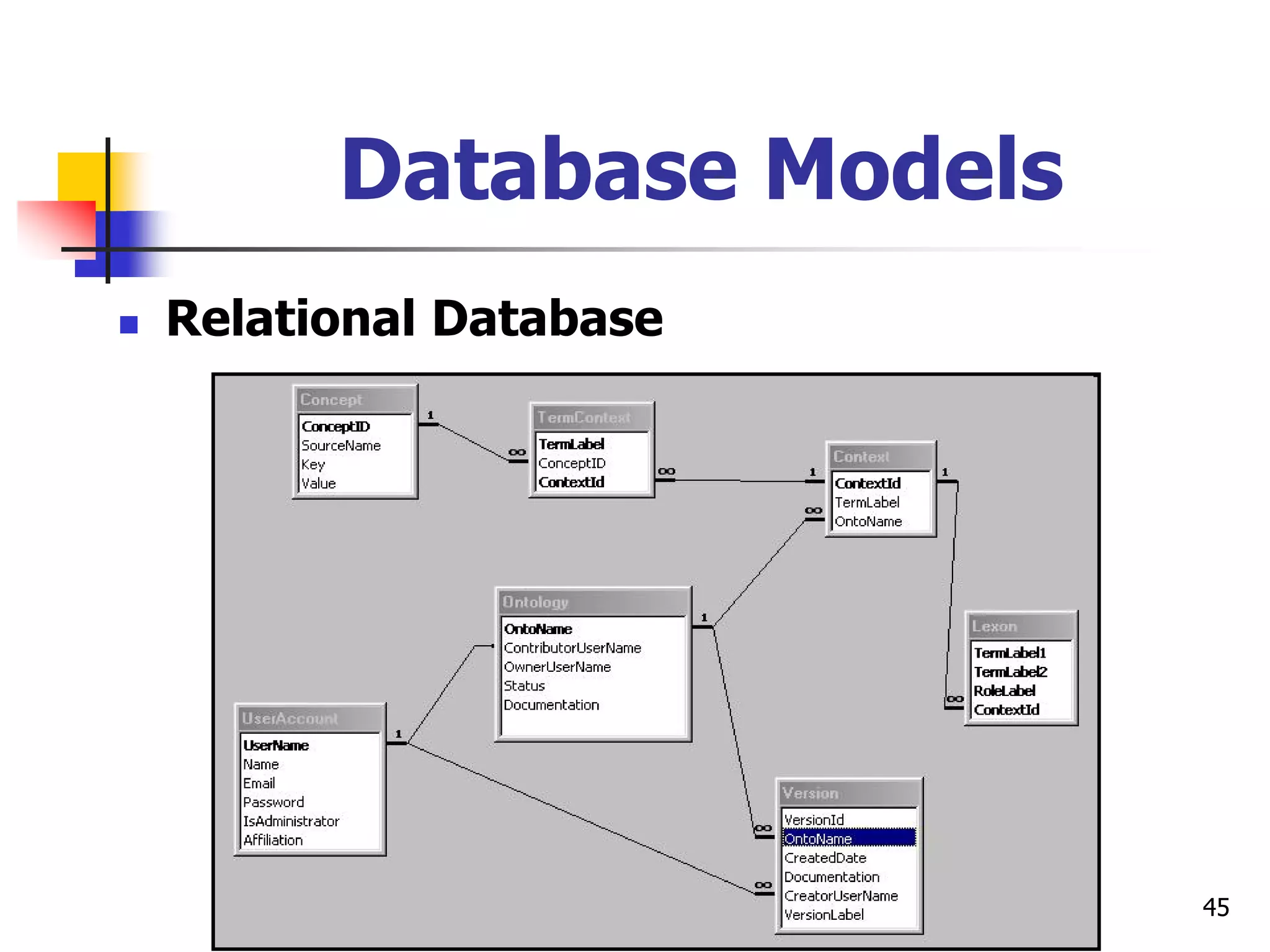
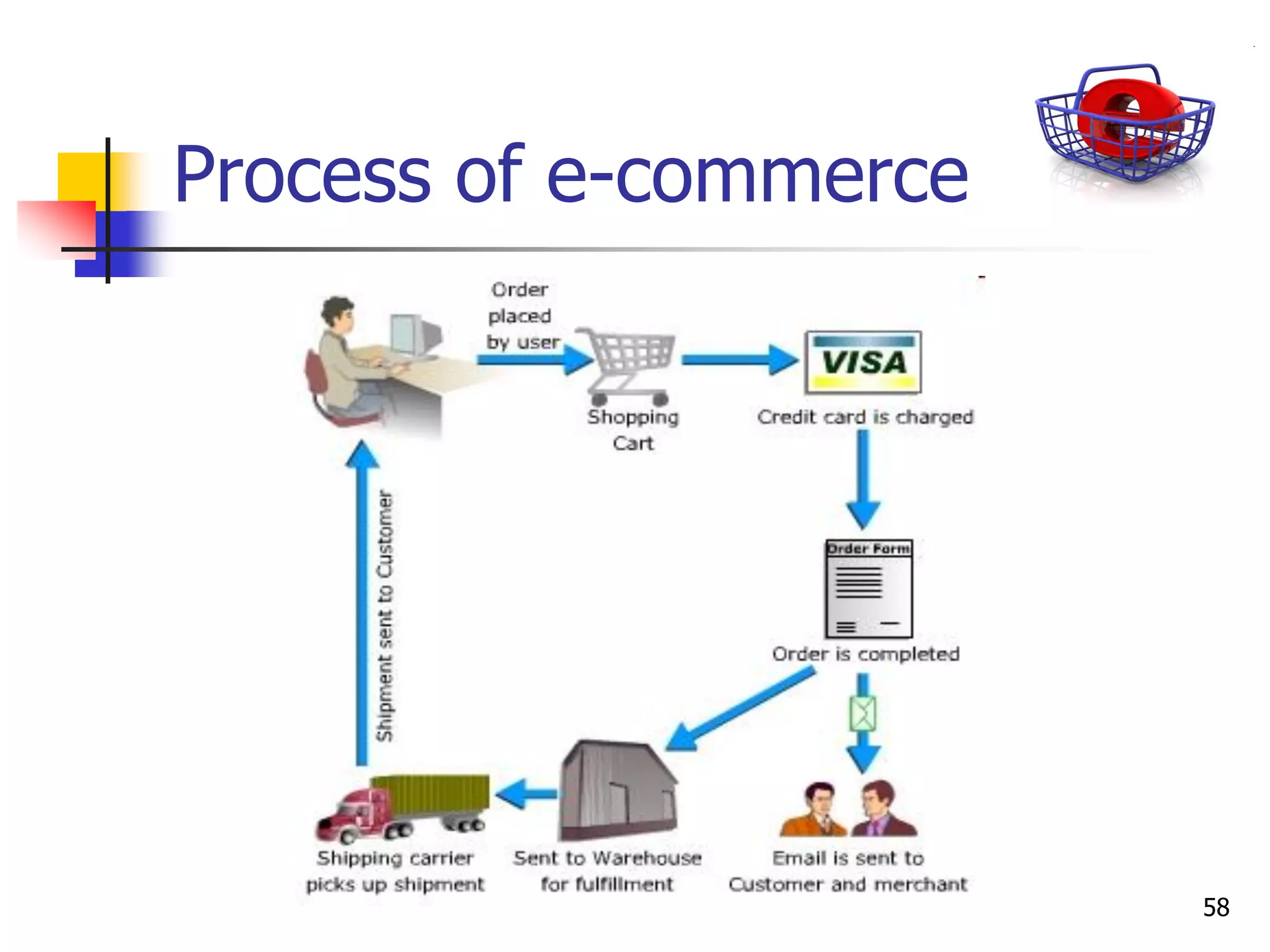
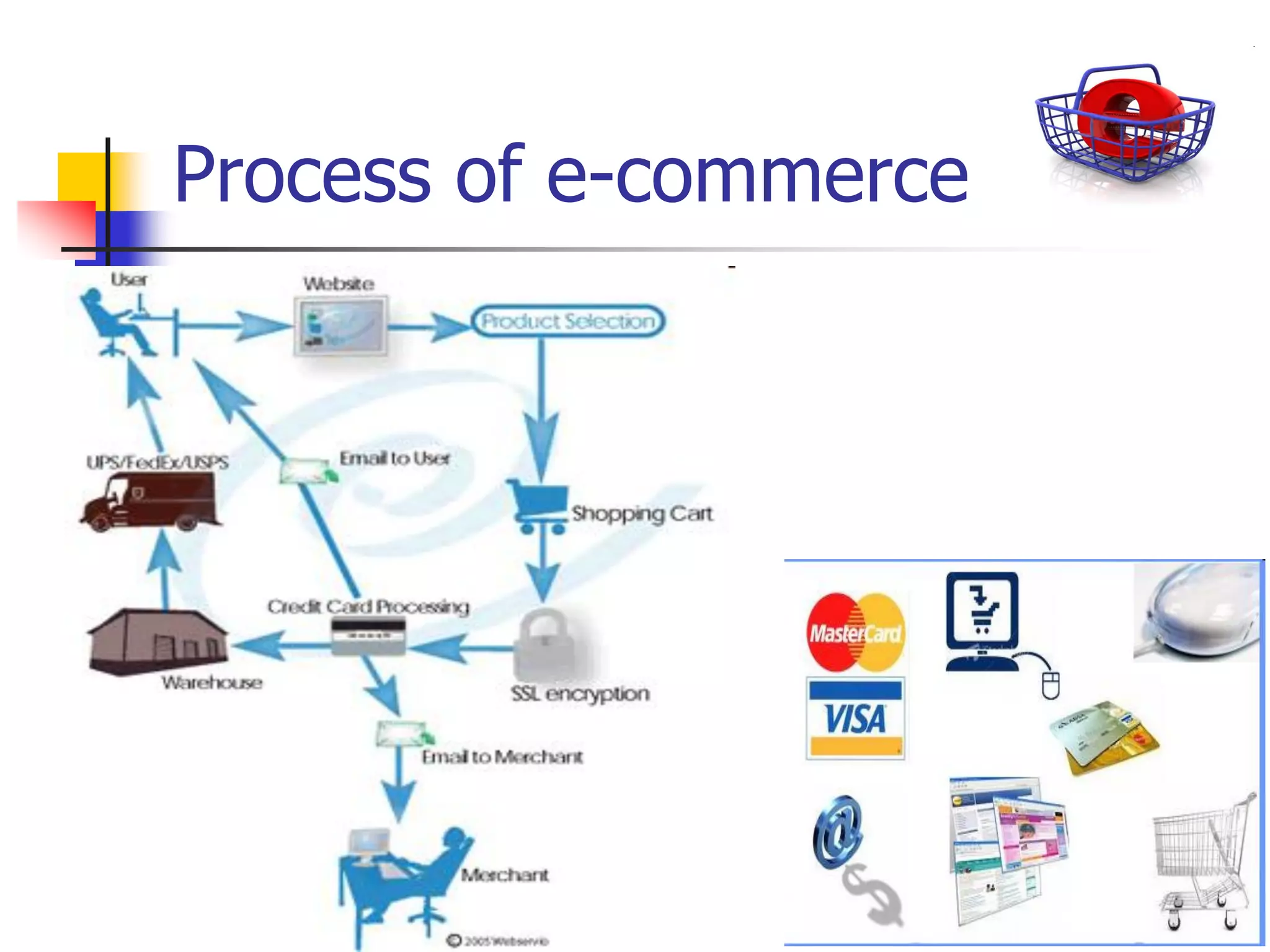
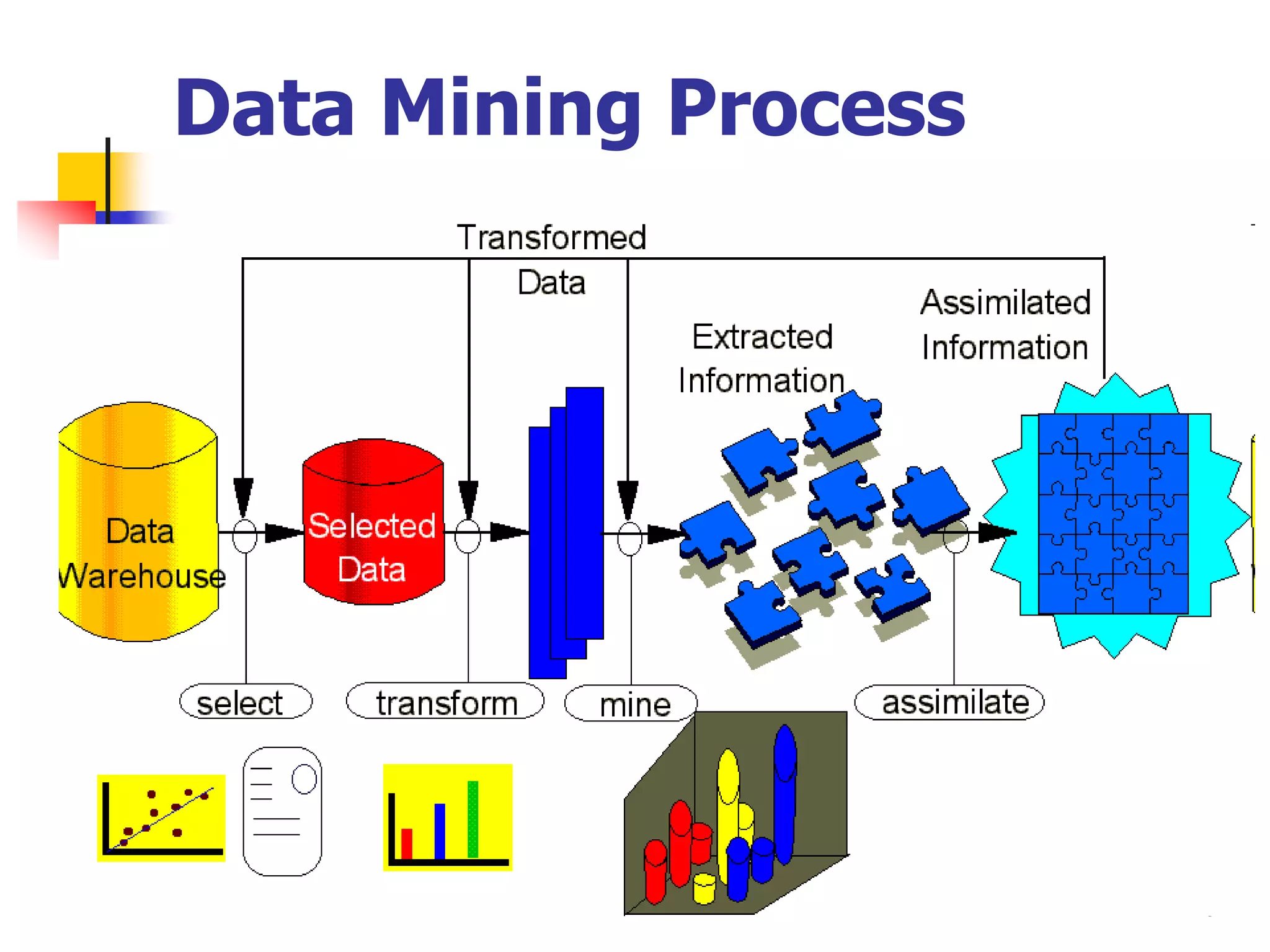
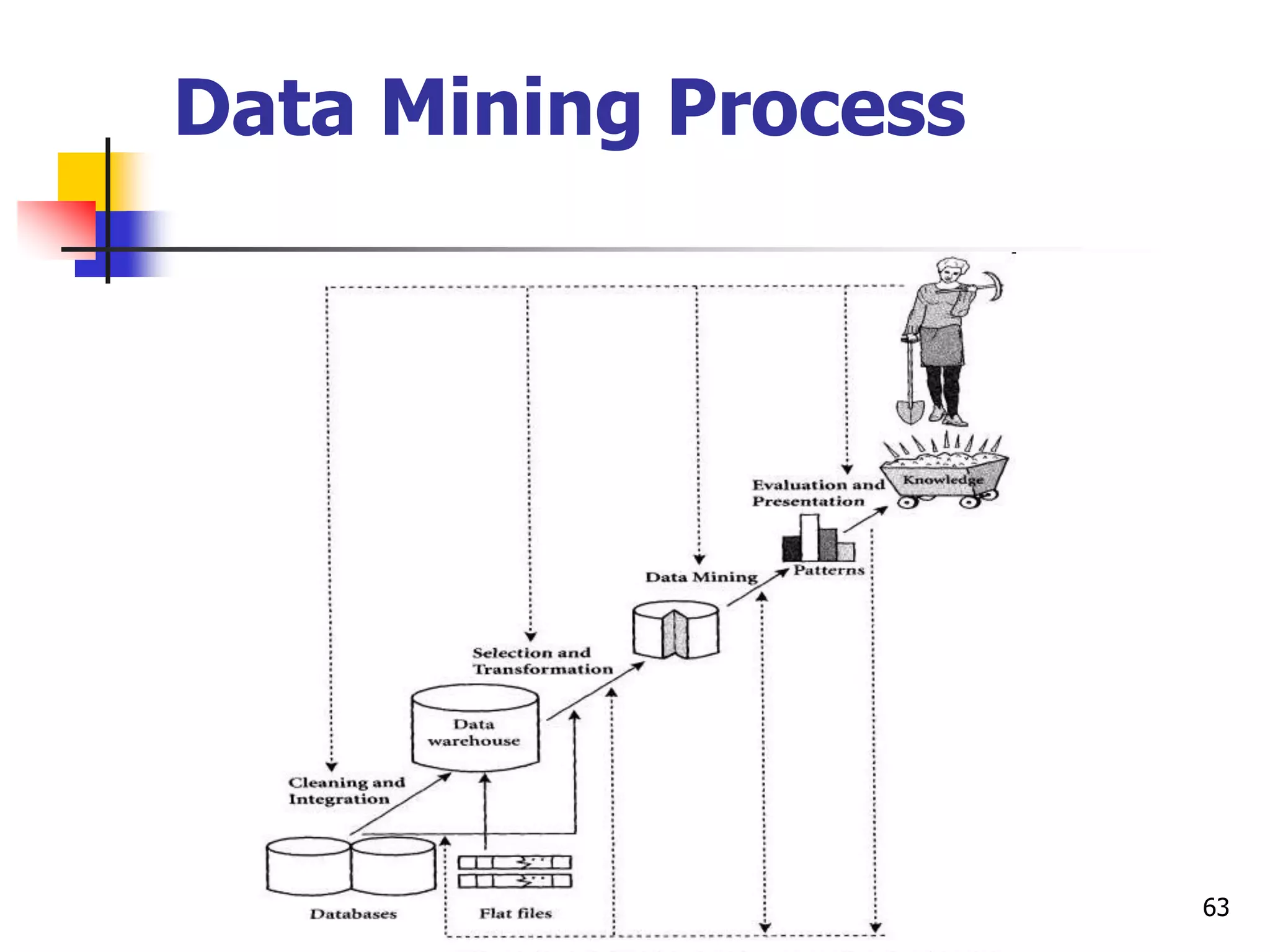
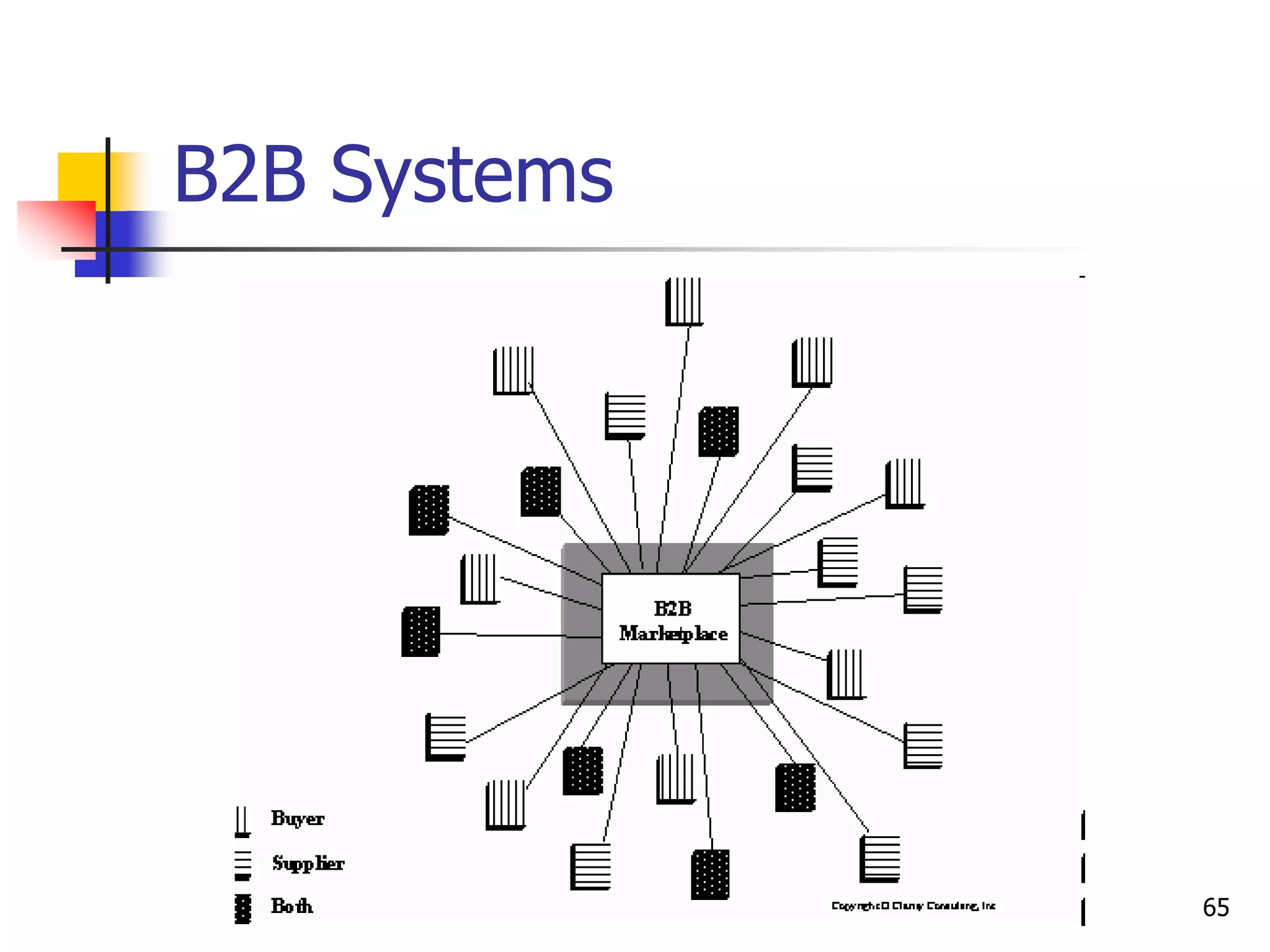
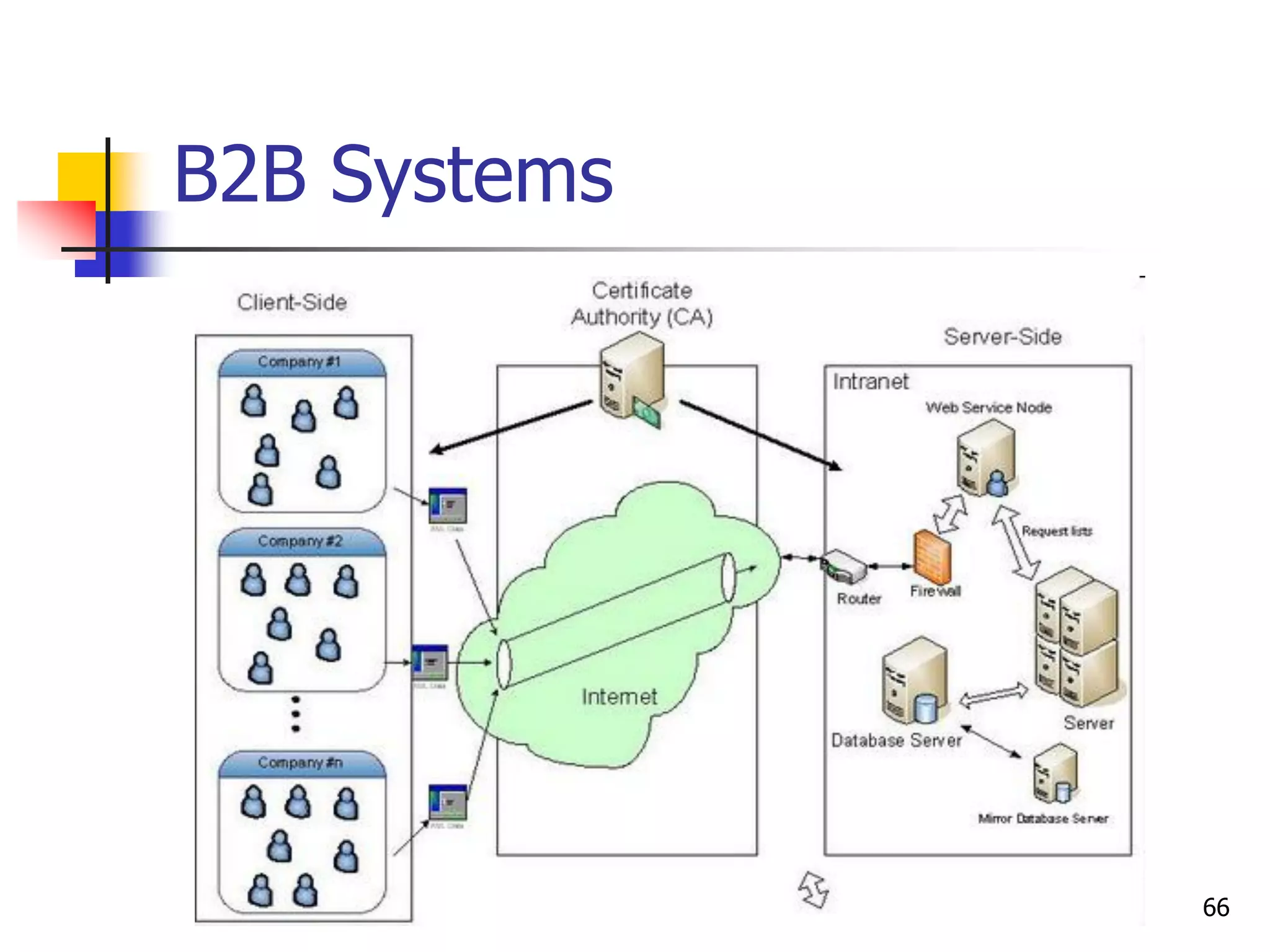
This document provides an outline for a course on electronic data processing and databases. It covers topics such as managing files, database management systems, database models like relational and hierarchical, features of DBMS including data dictionaries and security. It also discusses databases and the new economy including e-commerce and data mining. The last section discusses ethics around manipulating media and ensuring accuracy and privacy of databases.