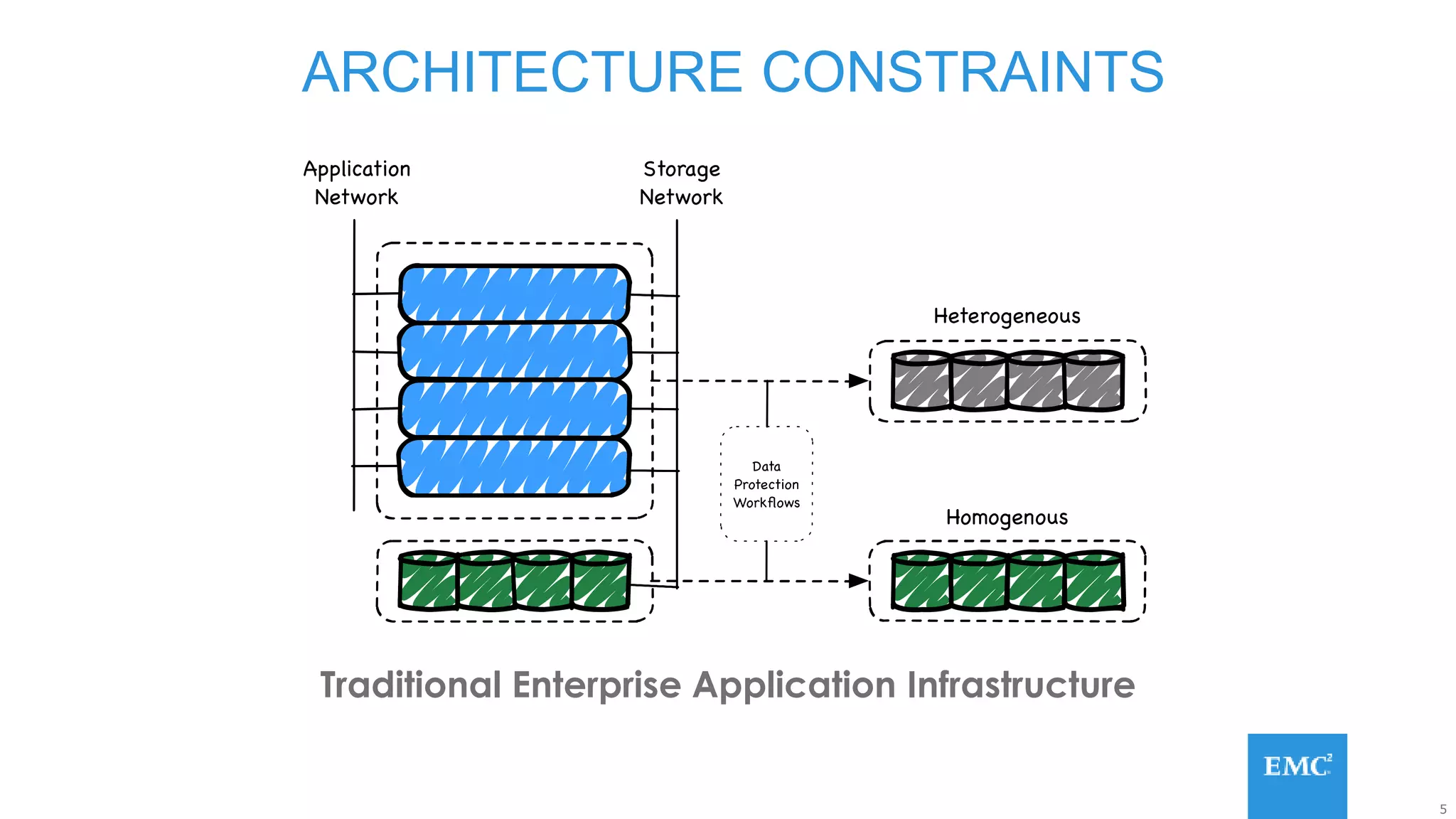
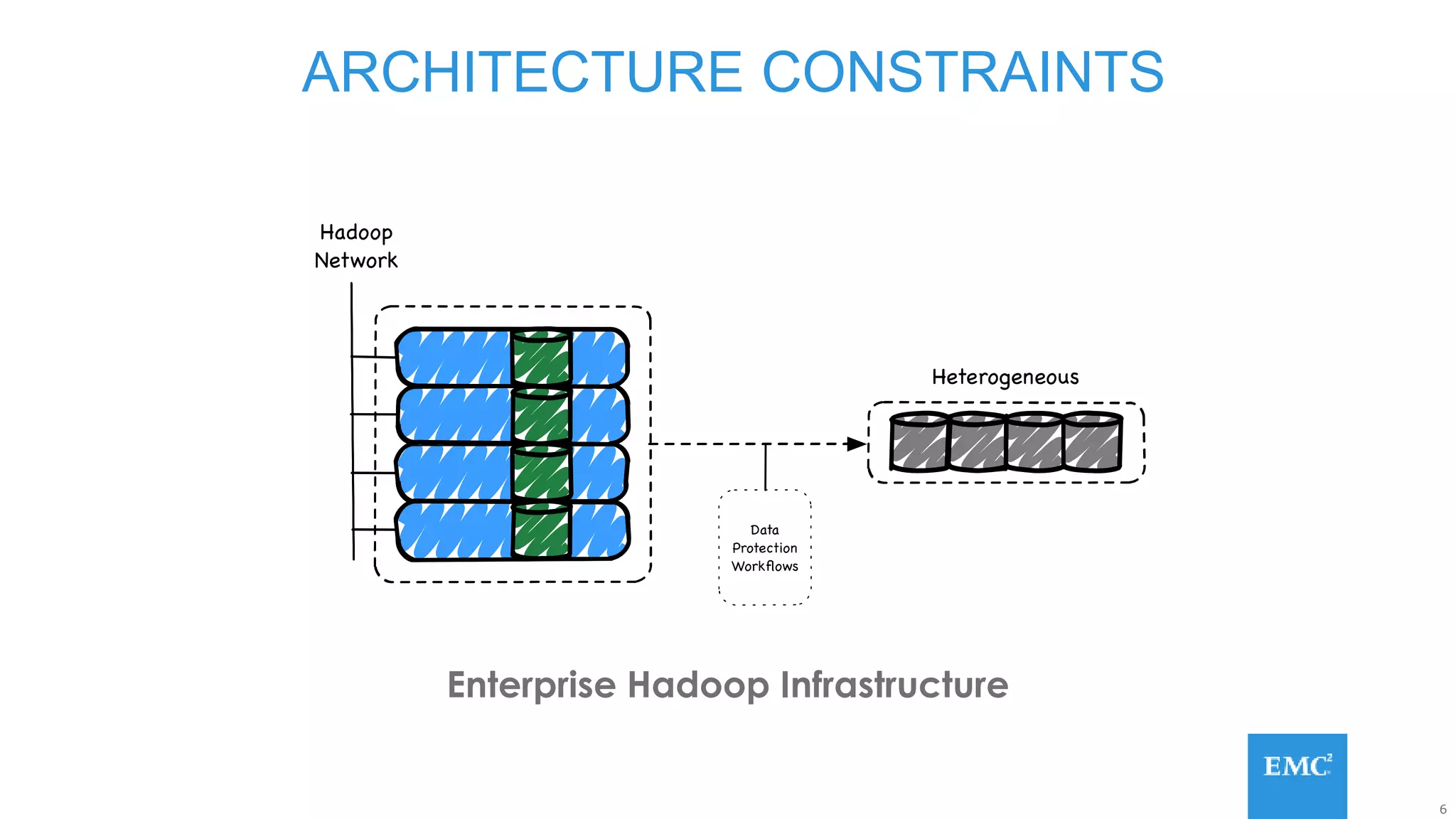
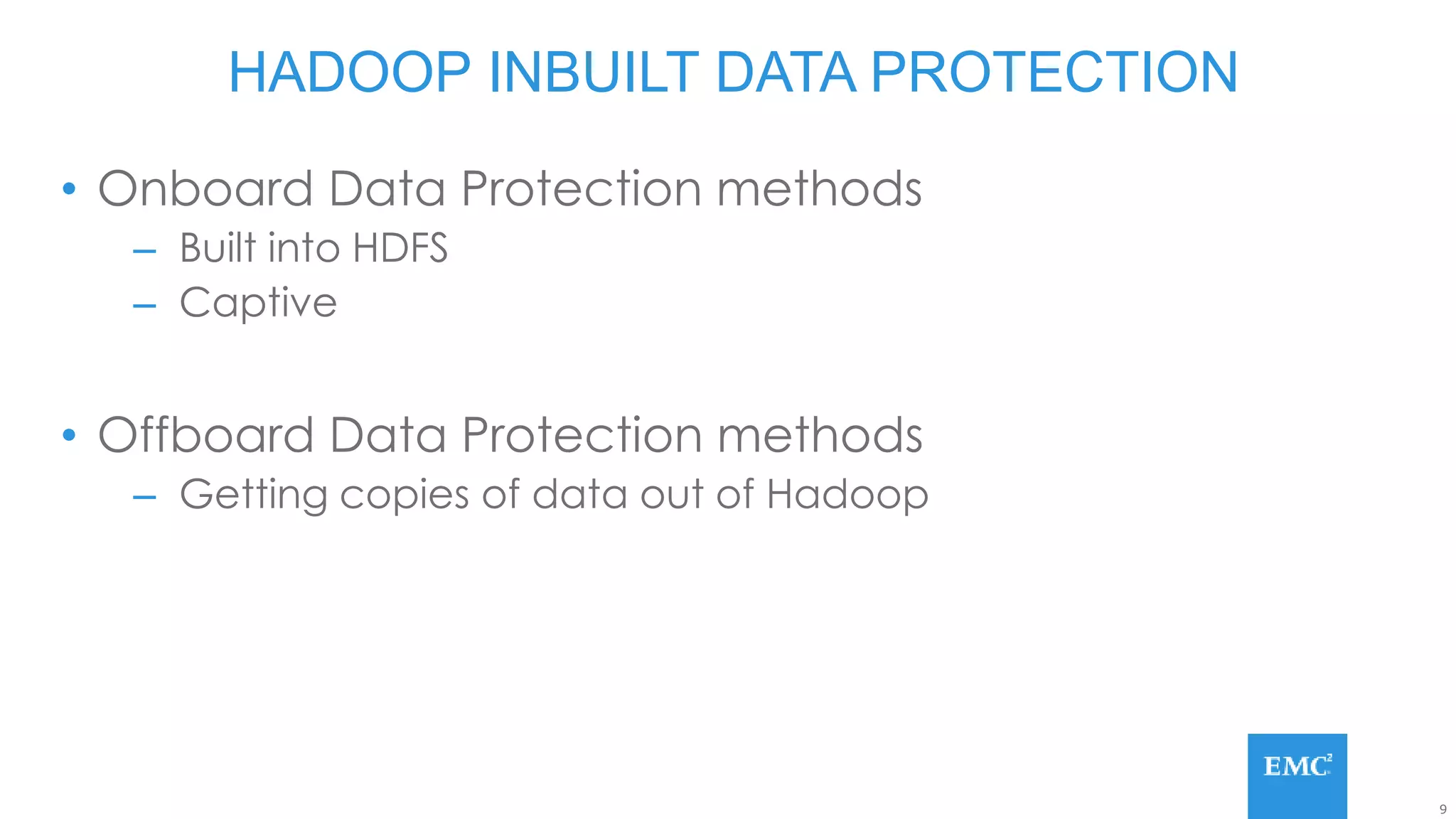
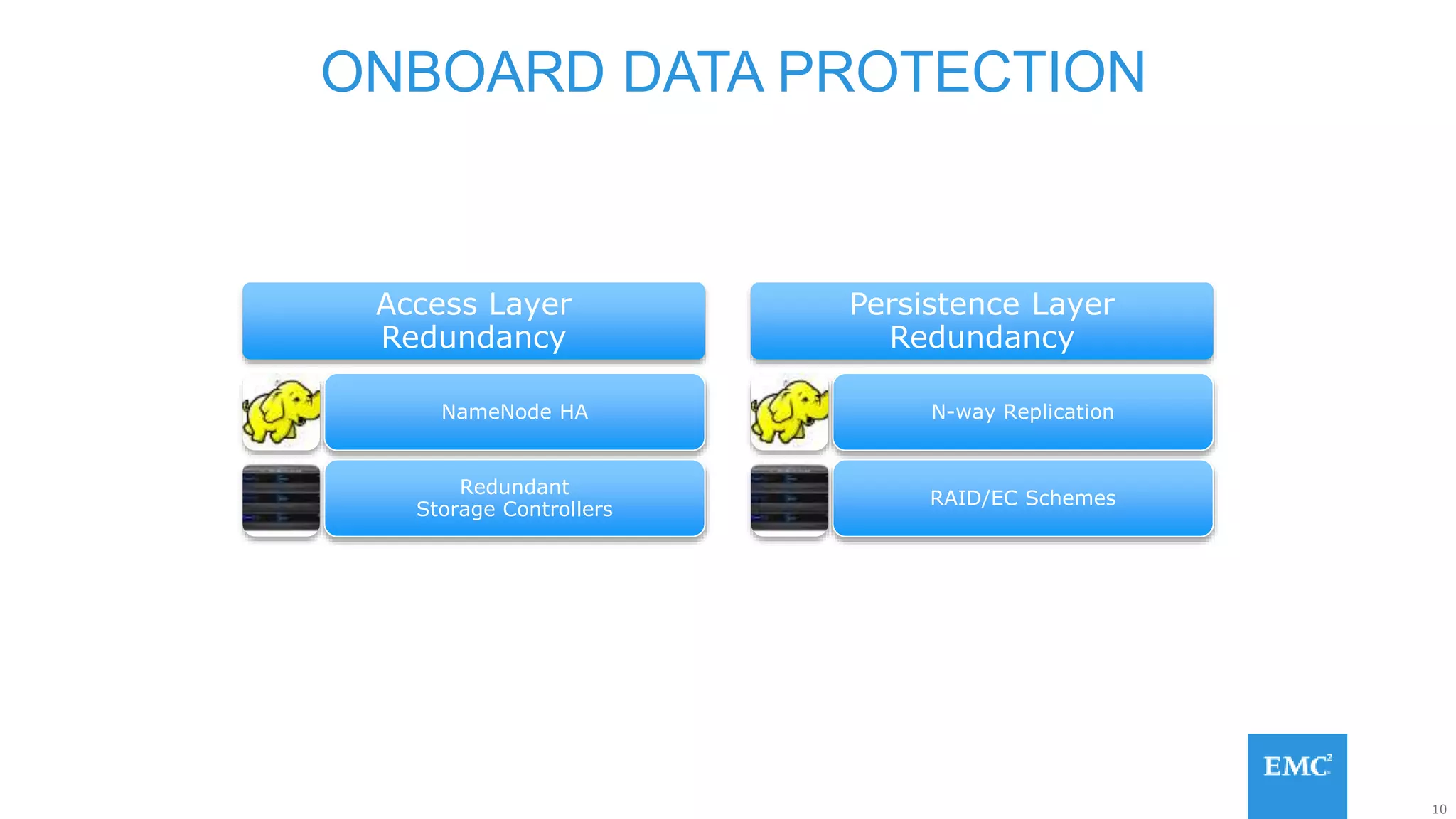
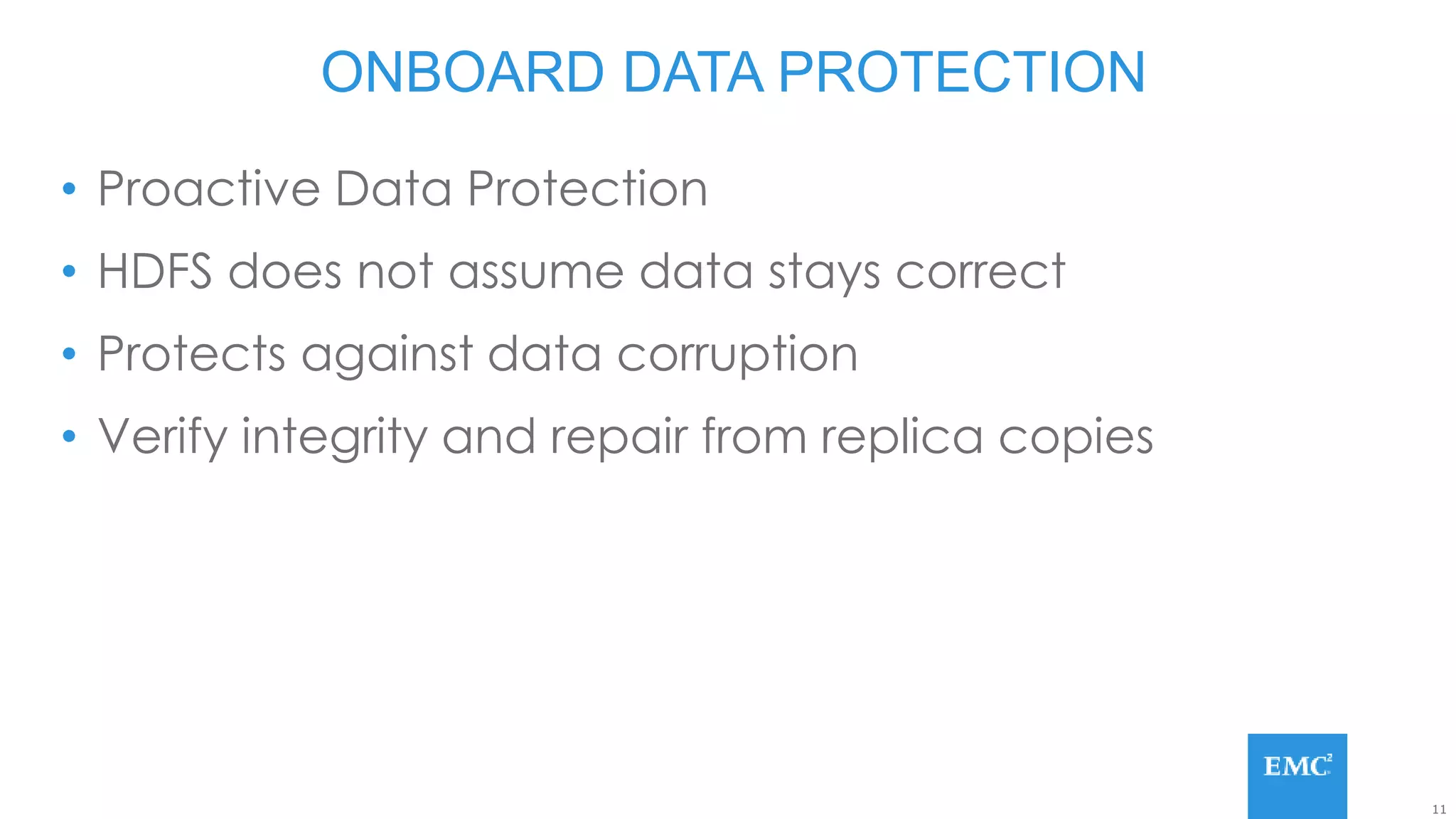
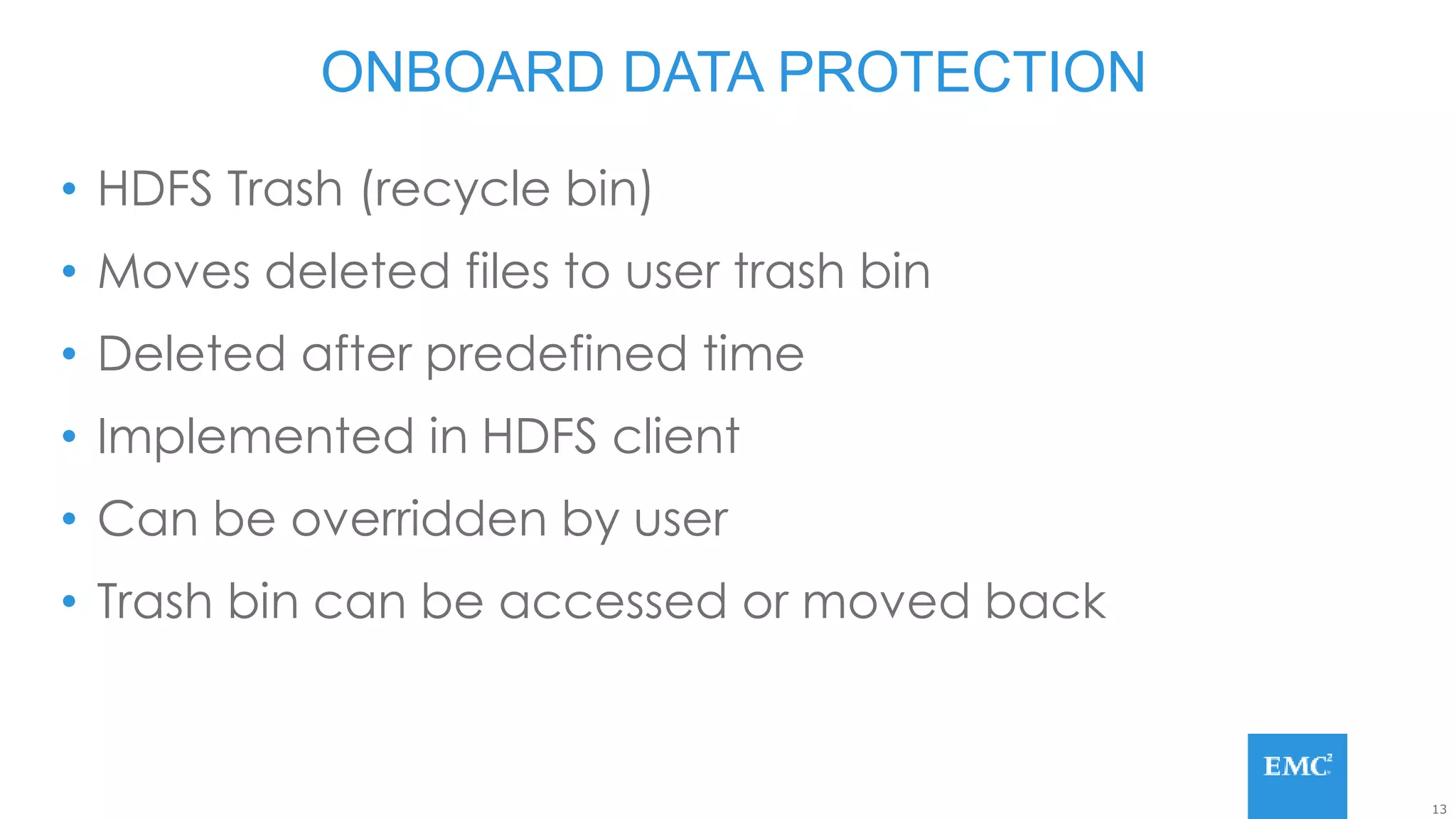
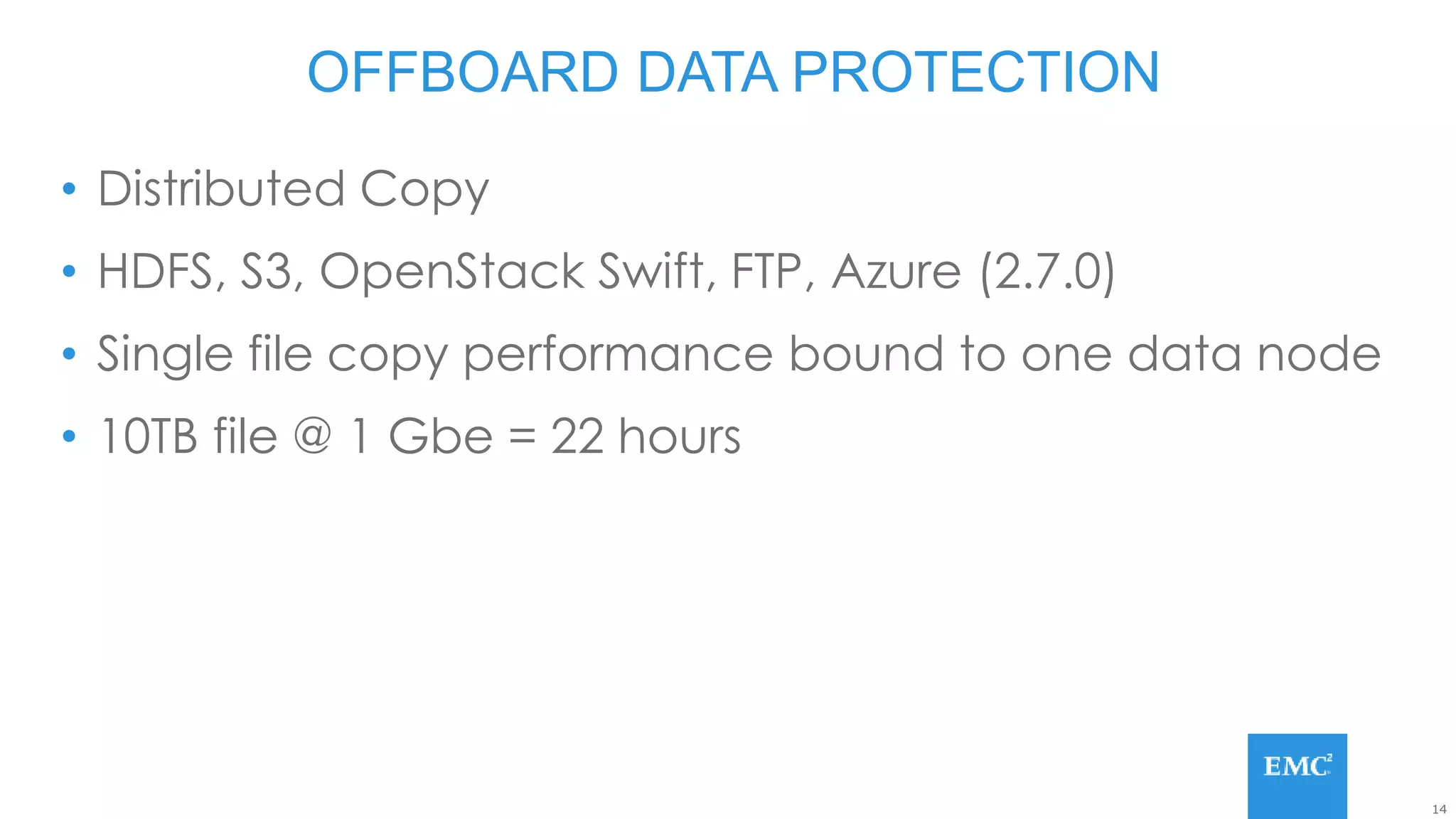
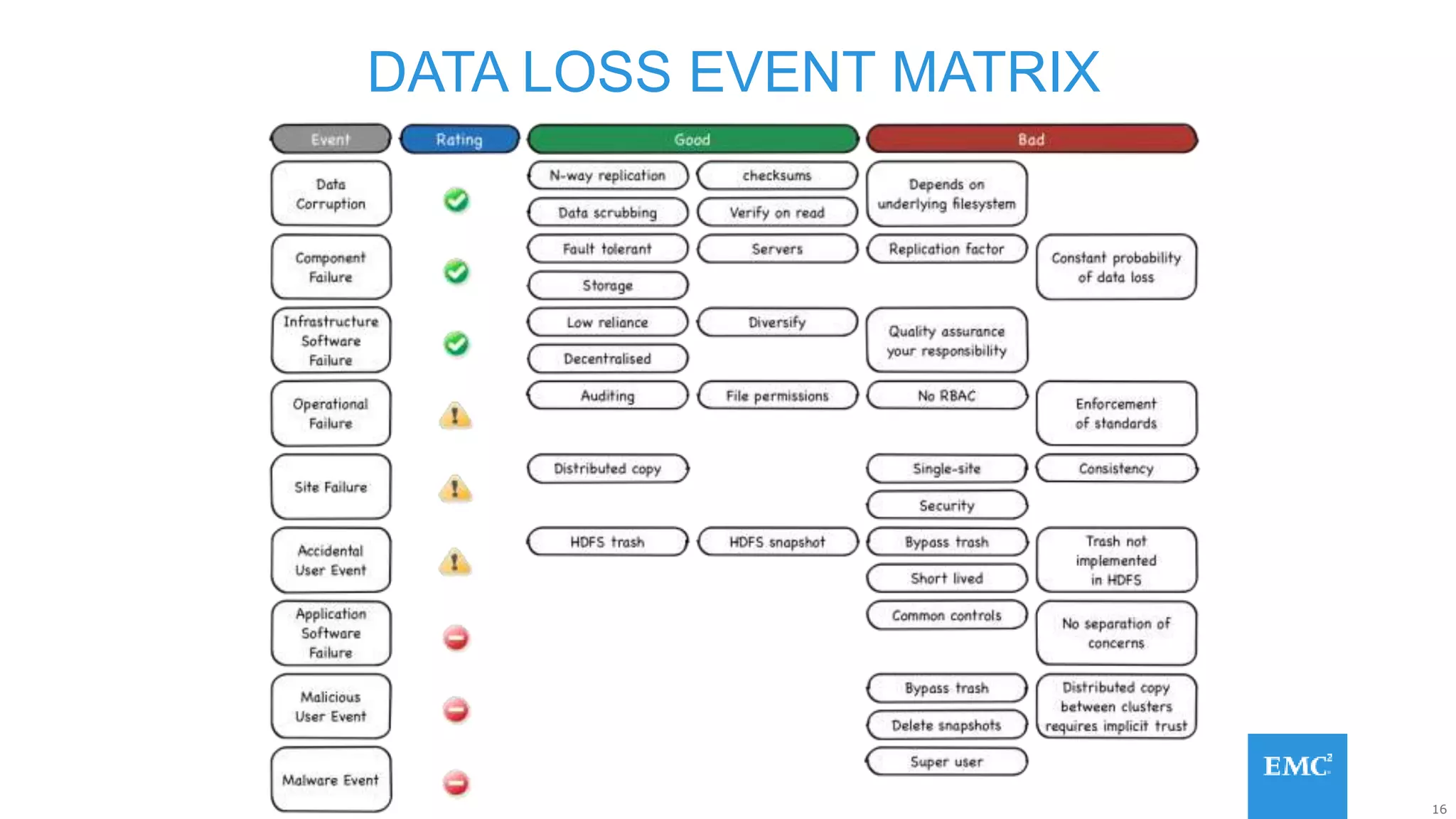
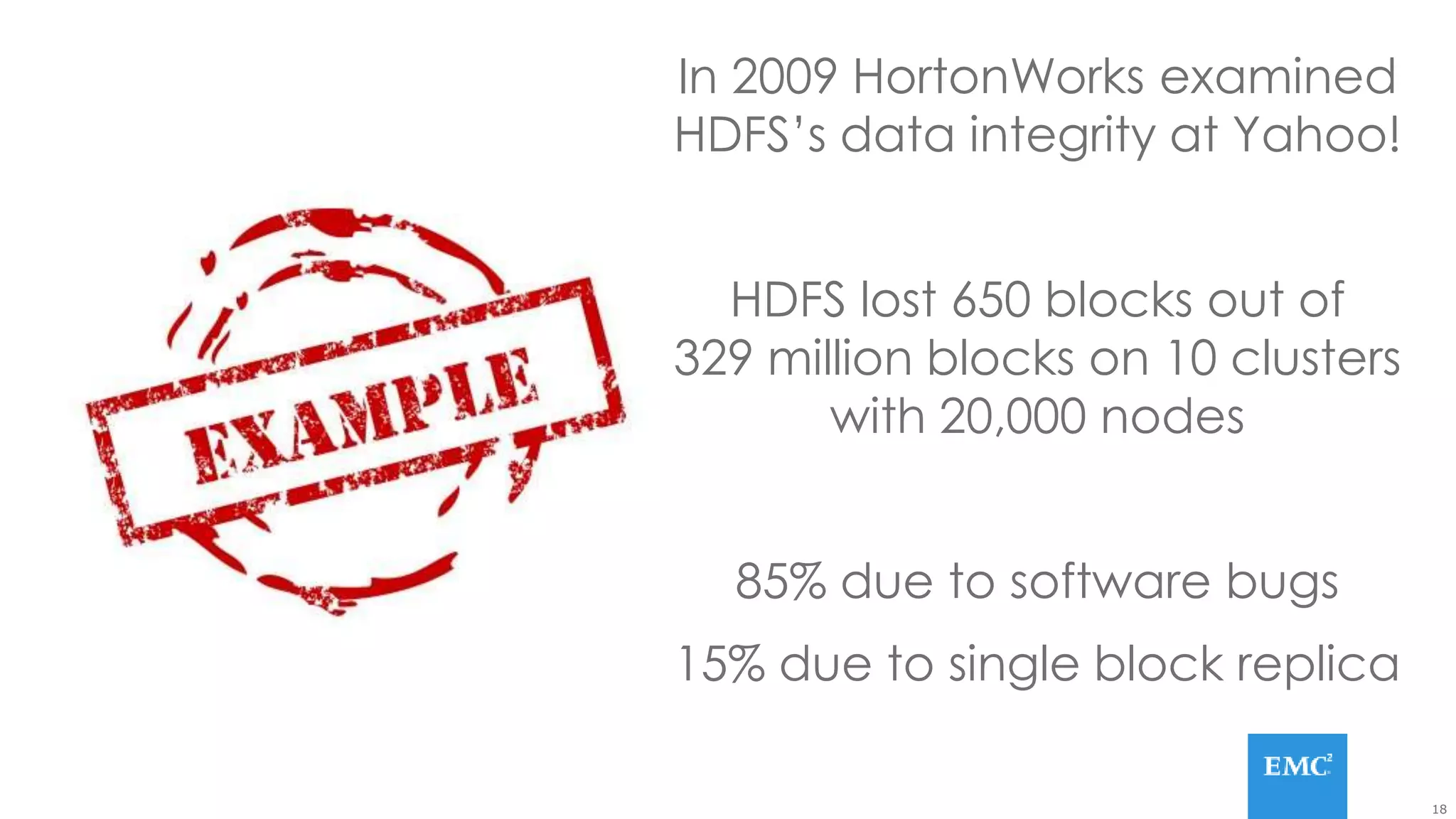
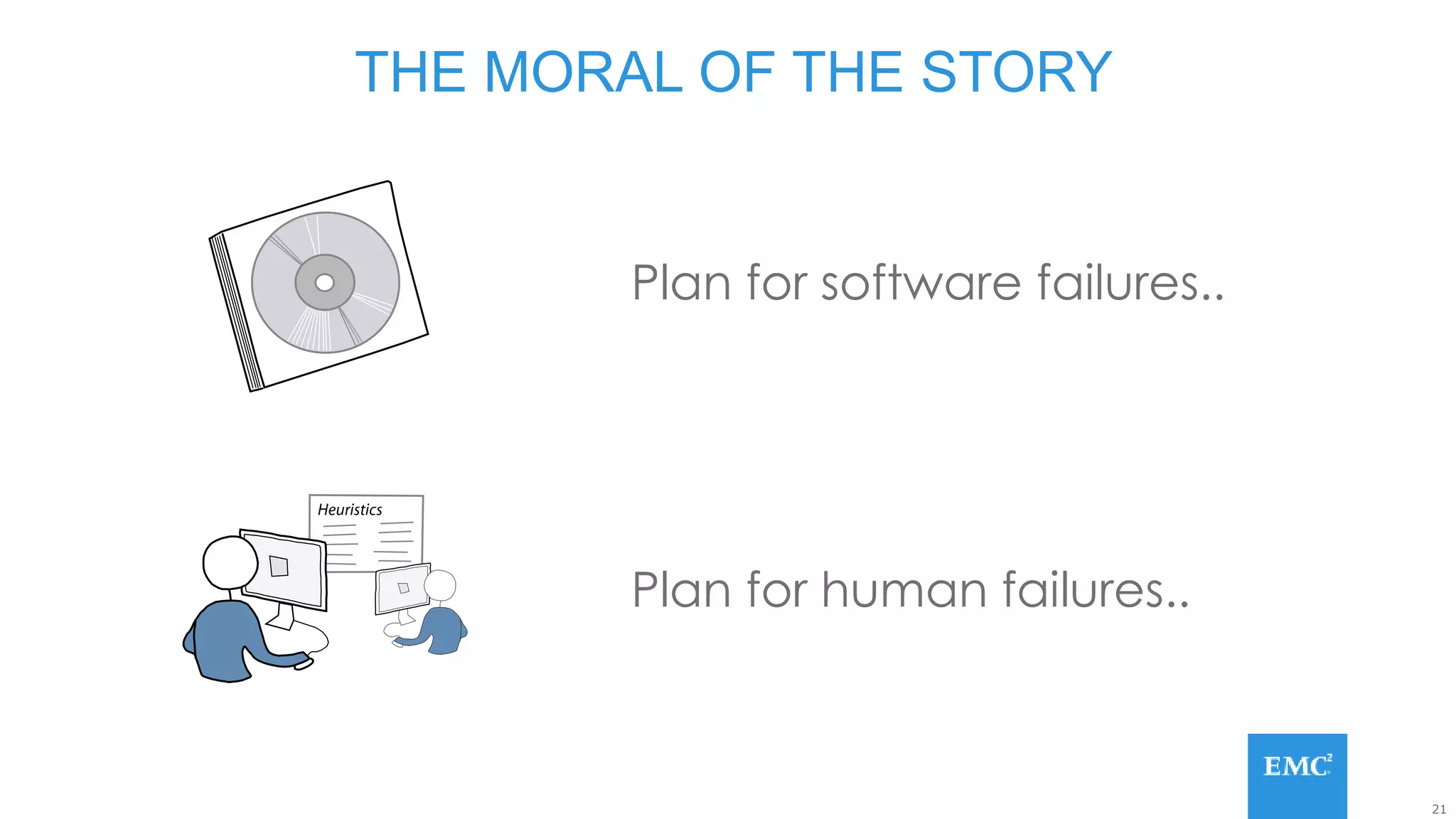
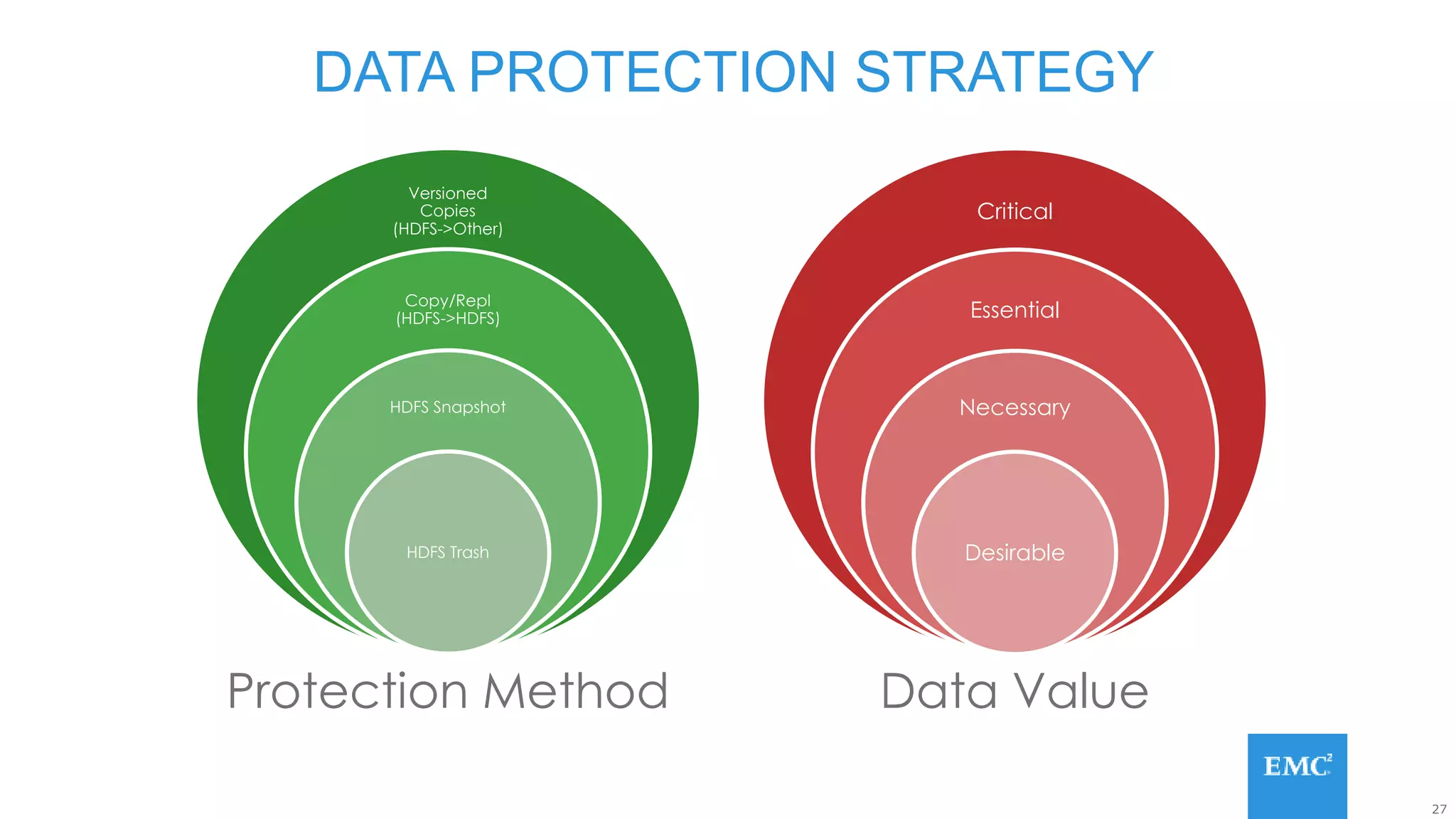
Hadoop has some built-in data protection features like replication, snapshots, and trash bins. However, these may not be sufficient on their own. Hadoop data can still be lost due to software bugs or human errors. A well-designed data protection strategy for Hadoop should include diversified copies of valuable data both within and outside the Hadoop environment. This protects against data loss from both software and hardware failures.