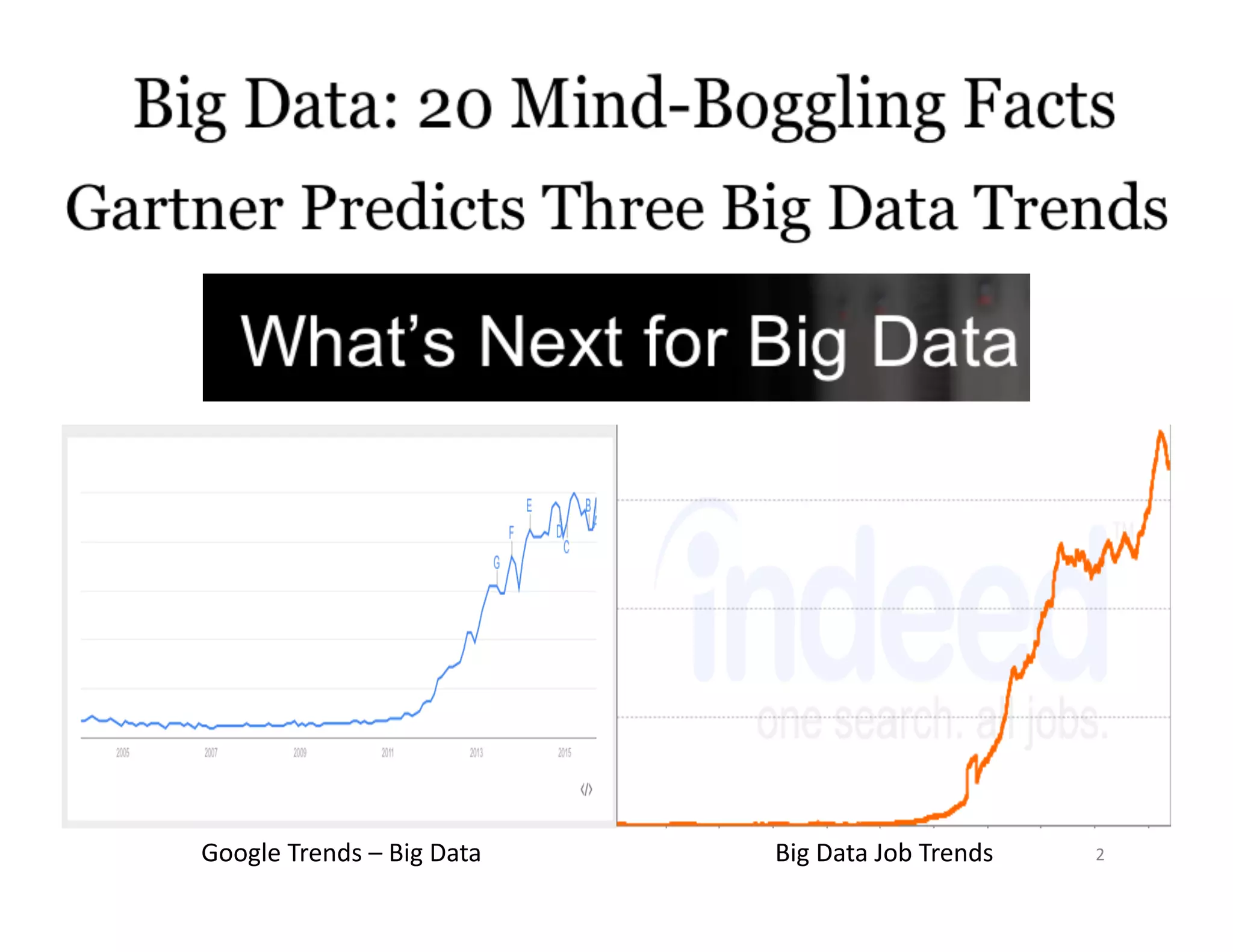
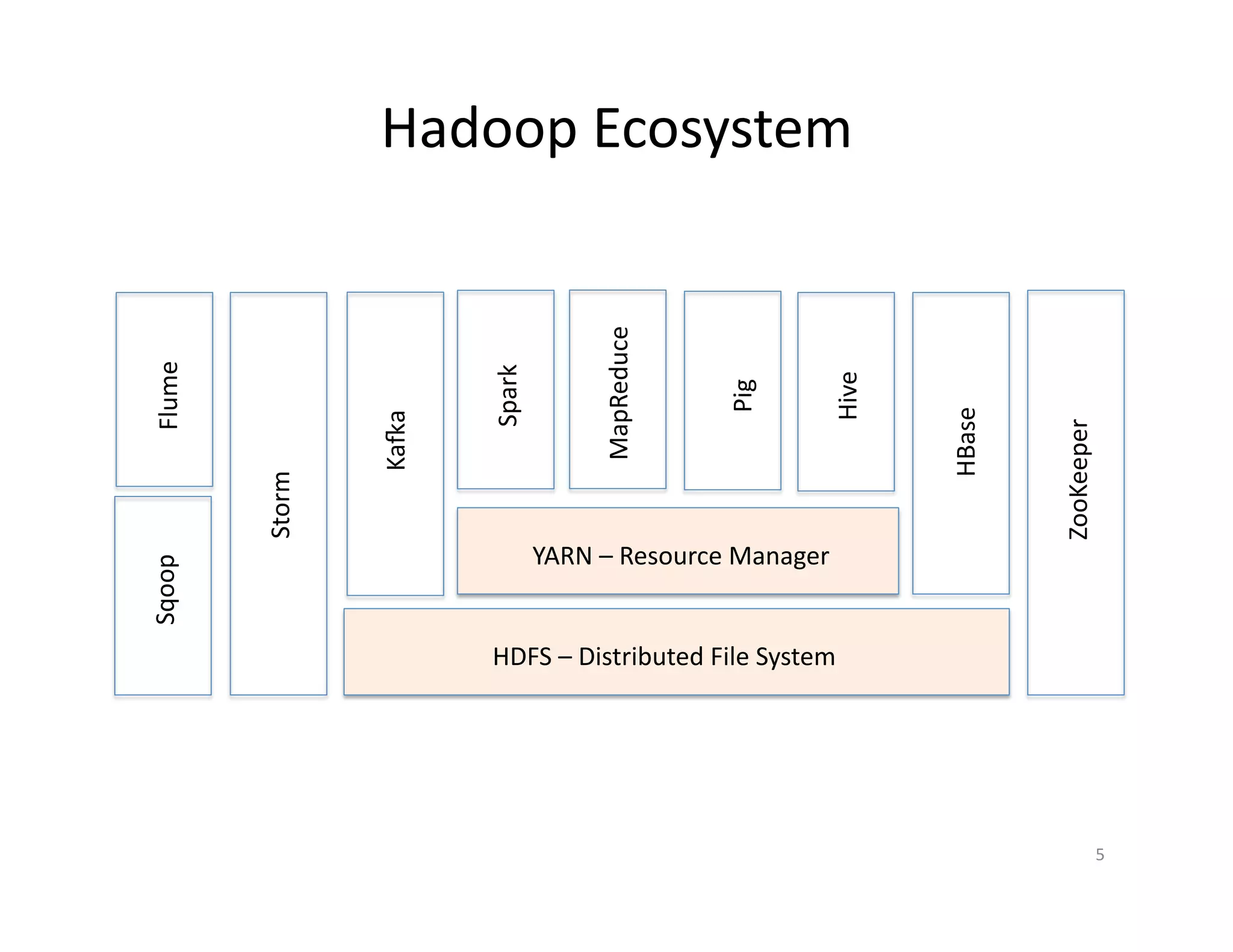
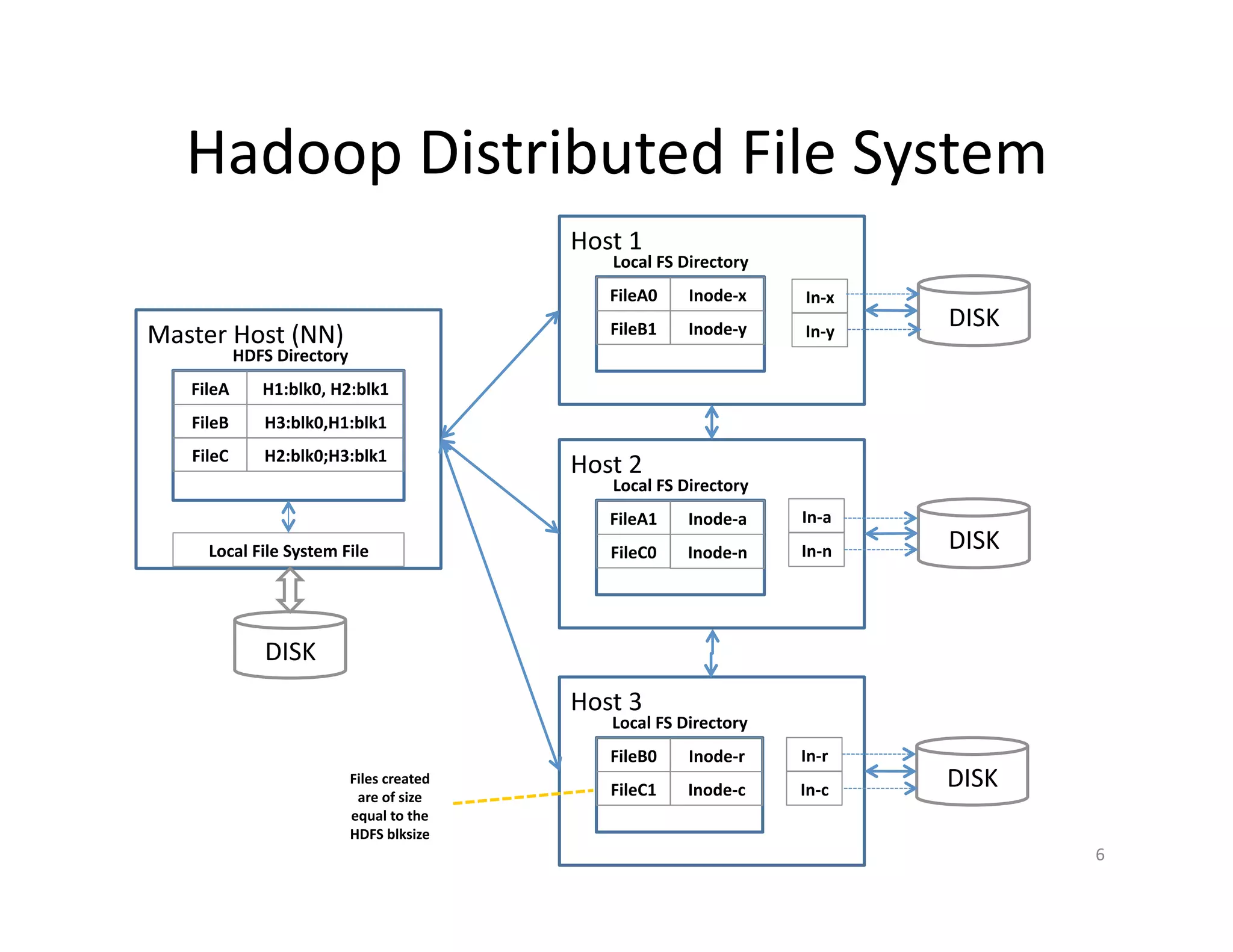
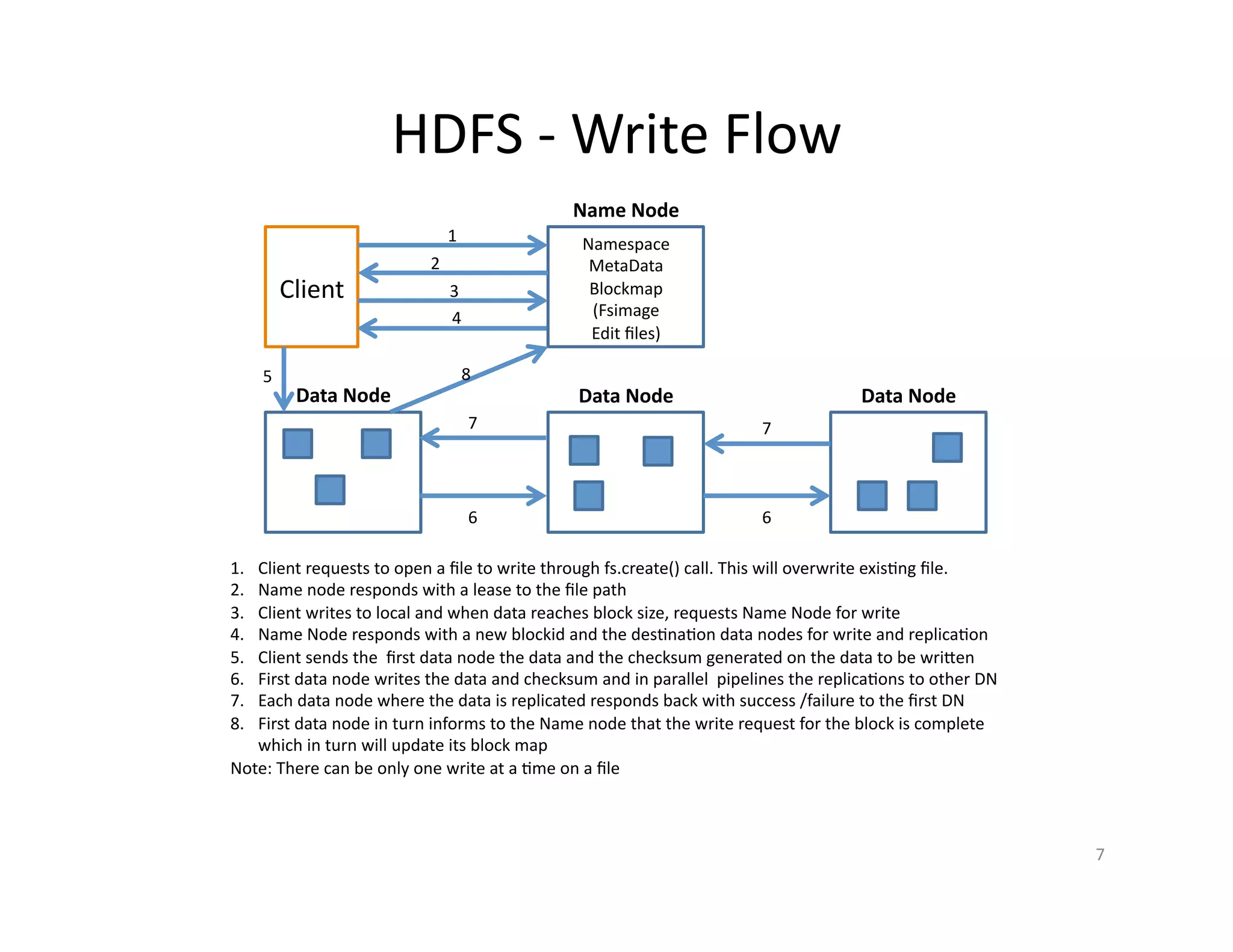
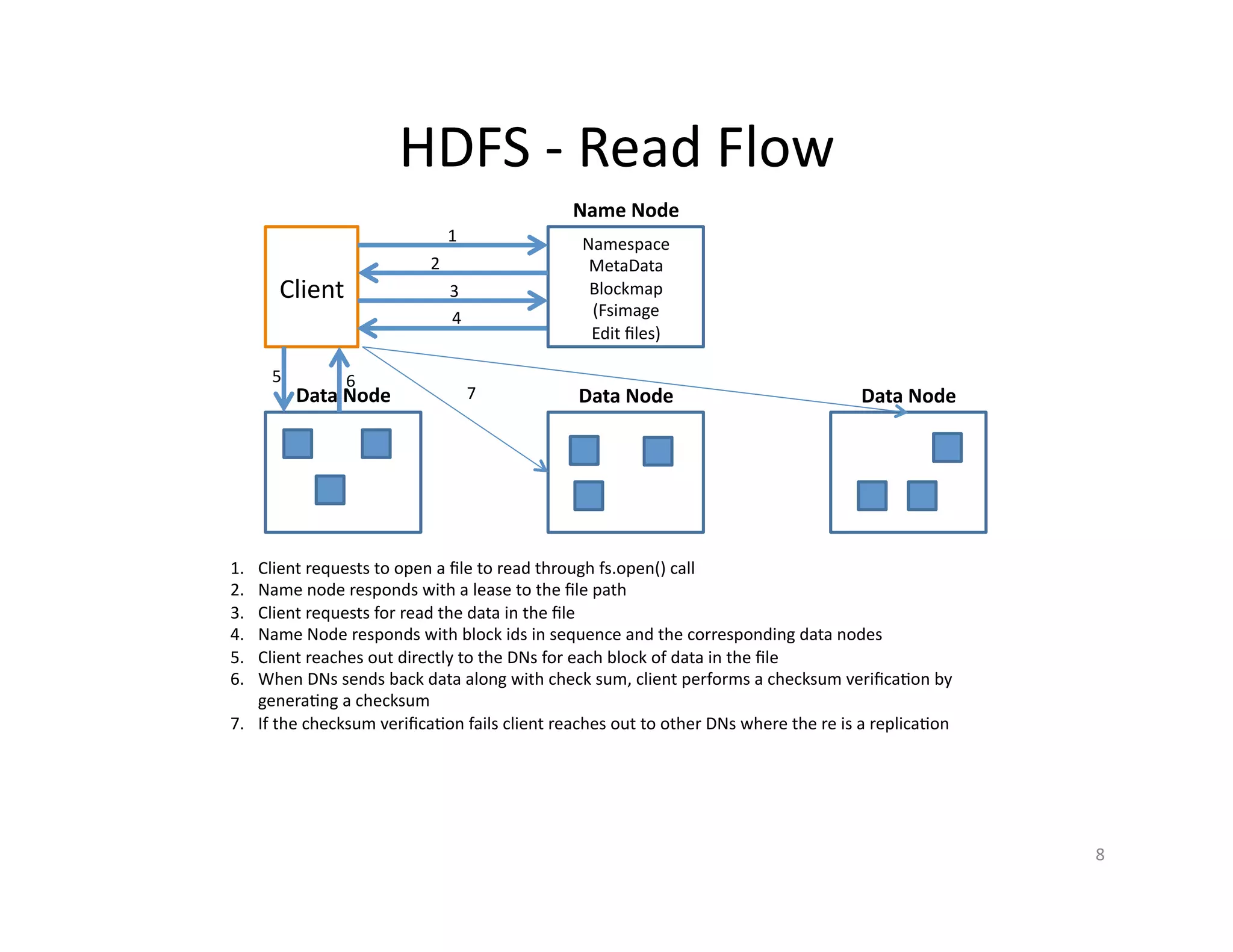
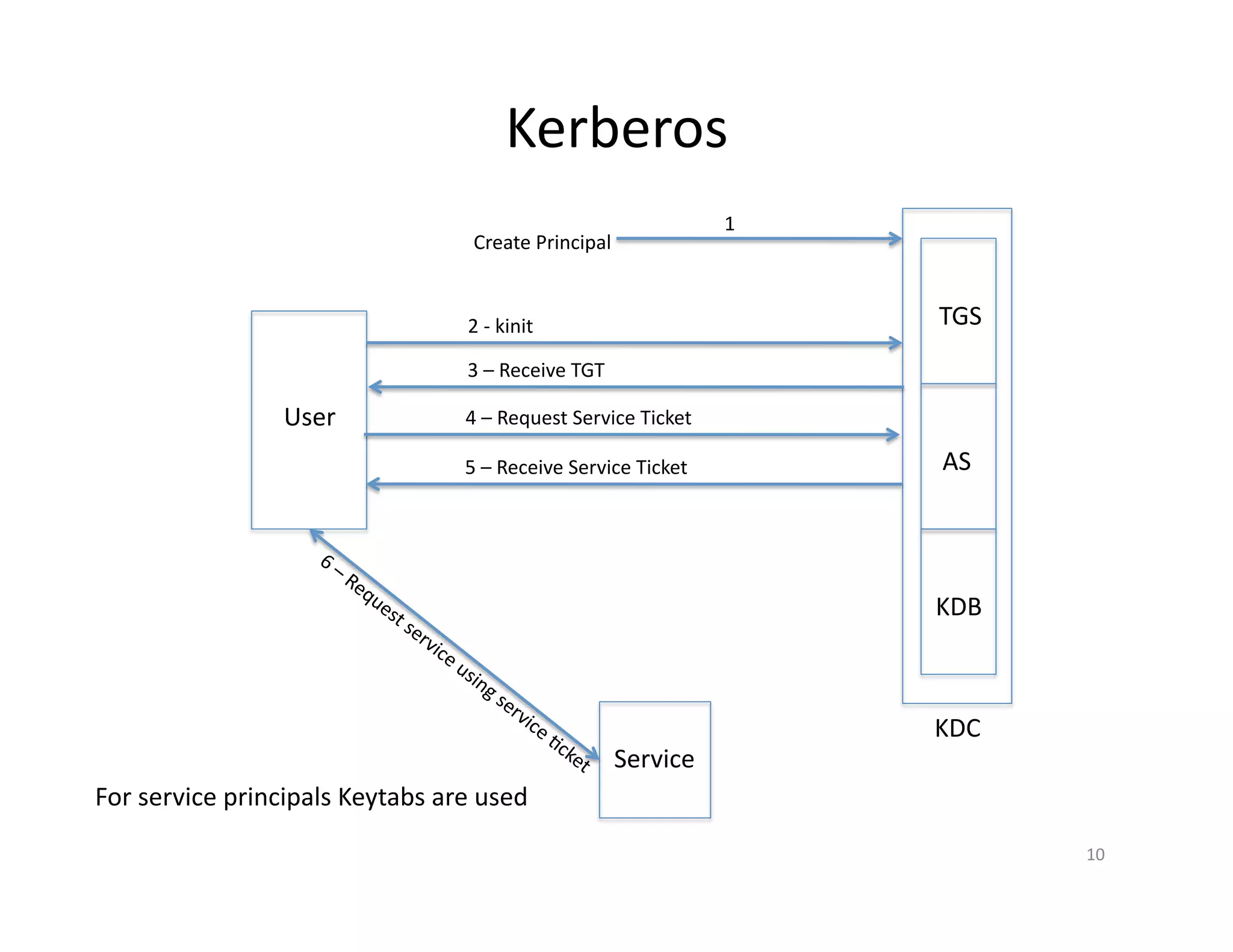
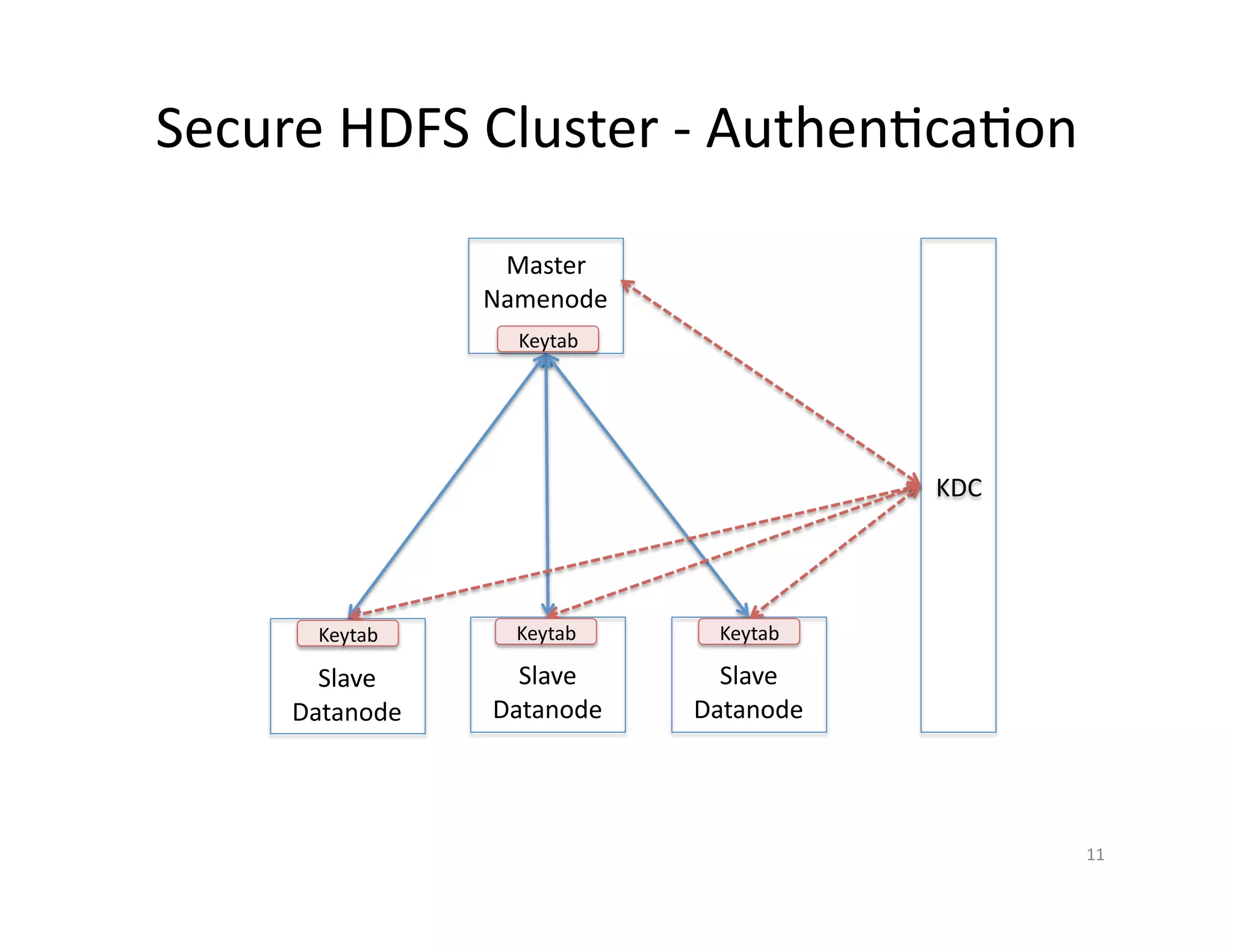
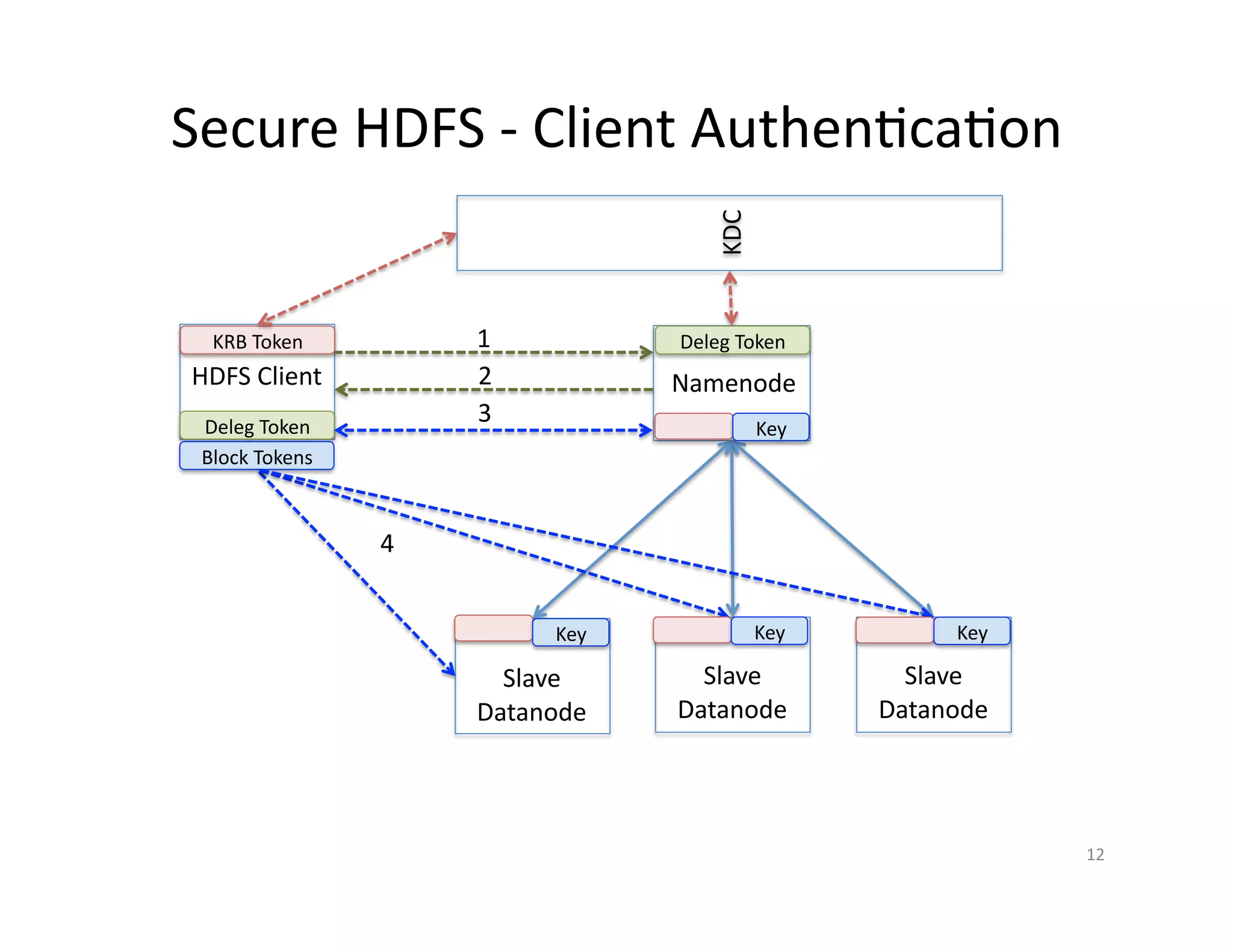
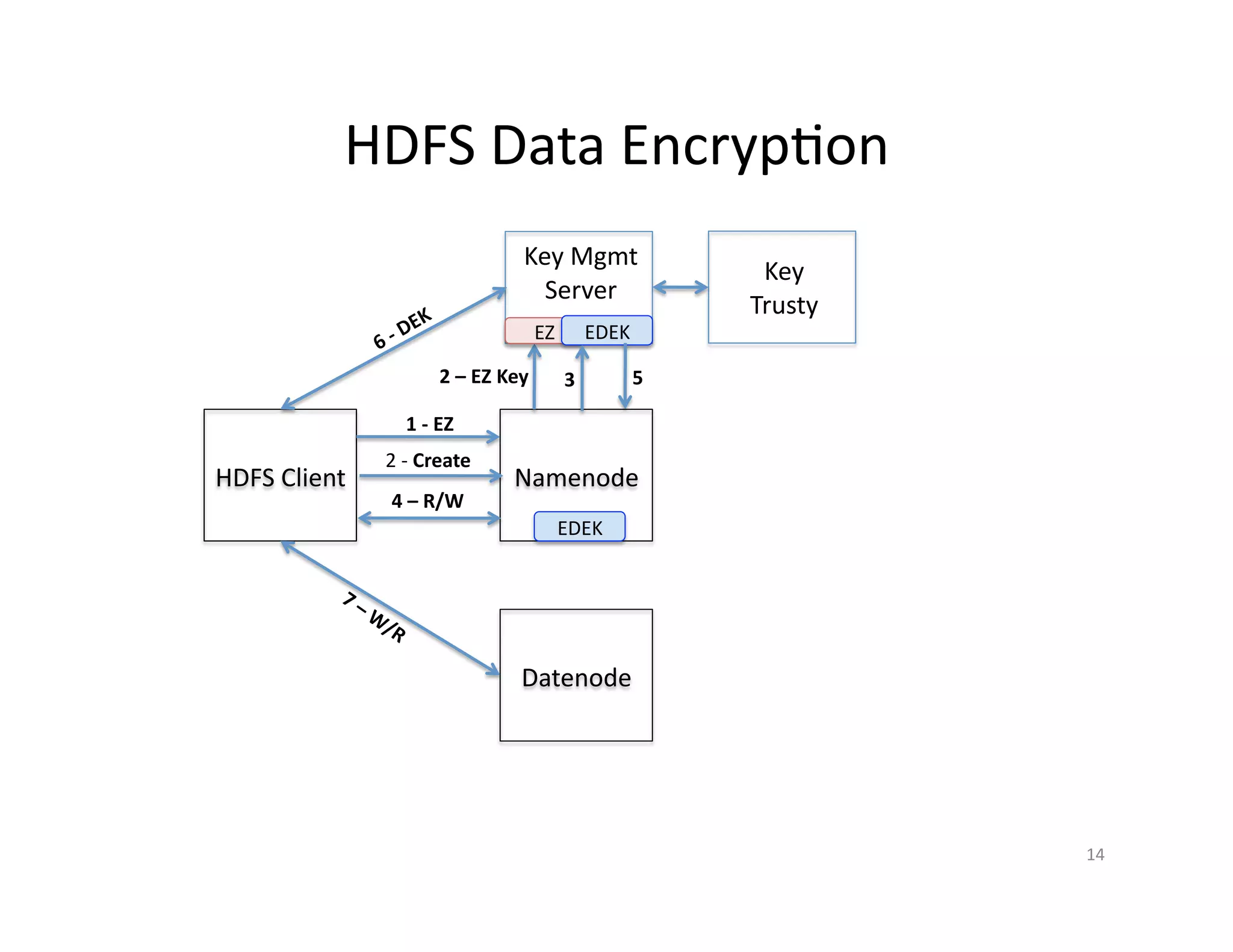
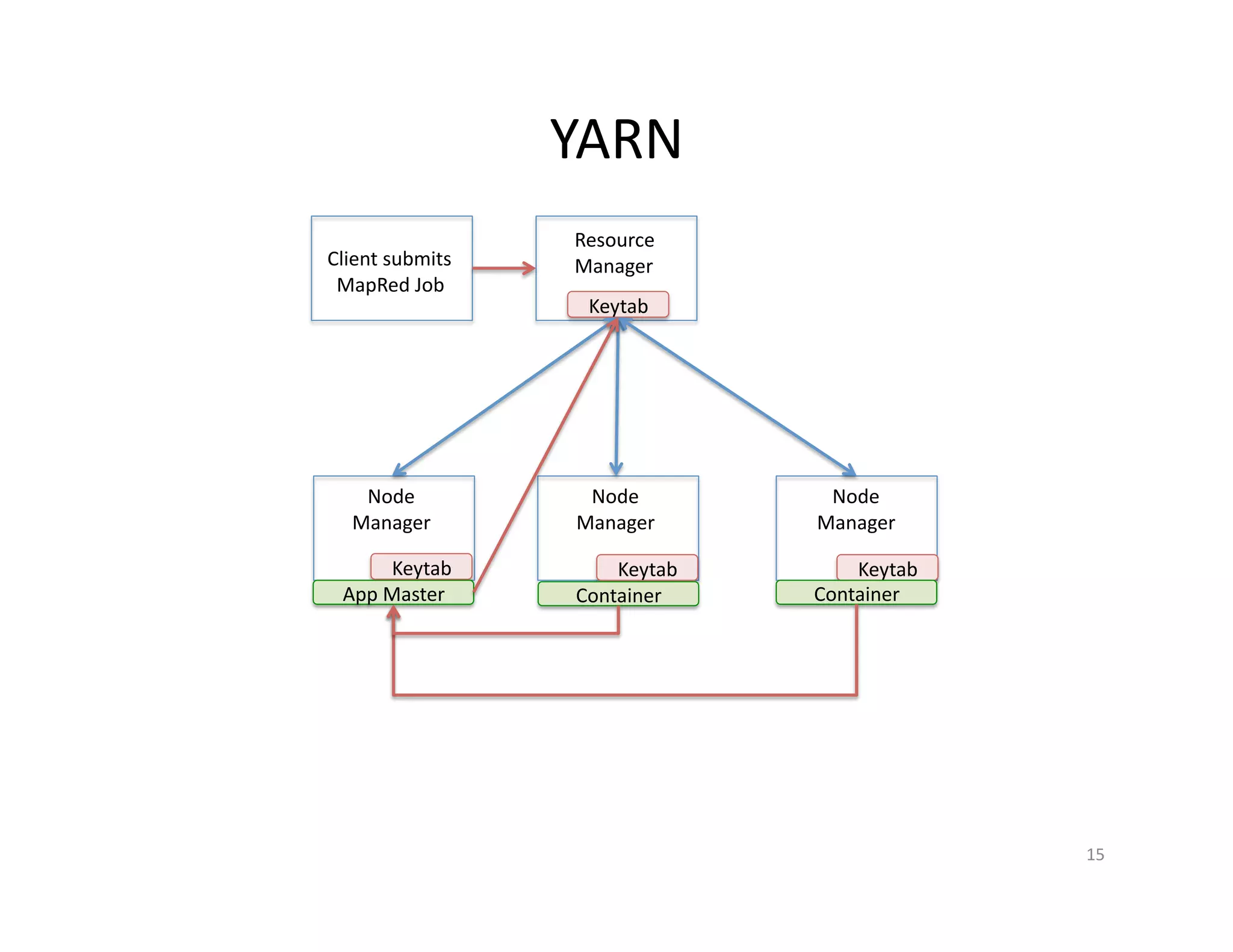
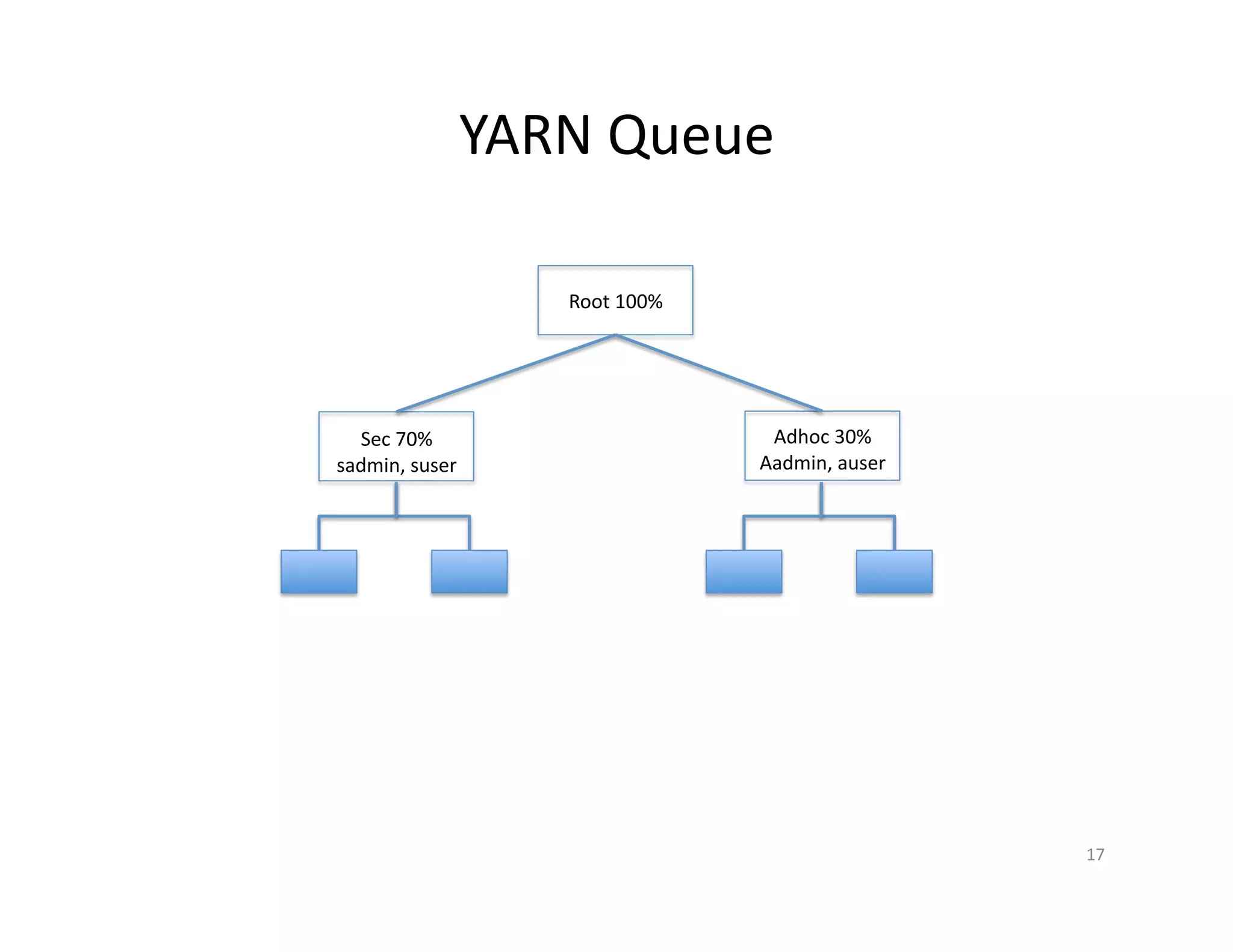
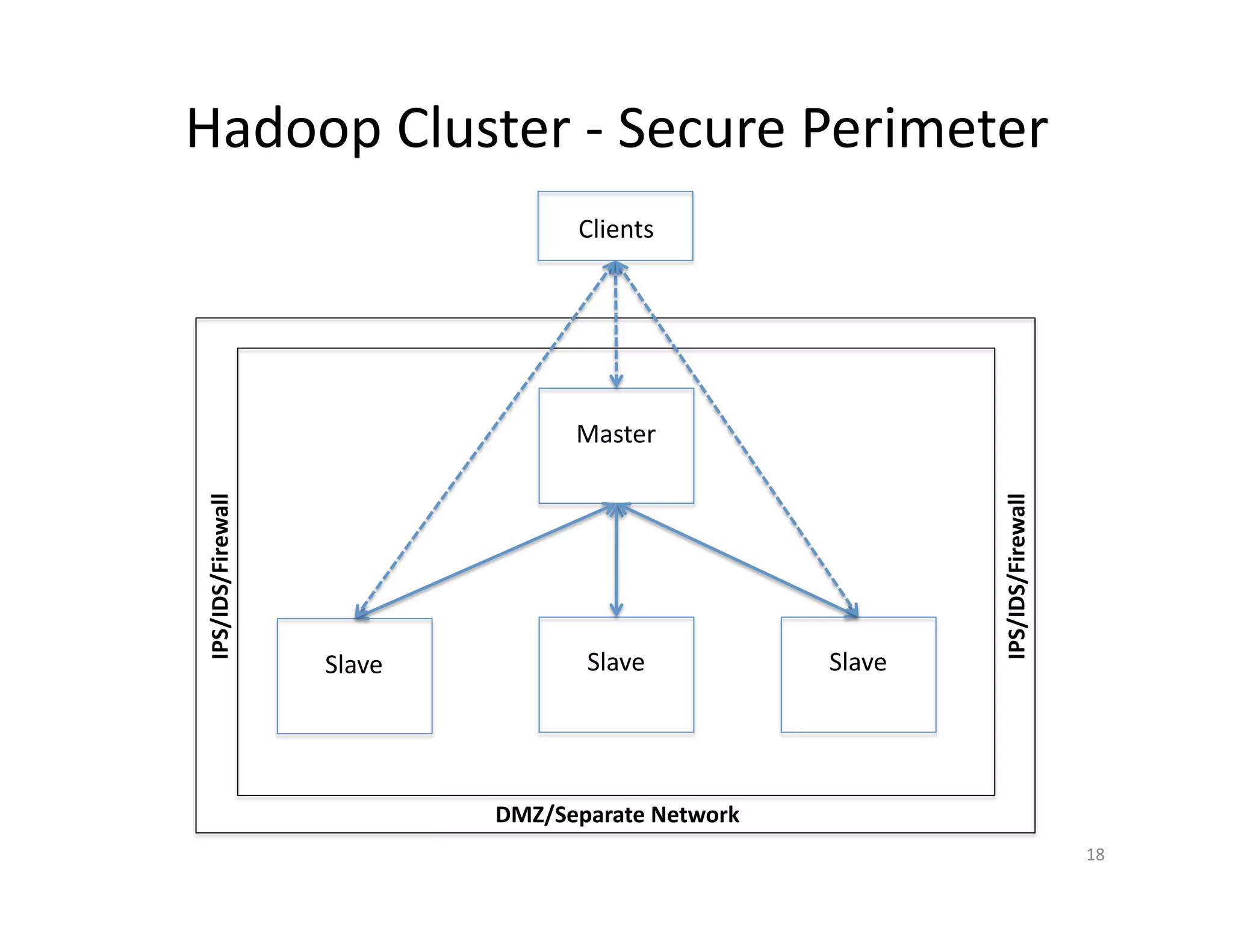
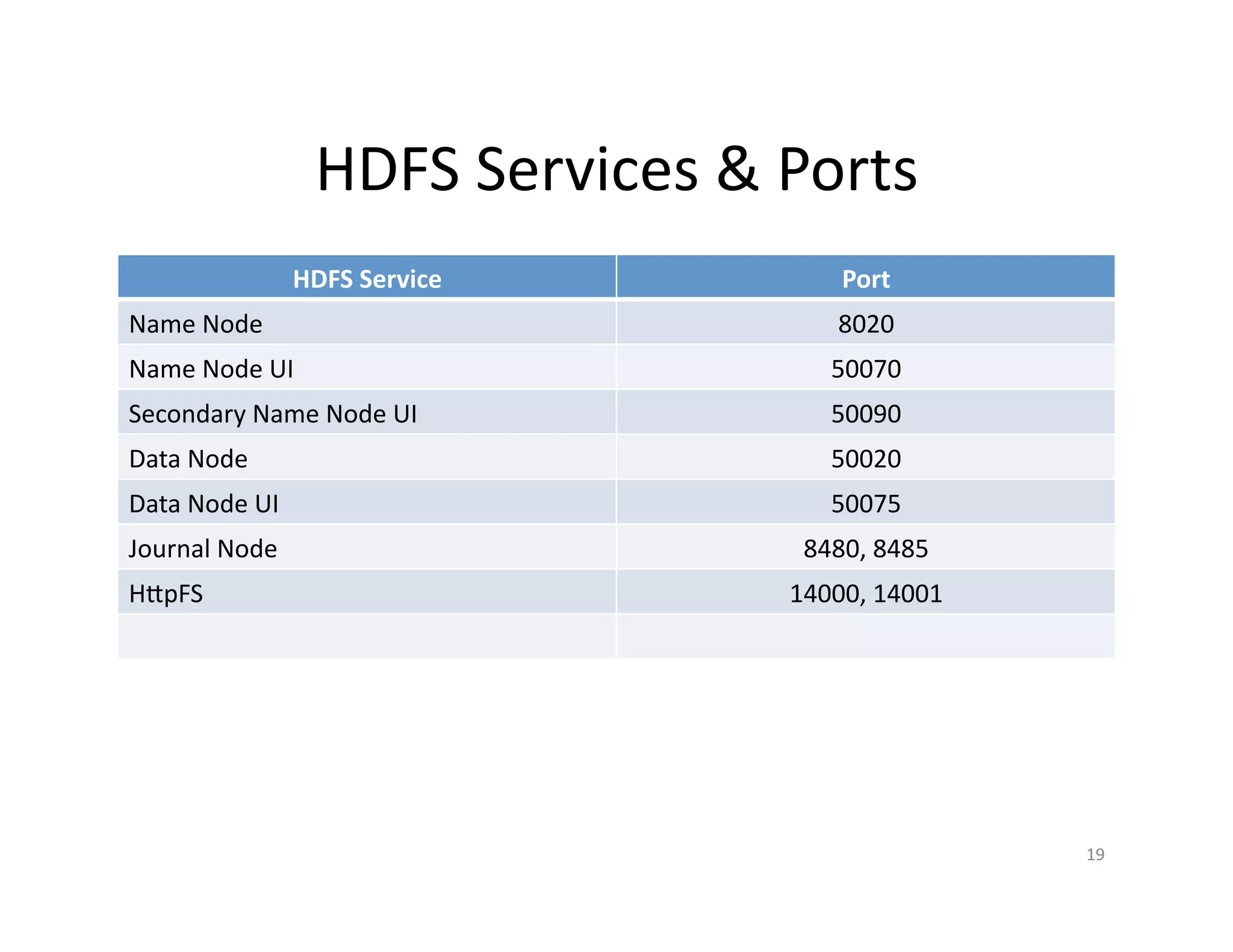
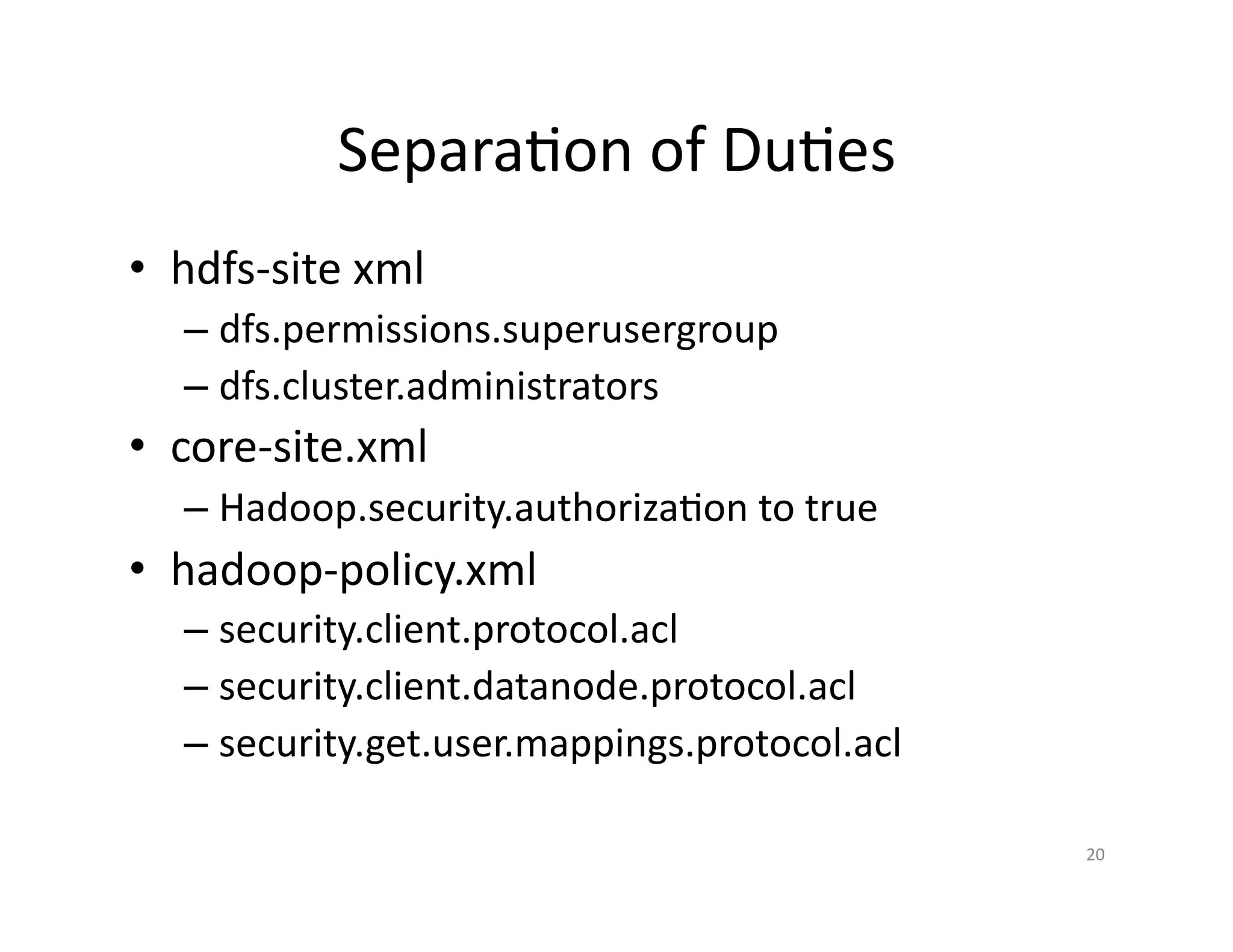
This document provides an overview of securing Hadoop applications and clusters. It discusses authentication using Kerberos, authorization using POSIX permissions and HDFS ACLs, encrypting HDFS data at rest, and configuring secure communication between Hadoop services and clients. The principles of least privilege and separating duties are important to apply for a secure Hadoop deployment. Application code may need changes to use Kerberos authentication when accessing Hadoop services.