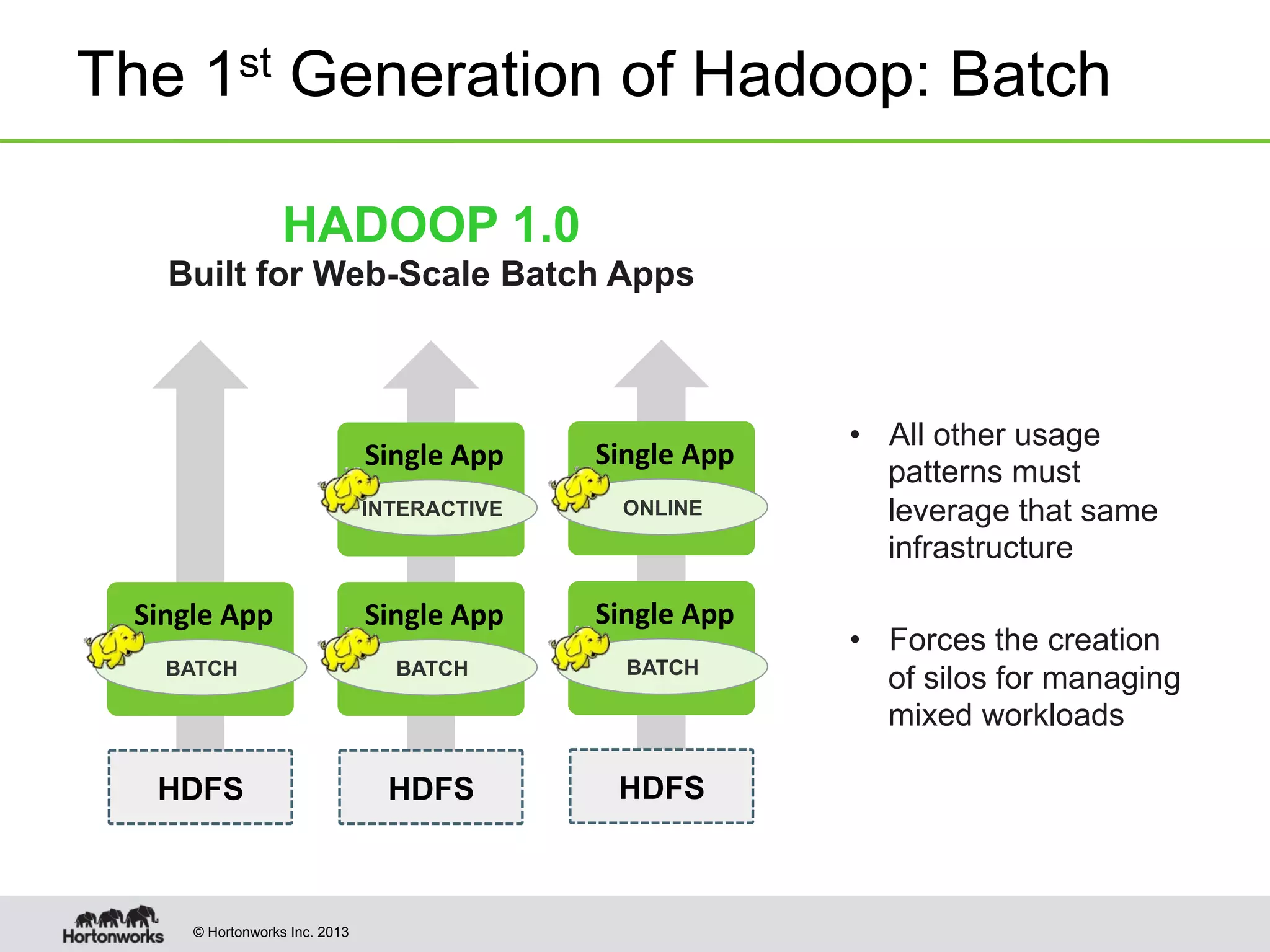
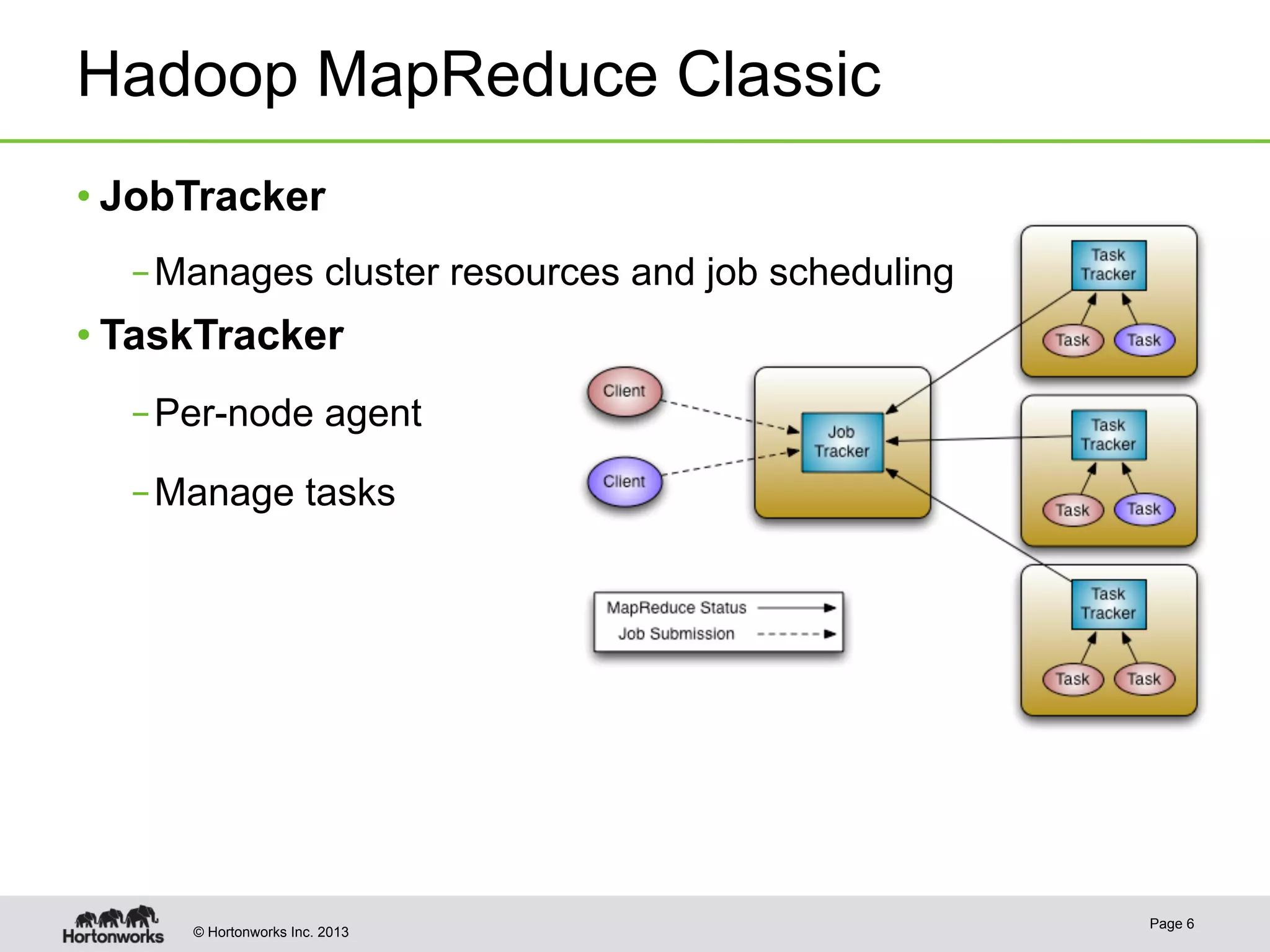
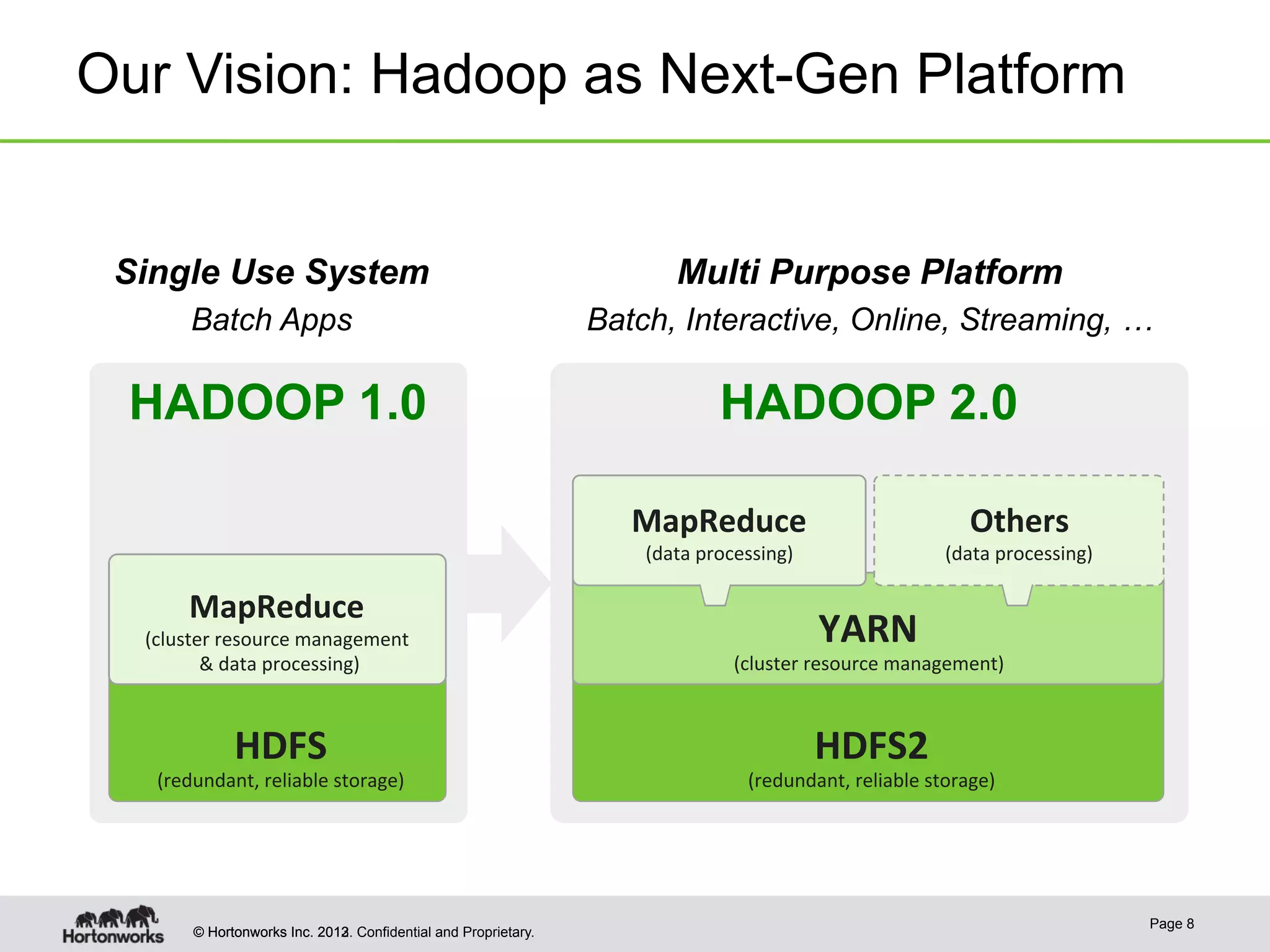
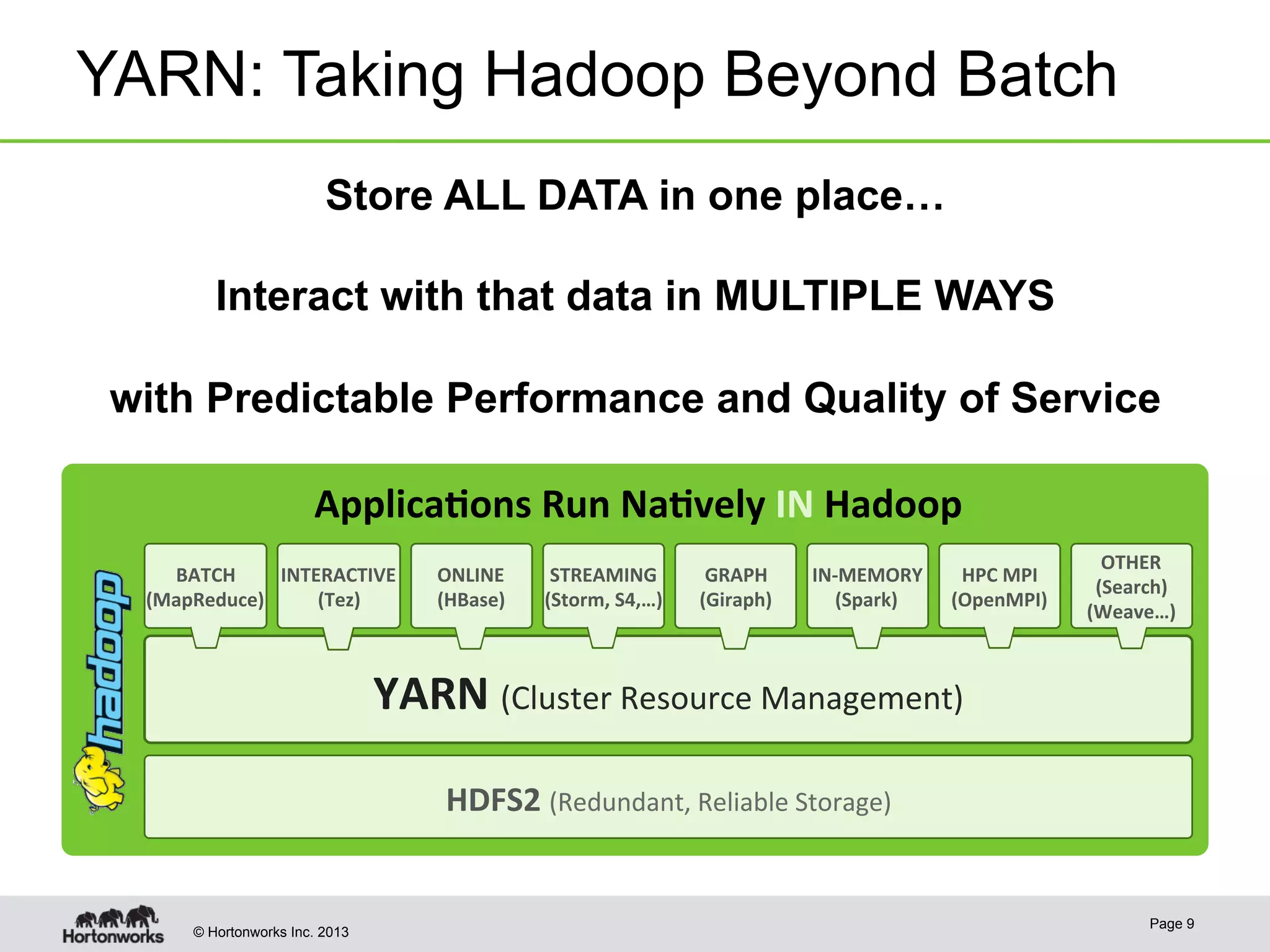
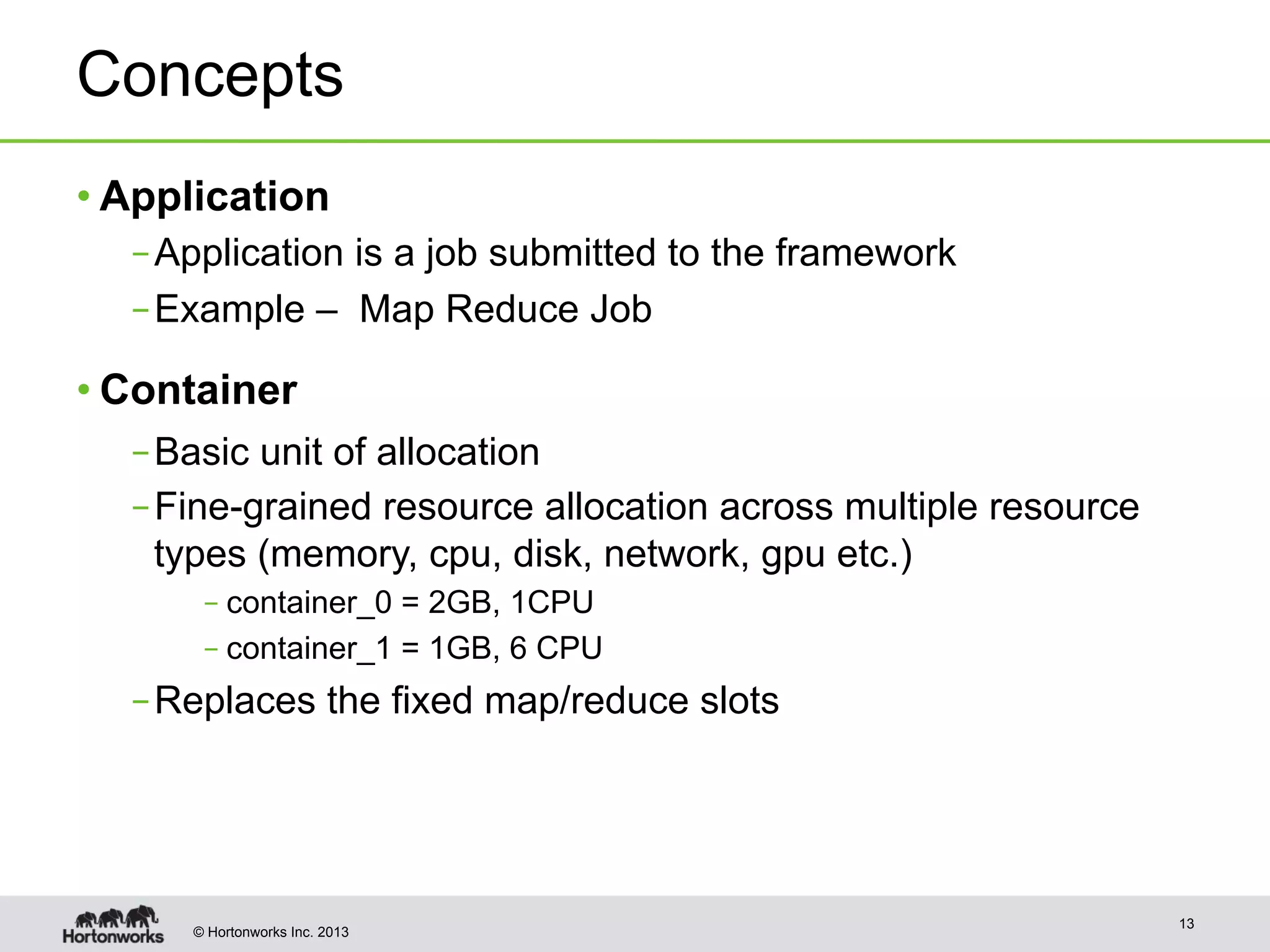
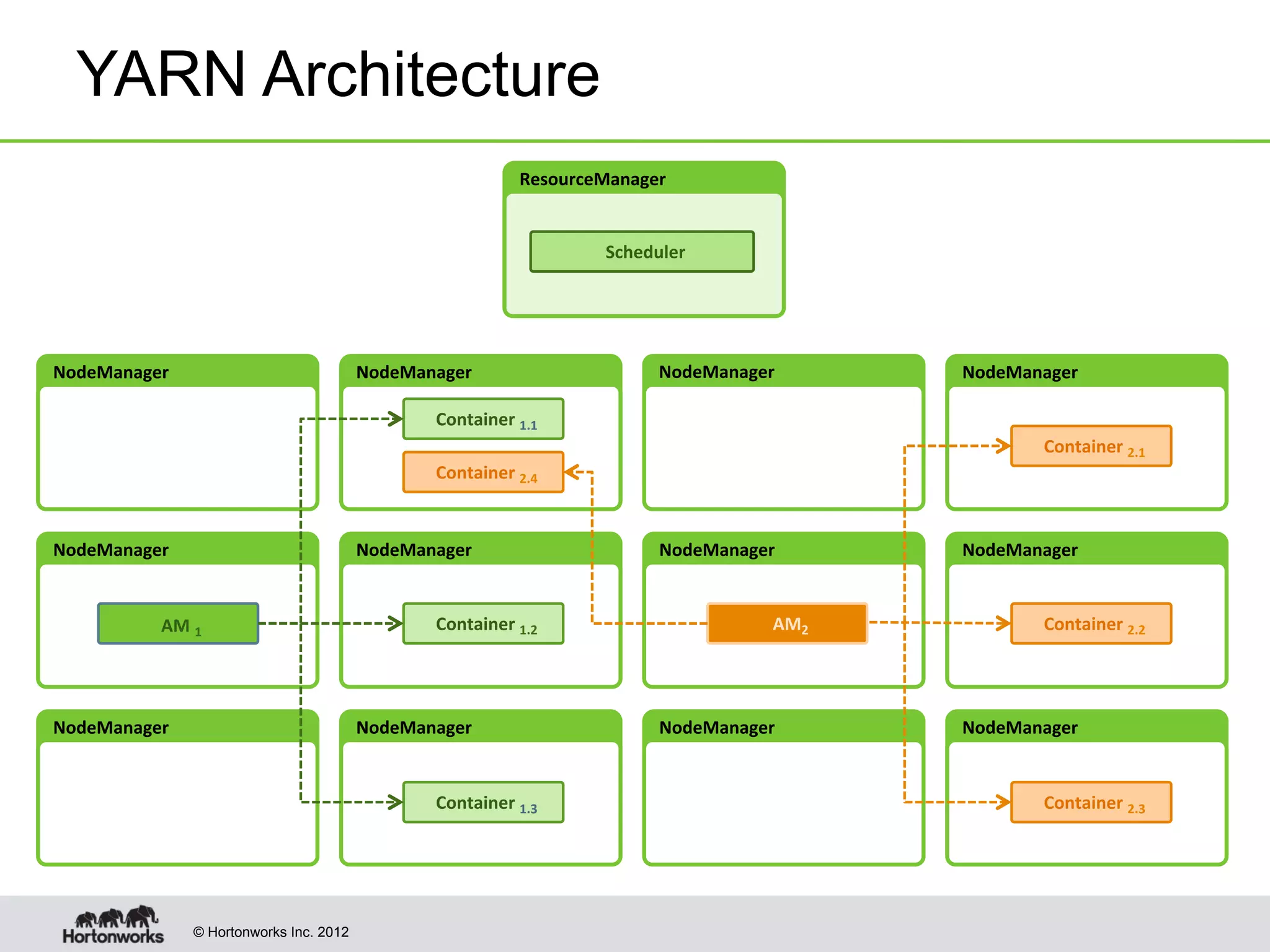
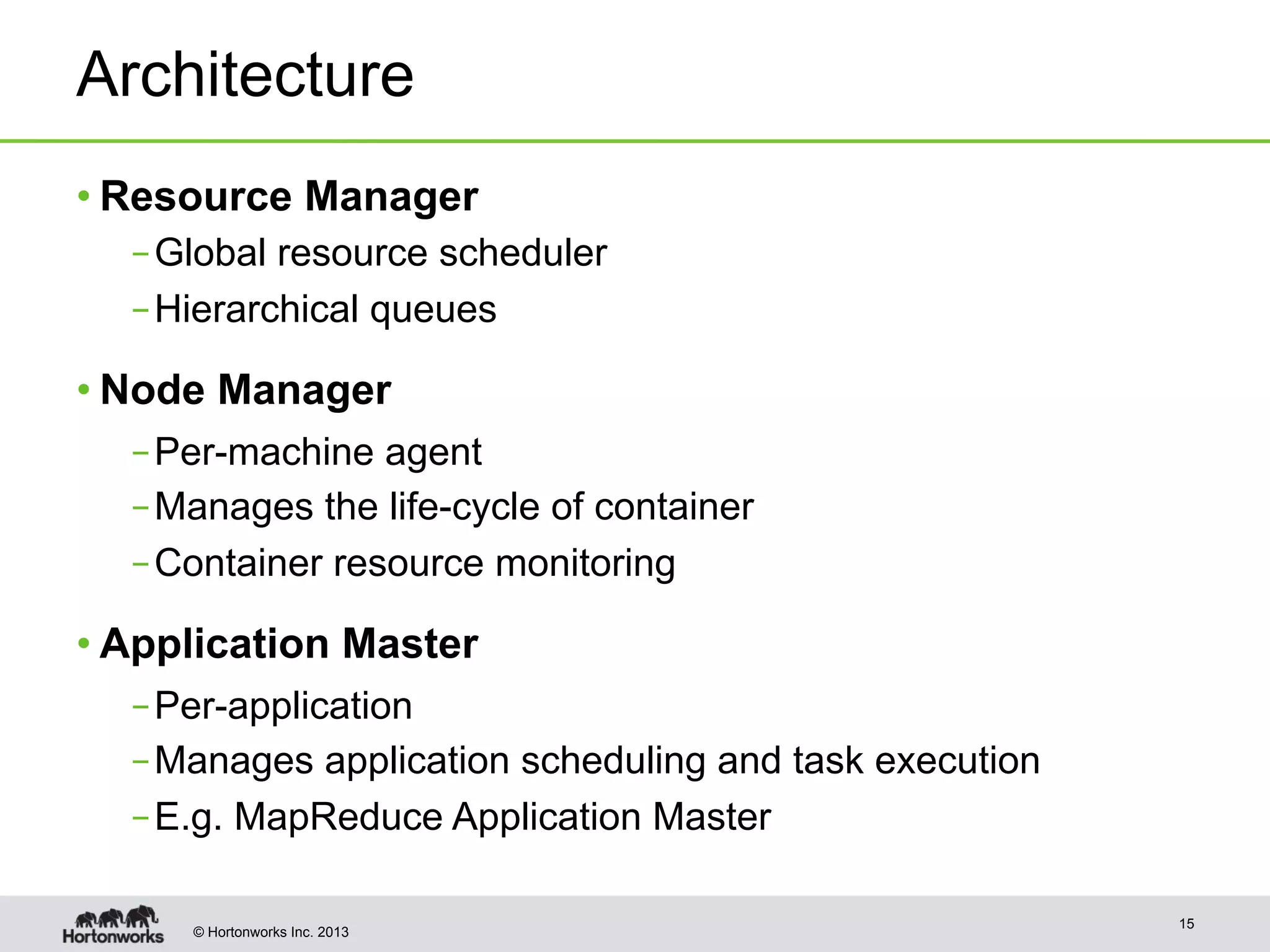
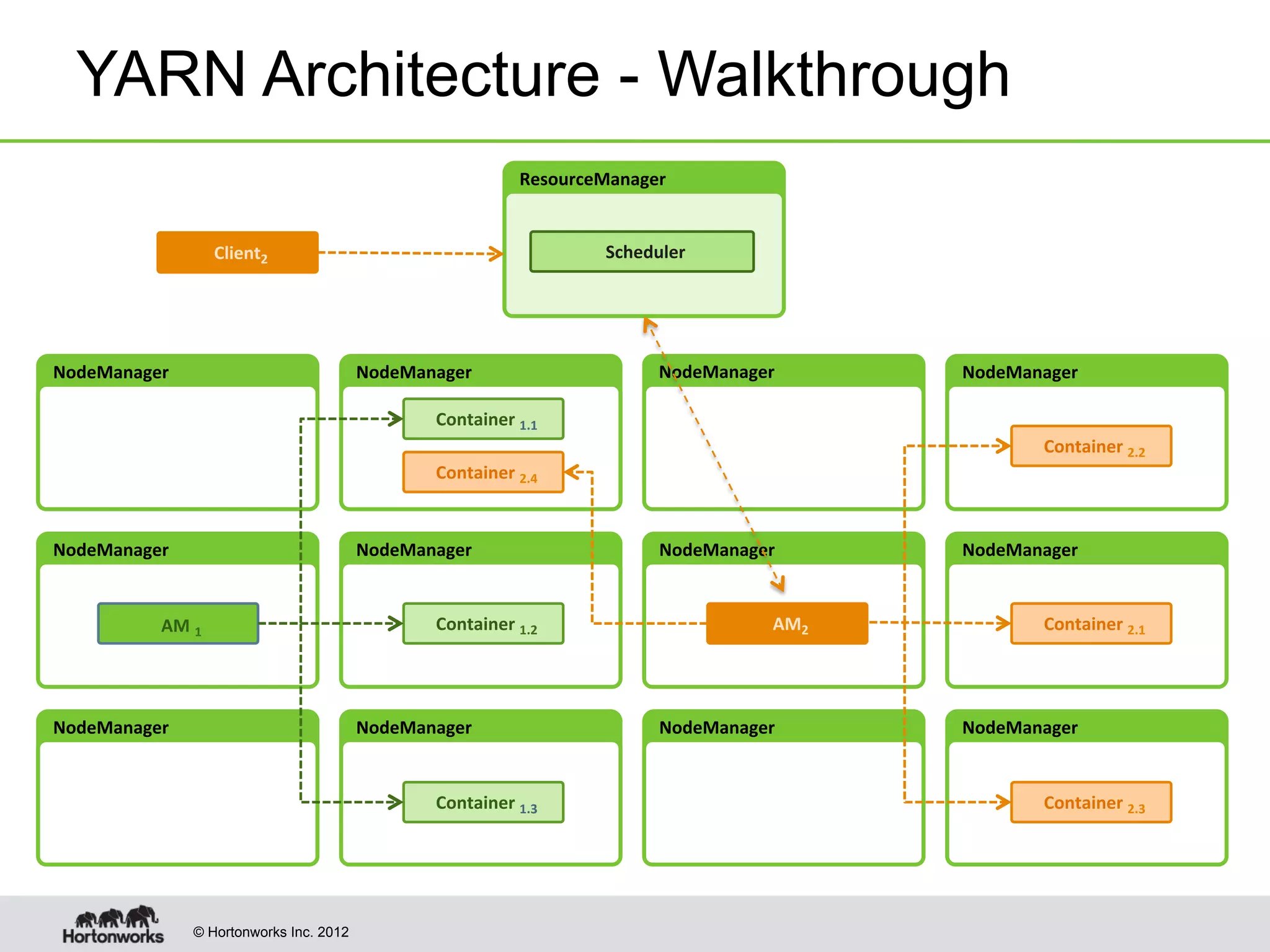
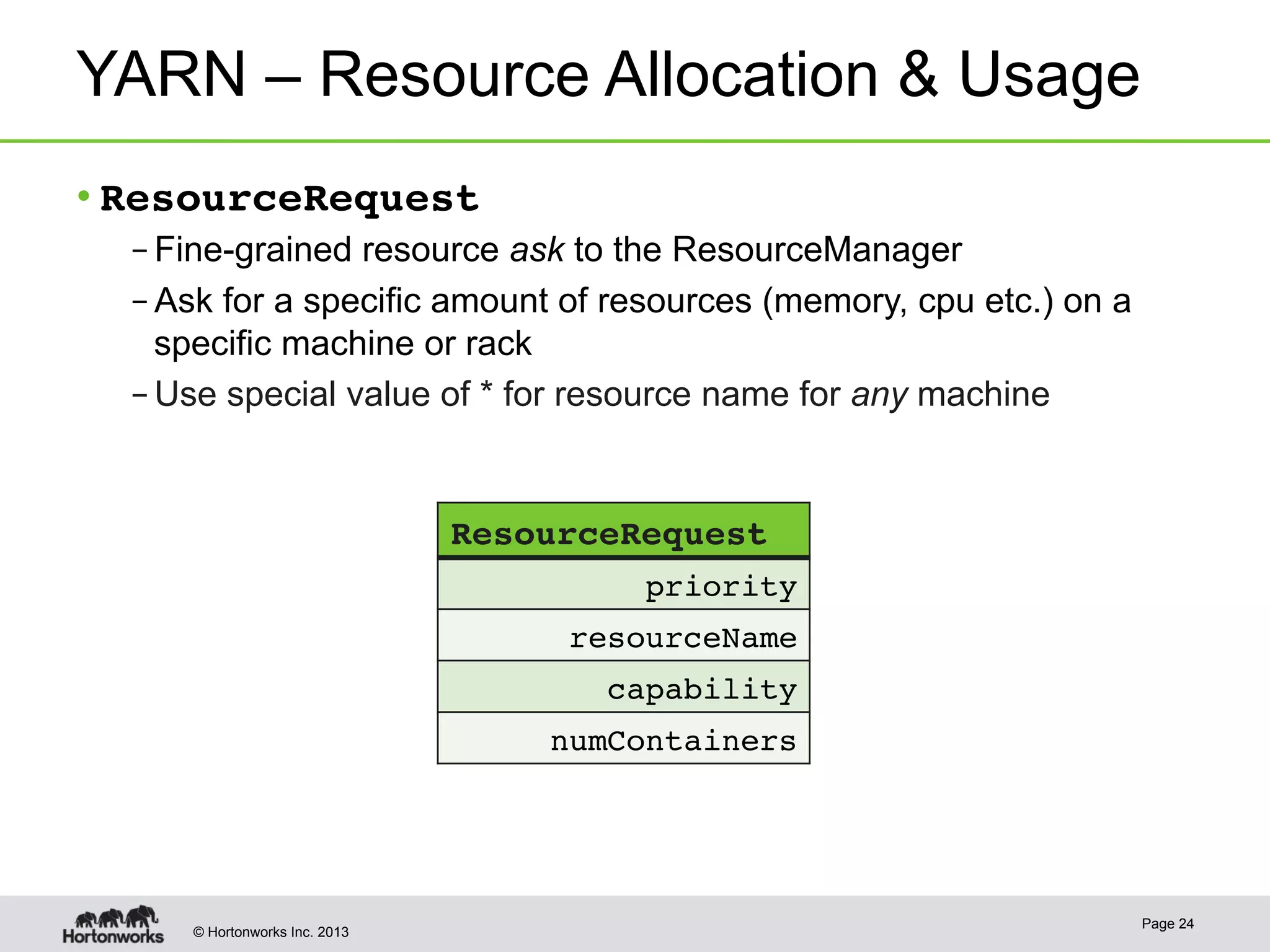
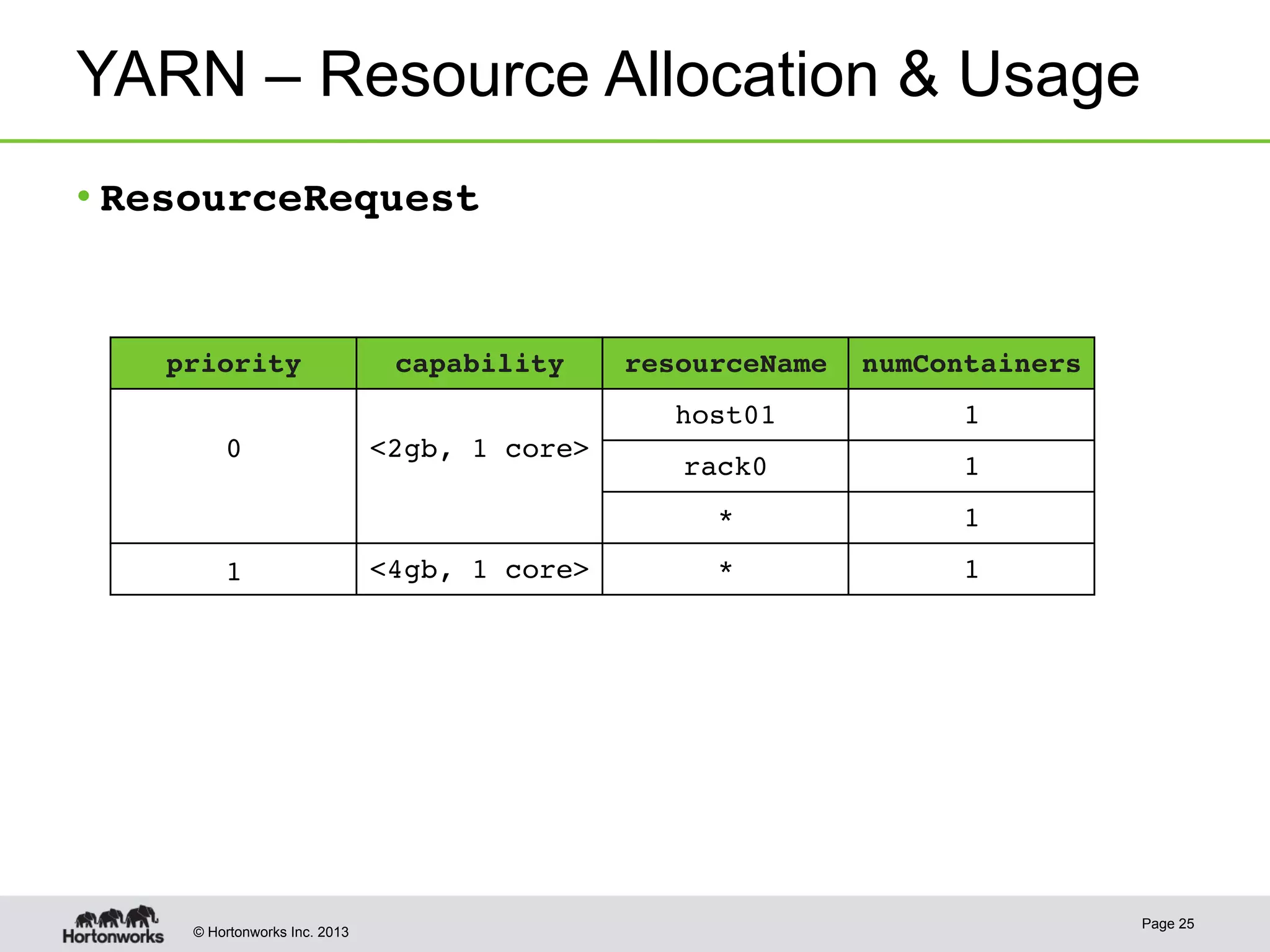
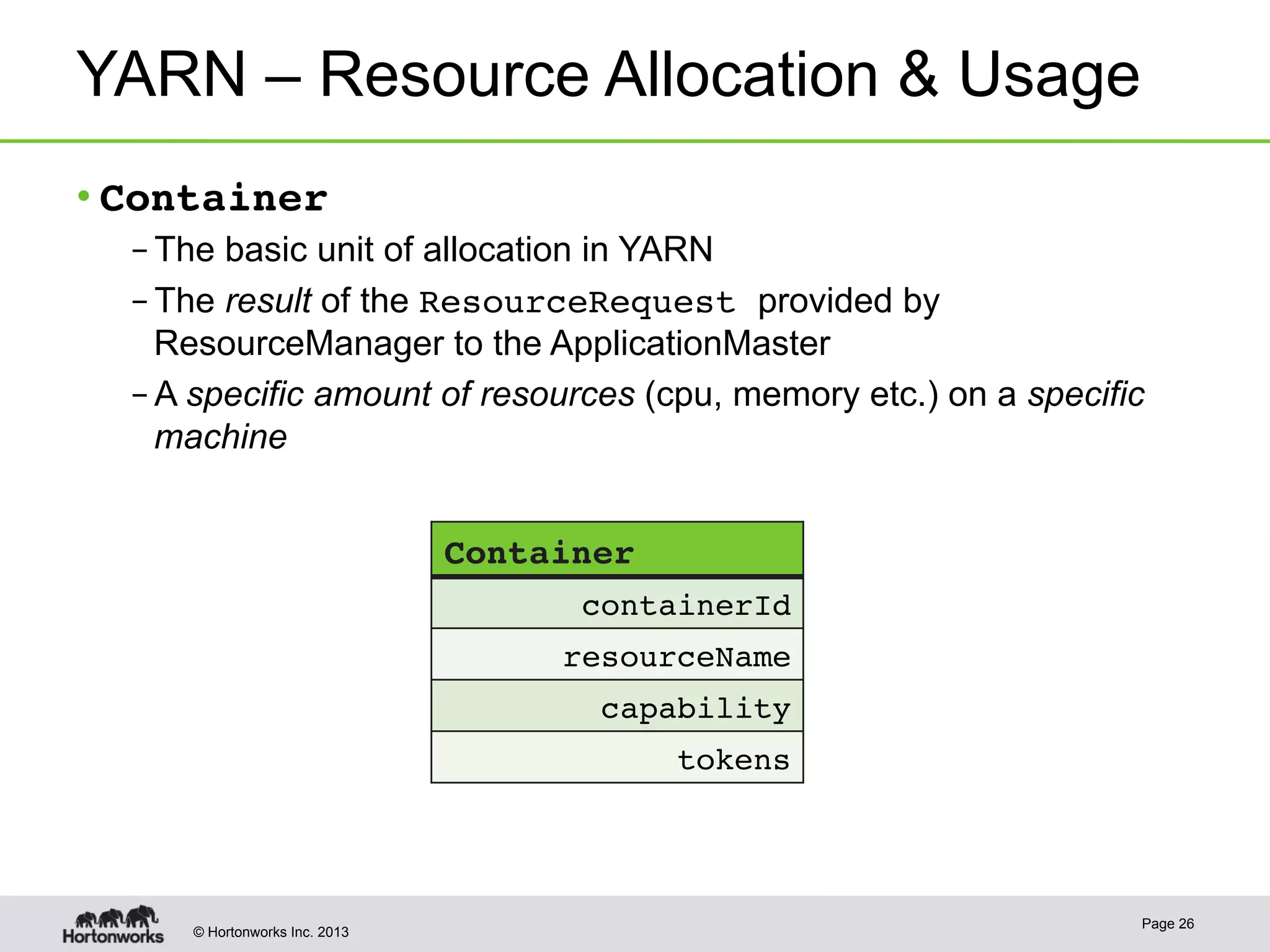
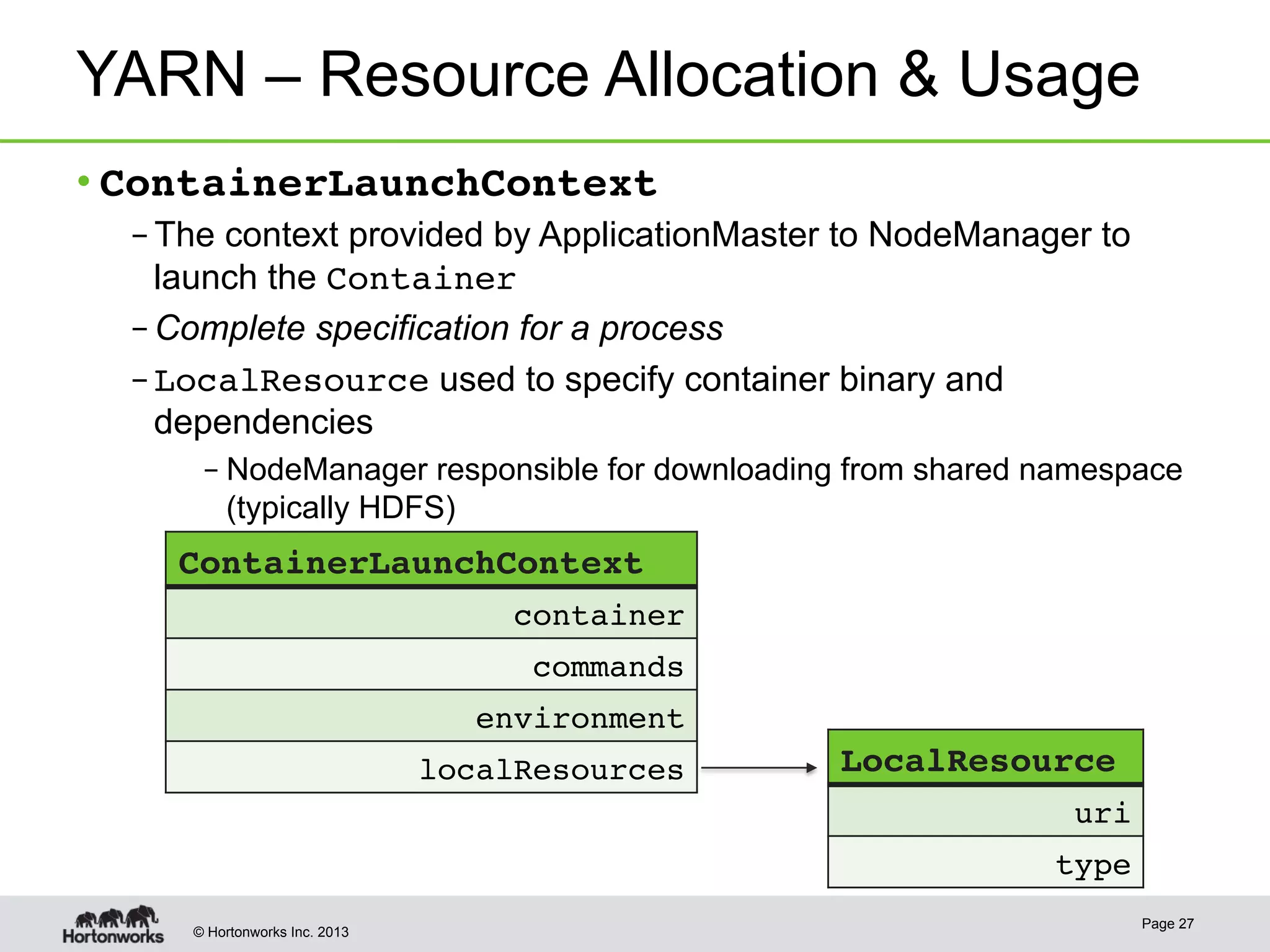
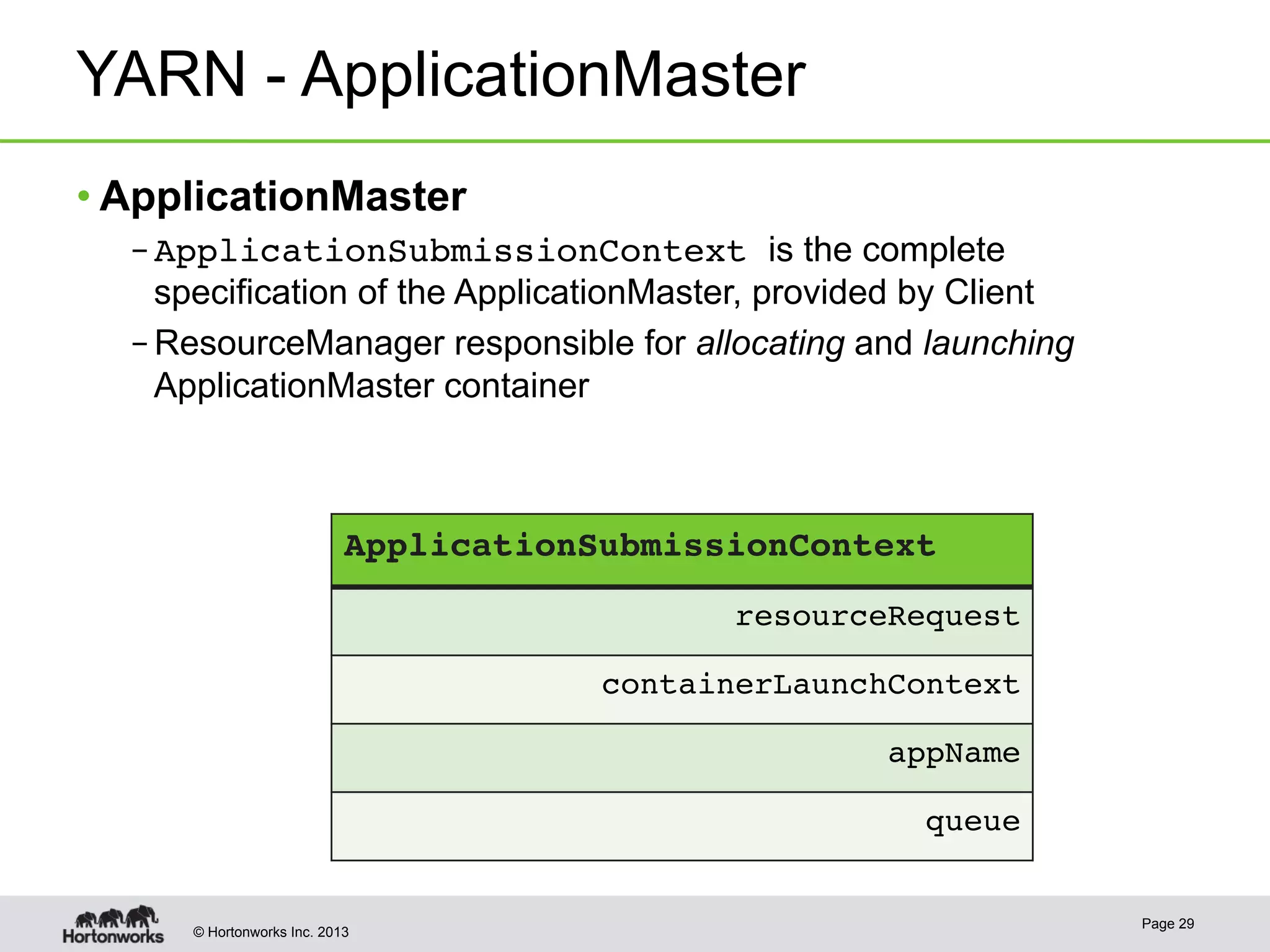
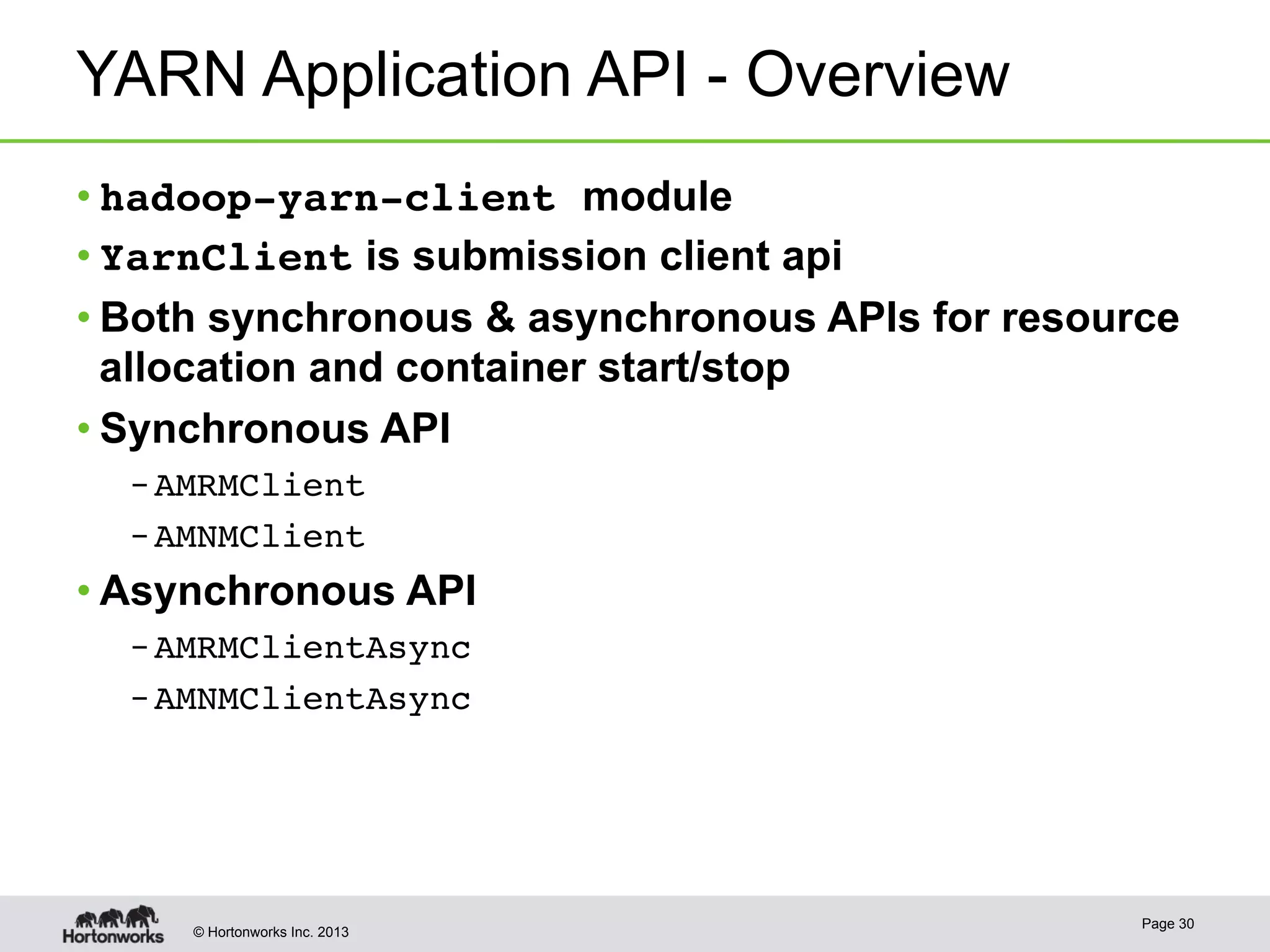
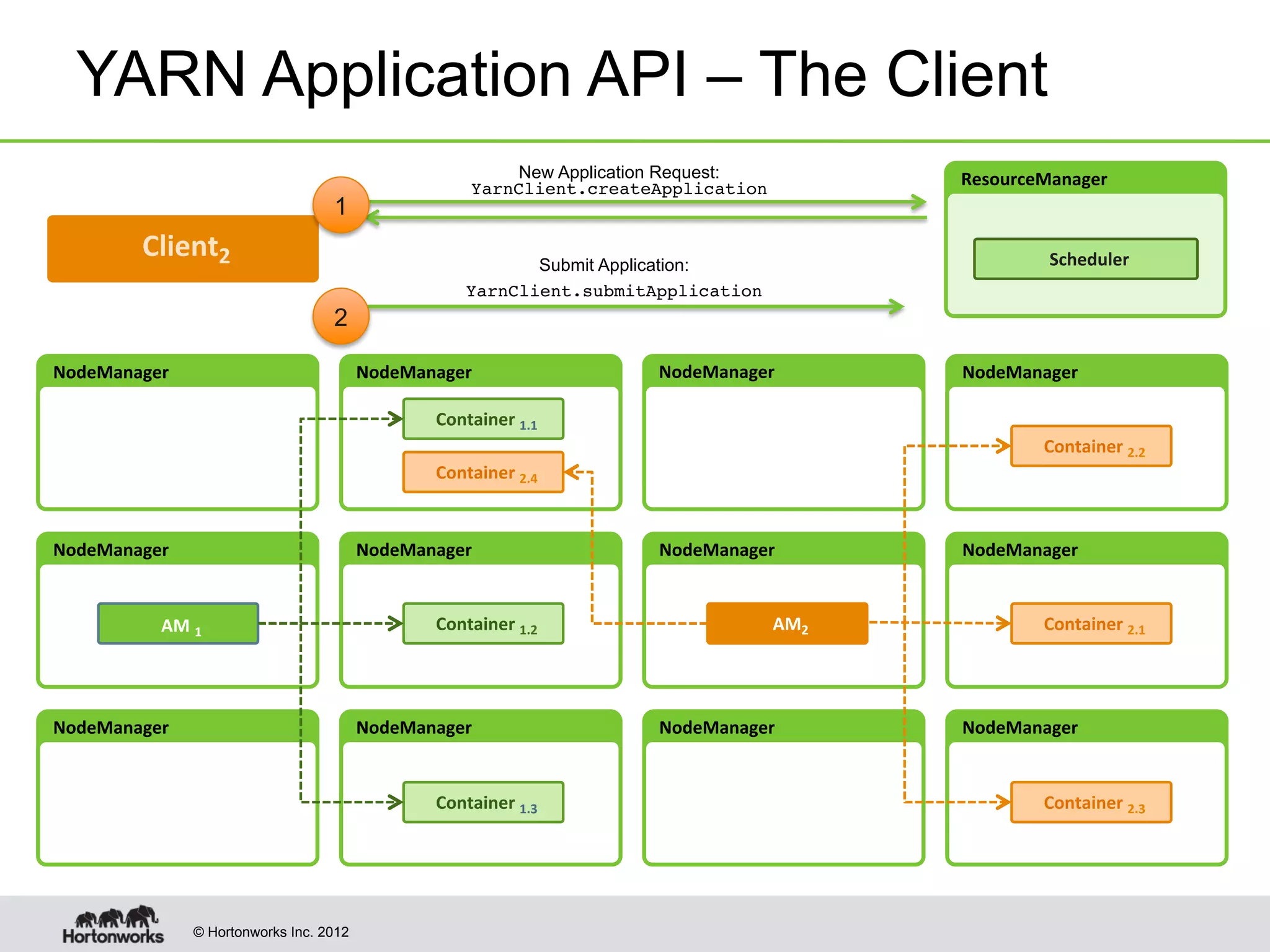
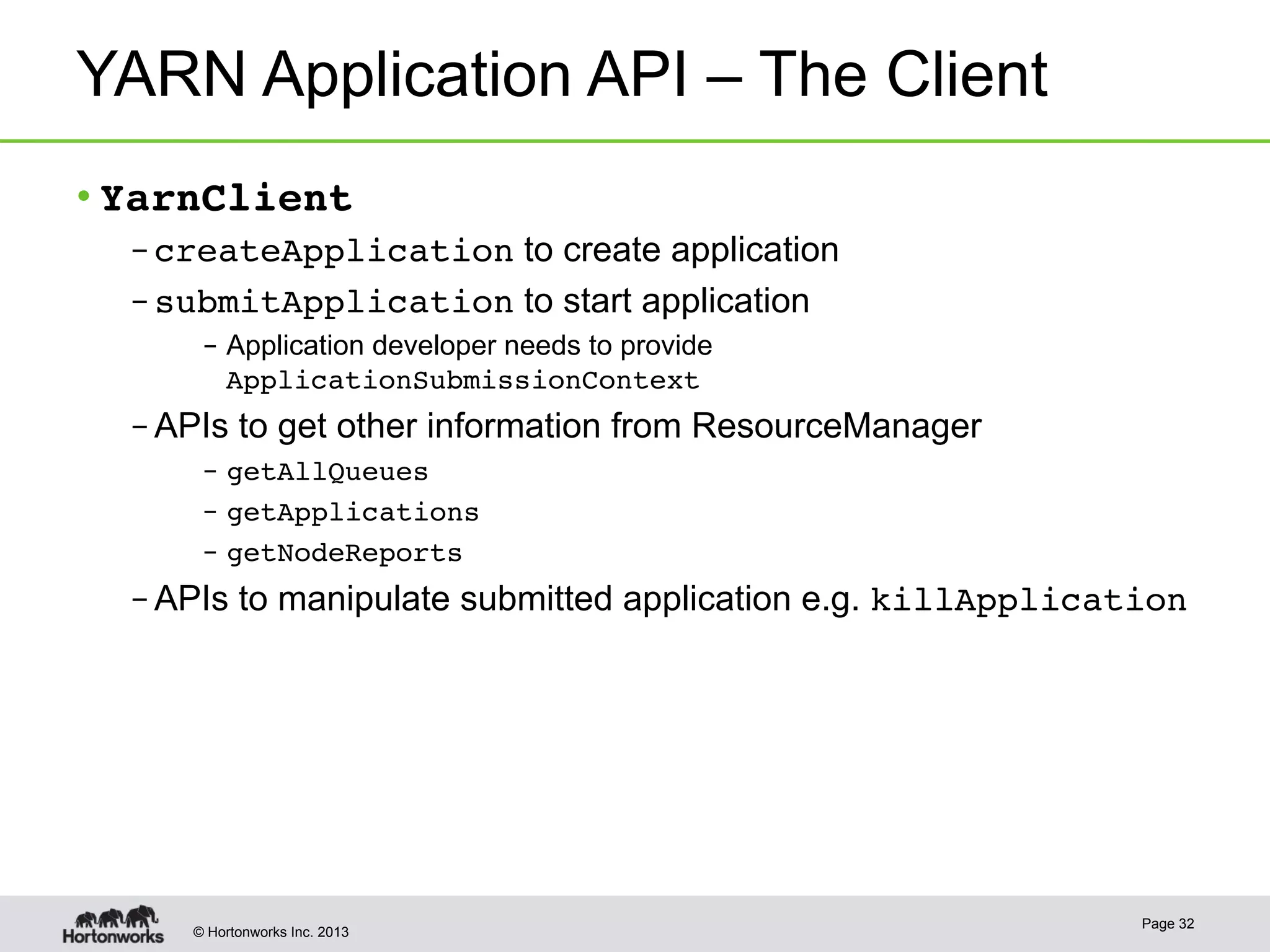
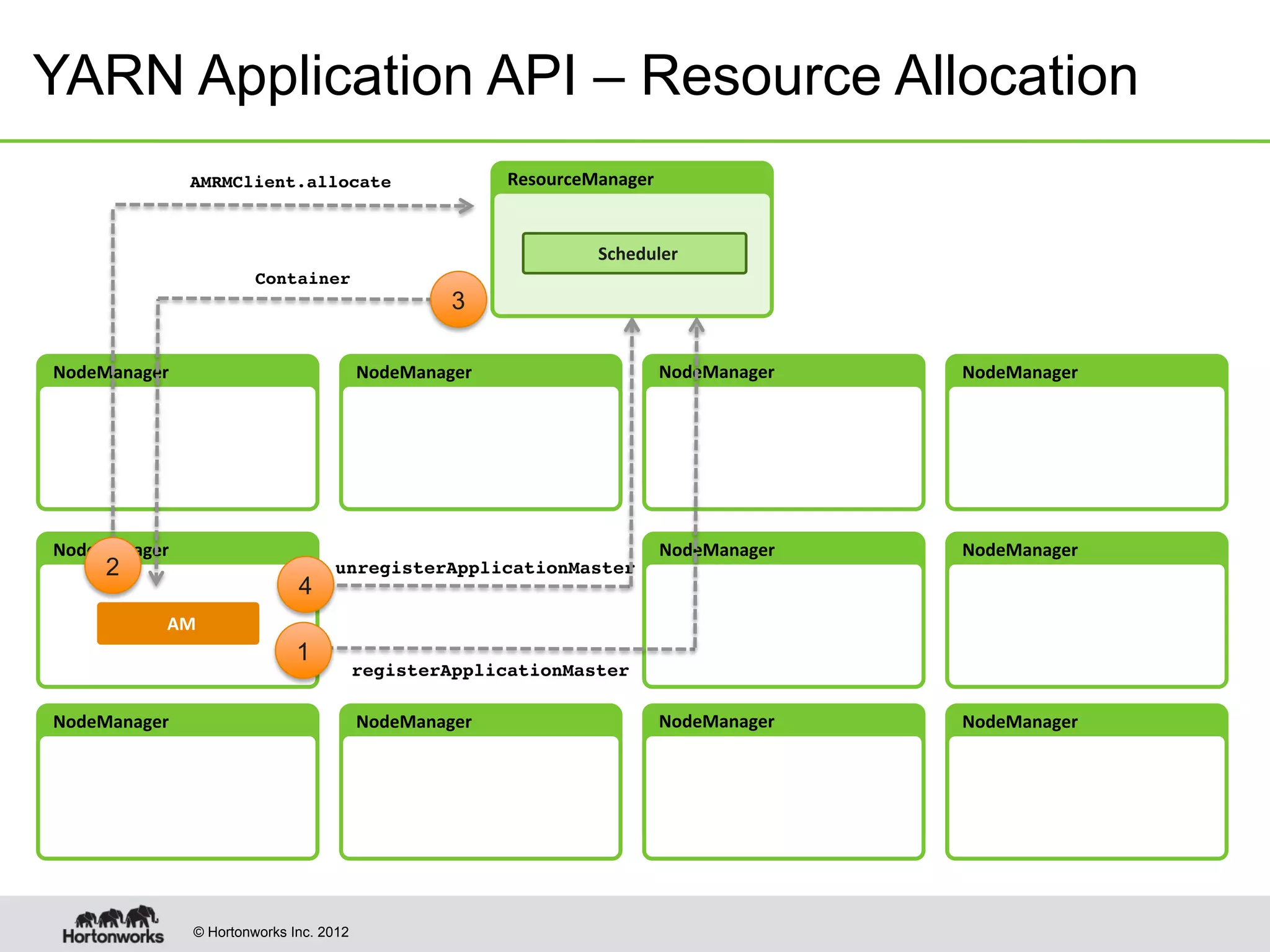
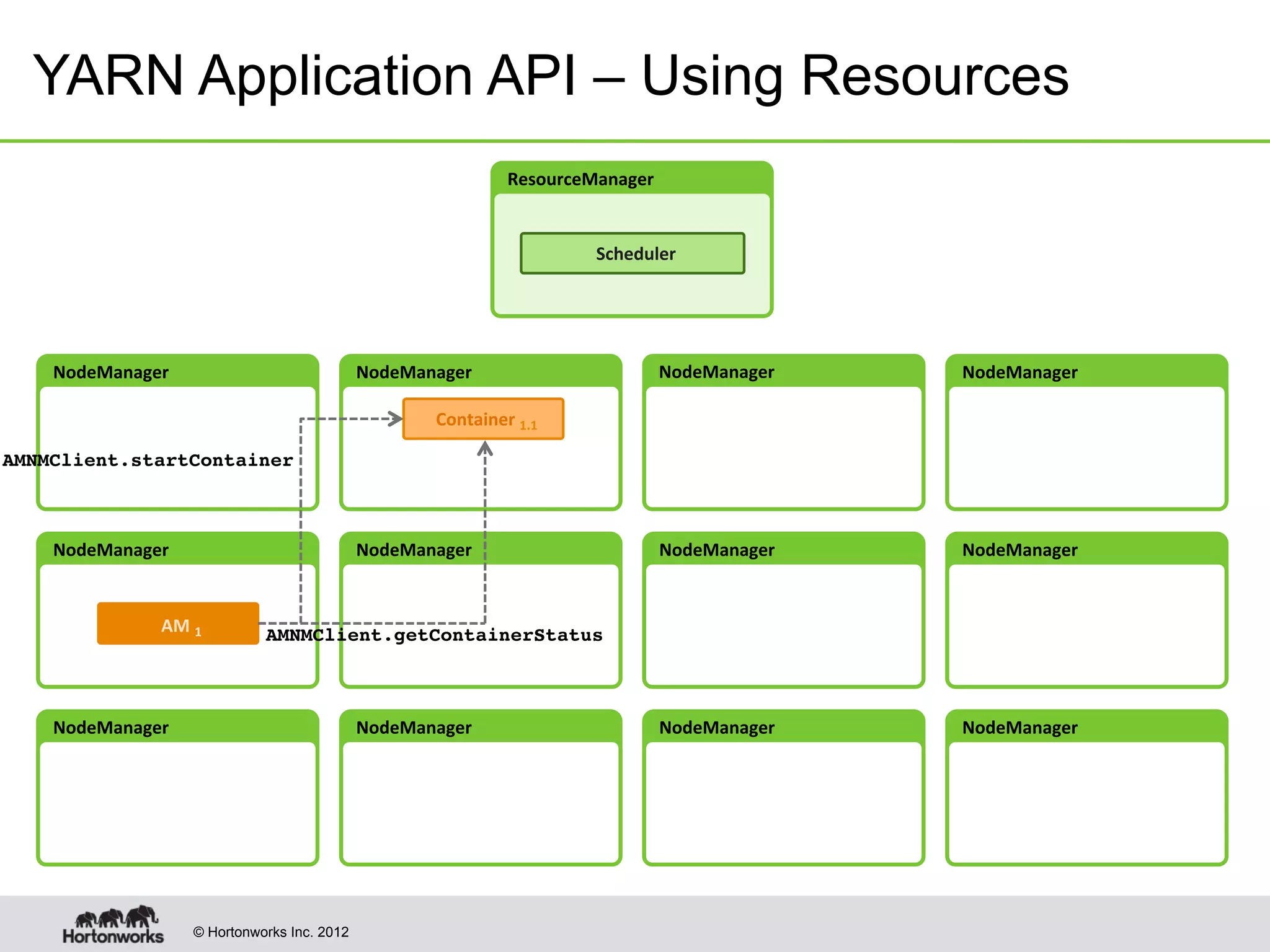
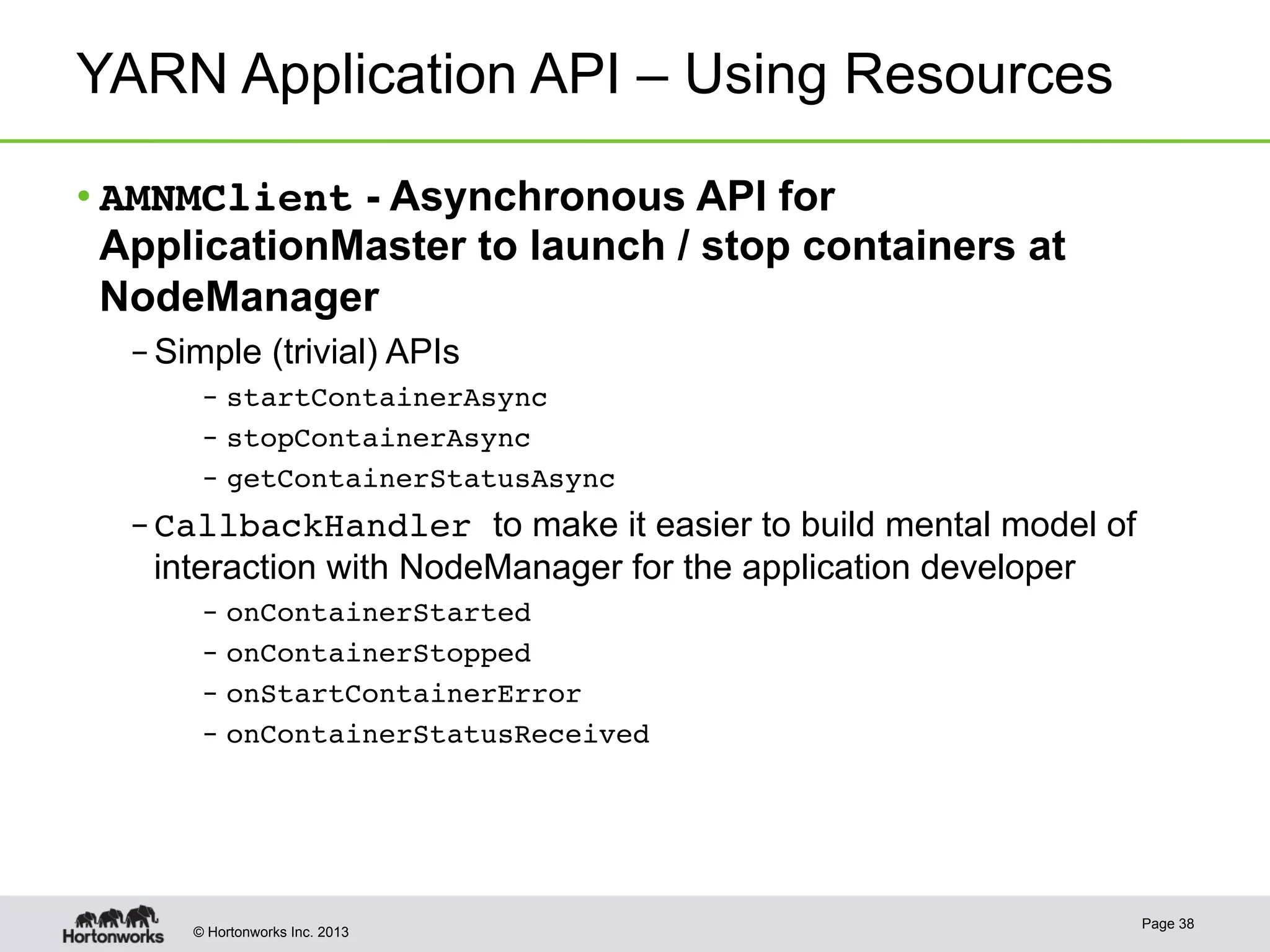
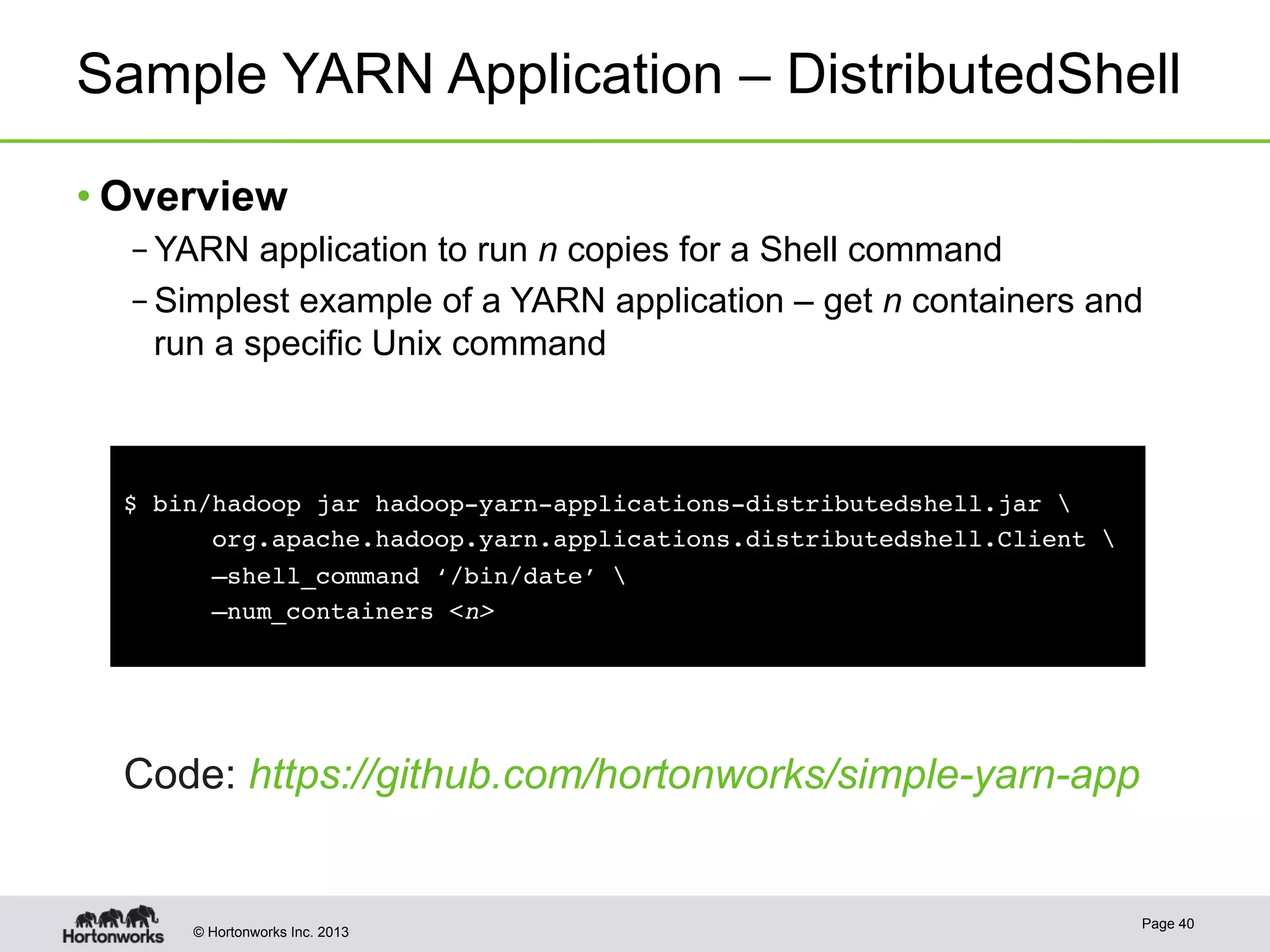
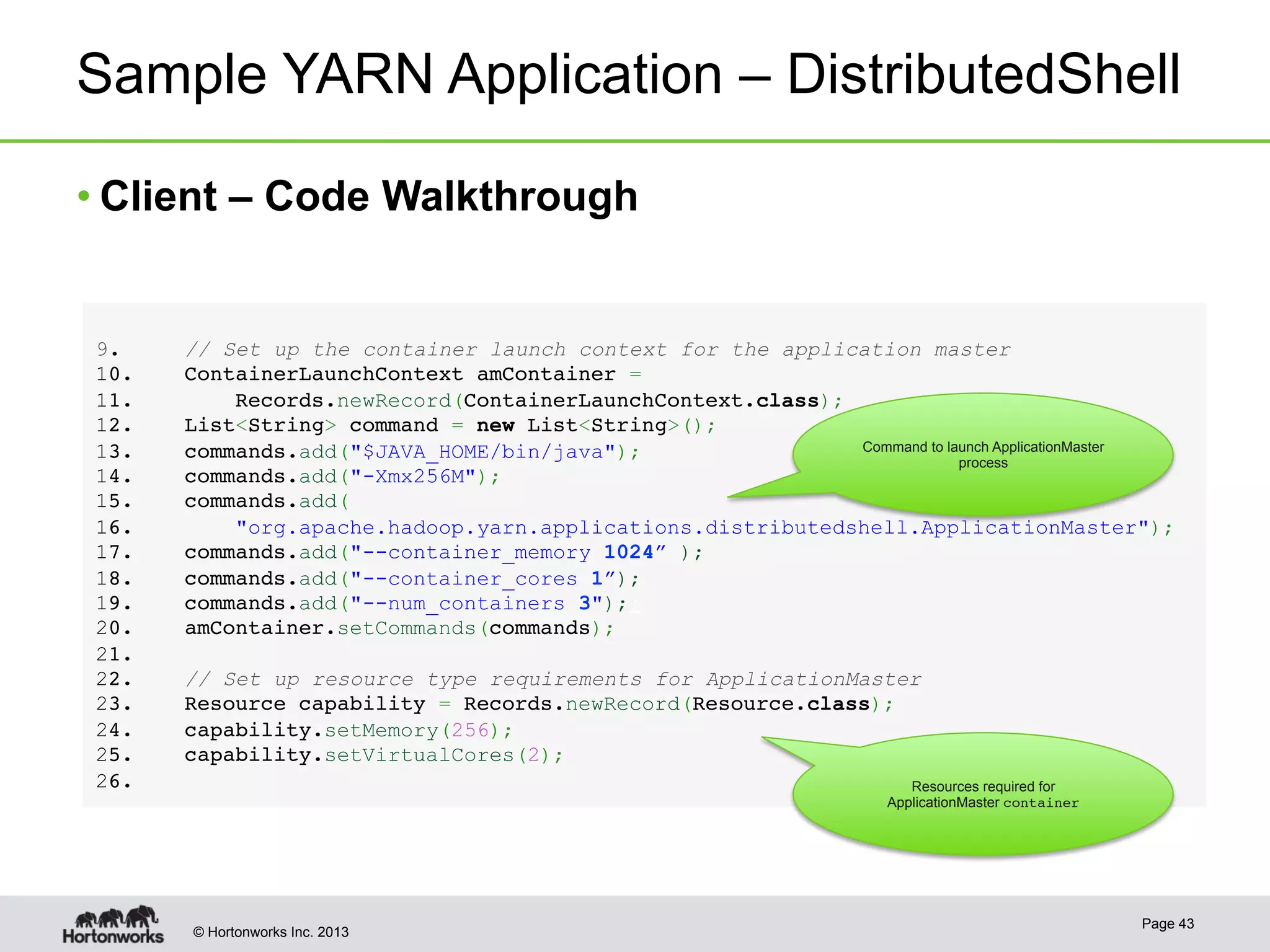
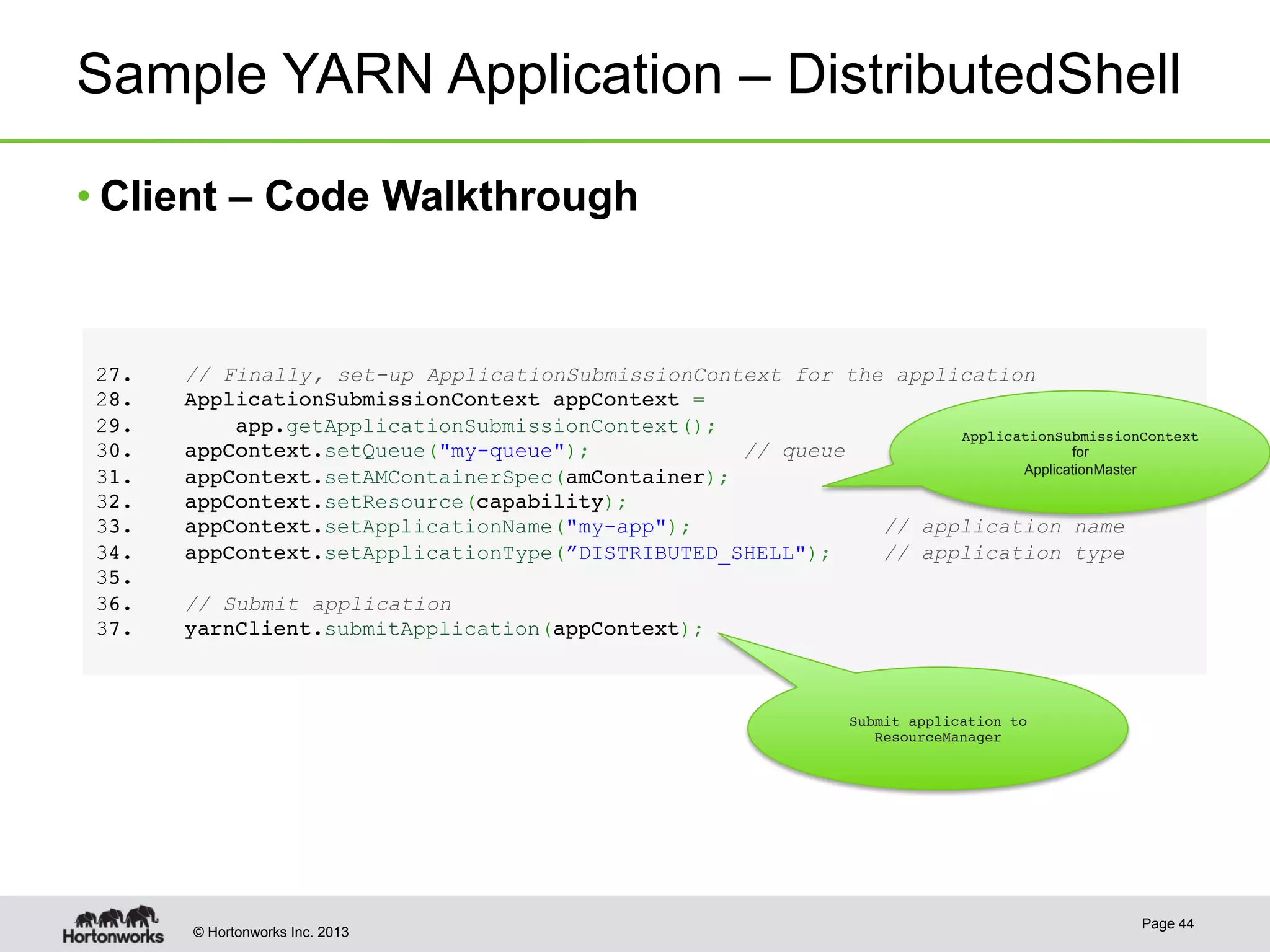
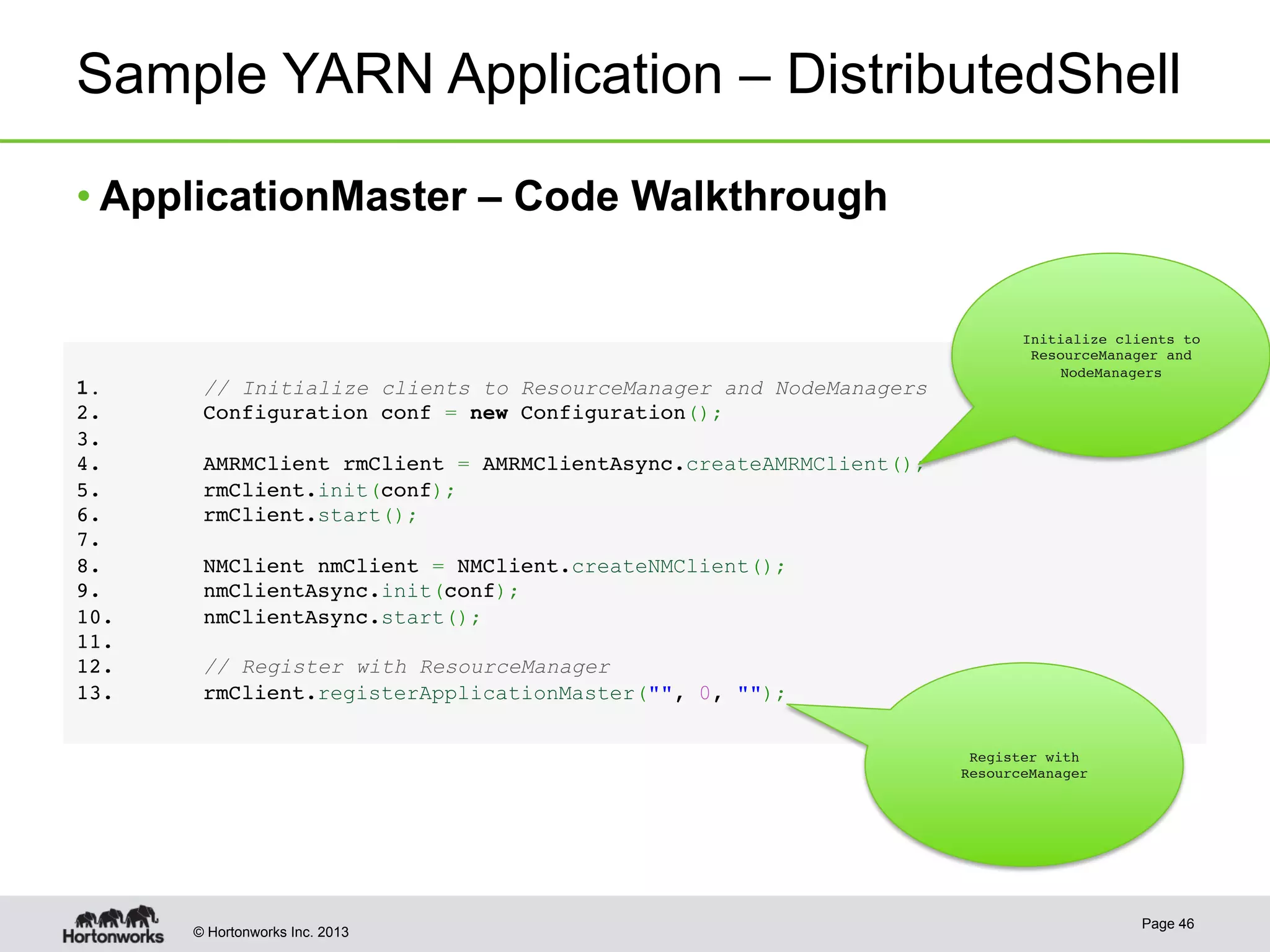
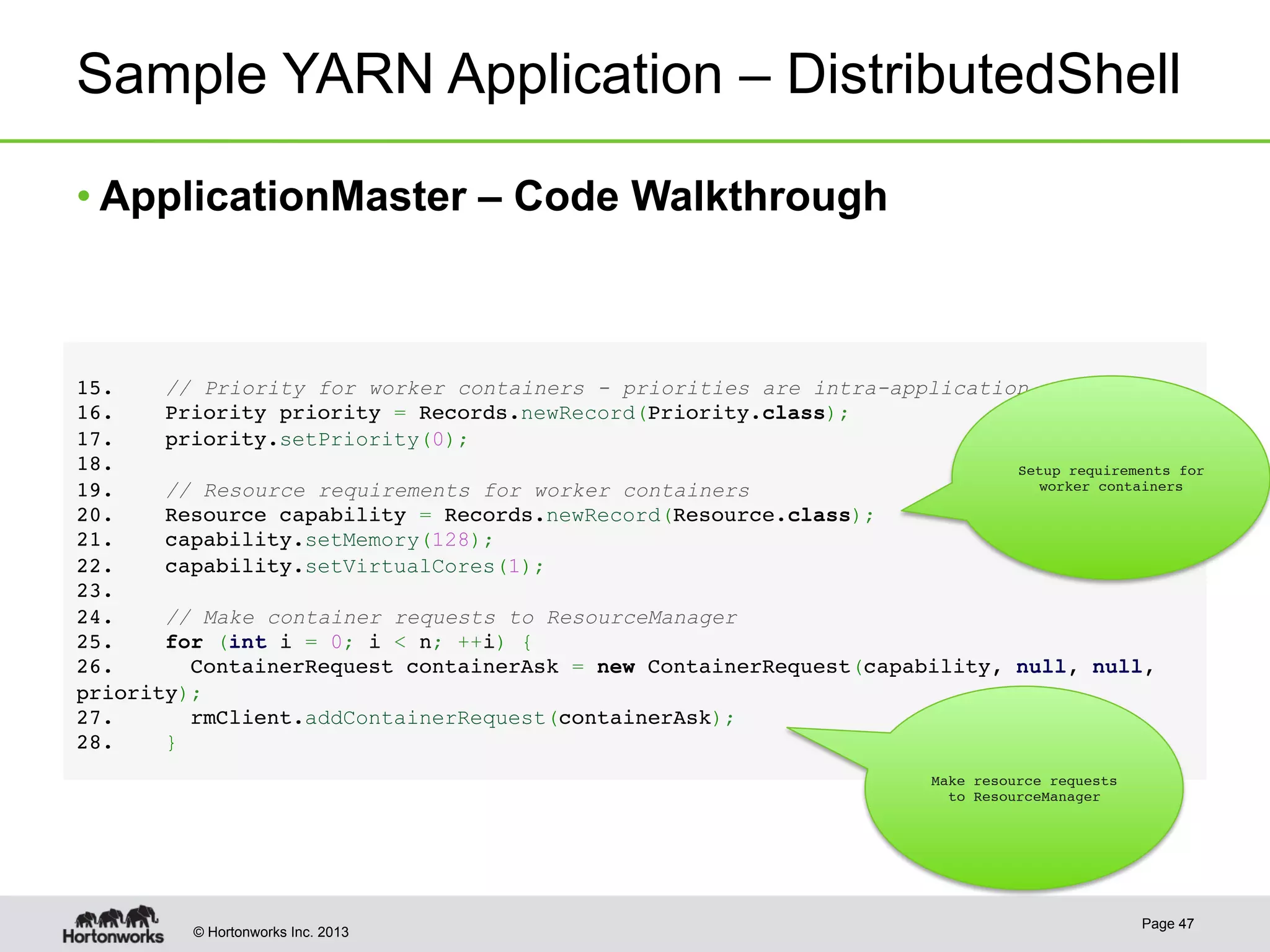
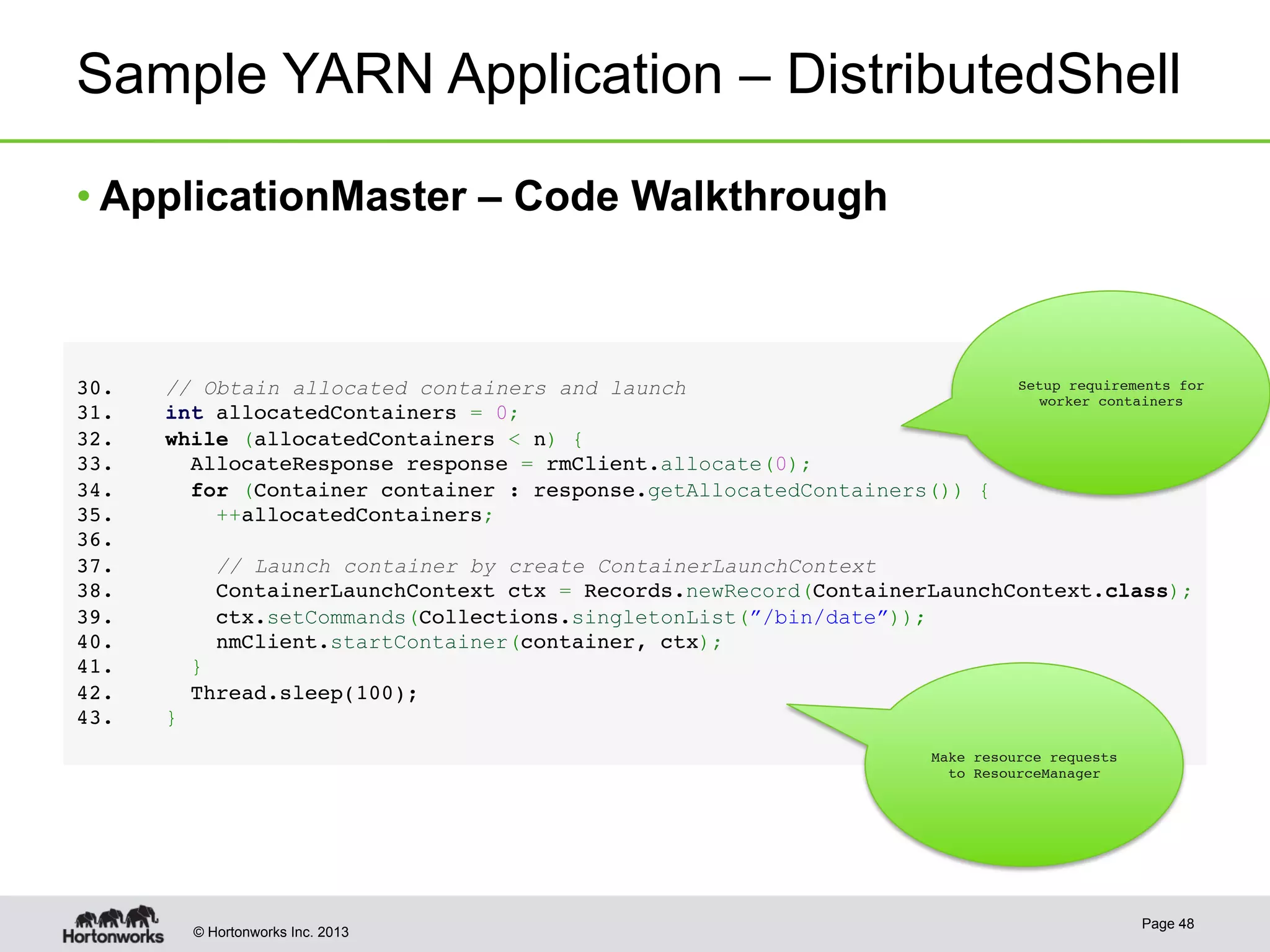
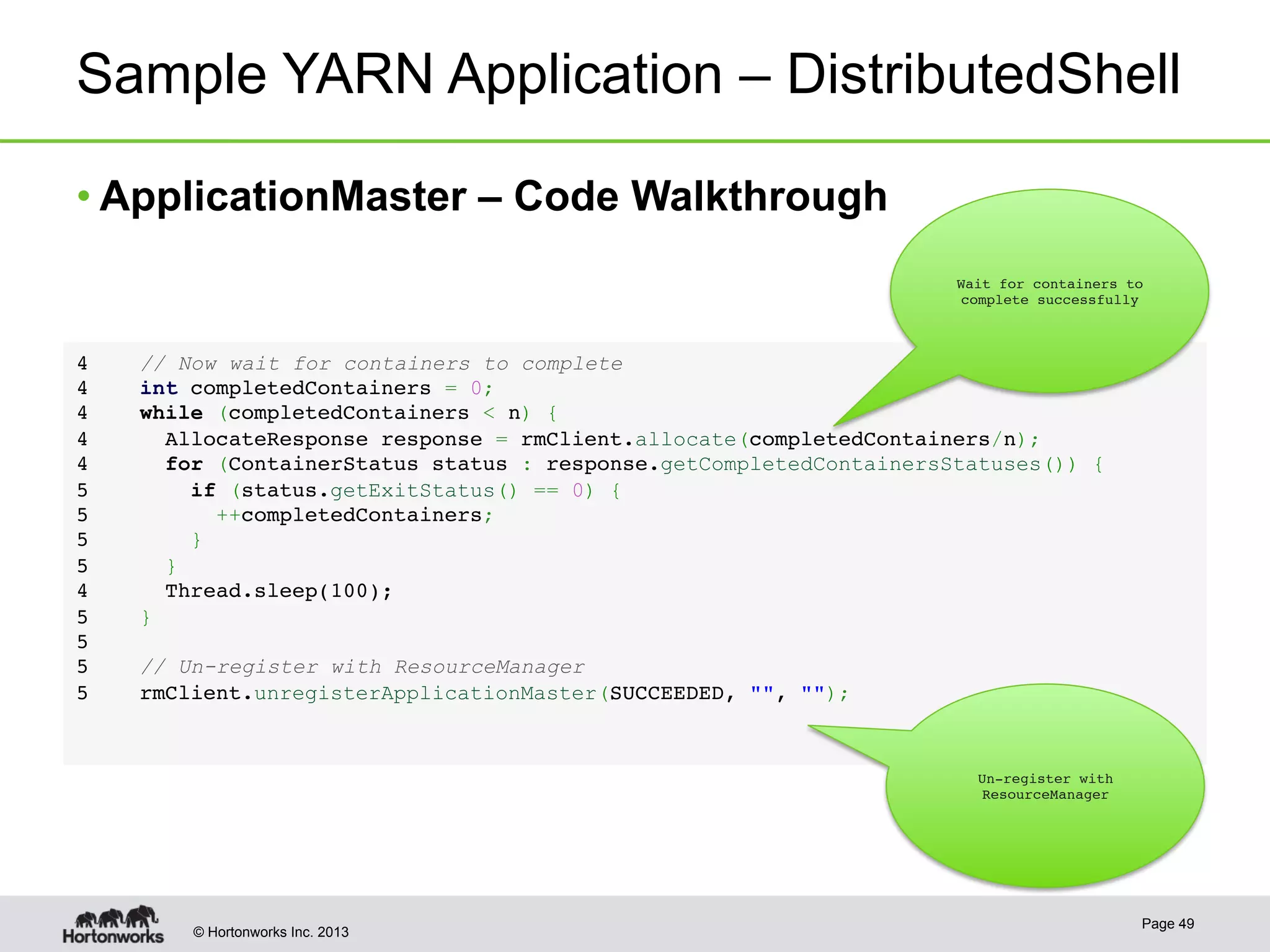
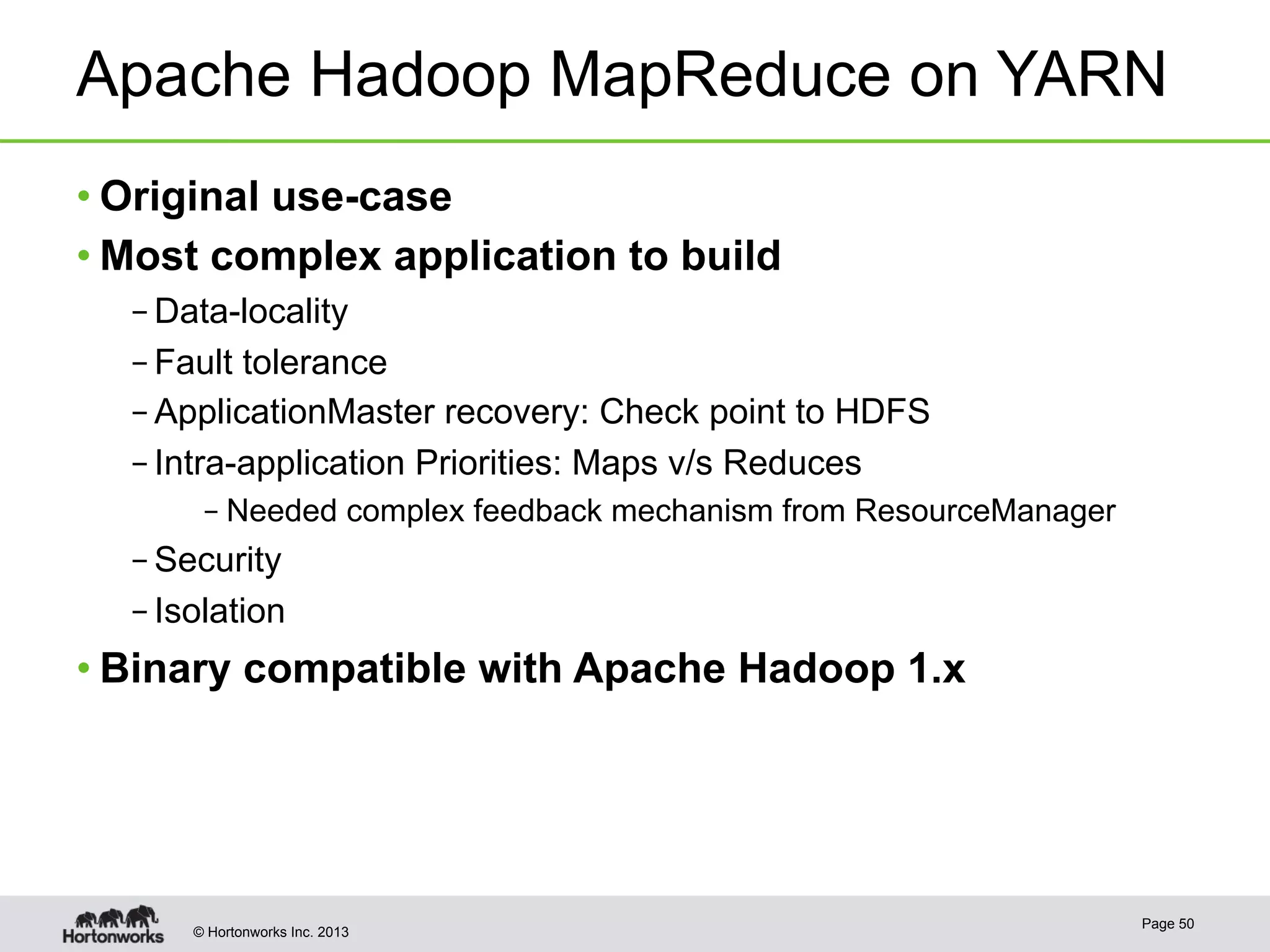
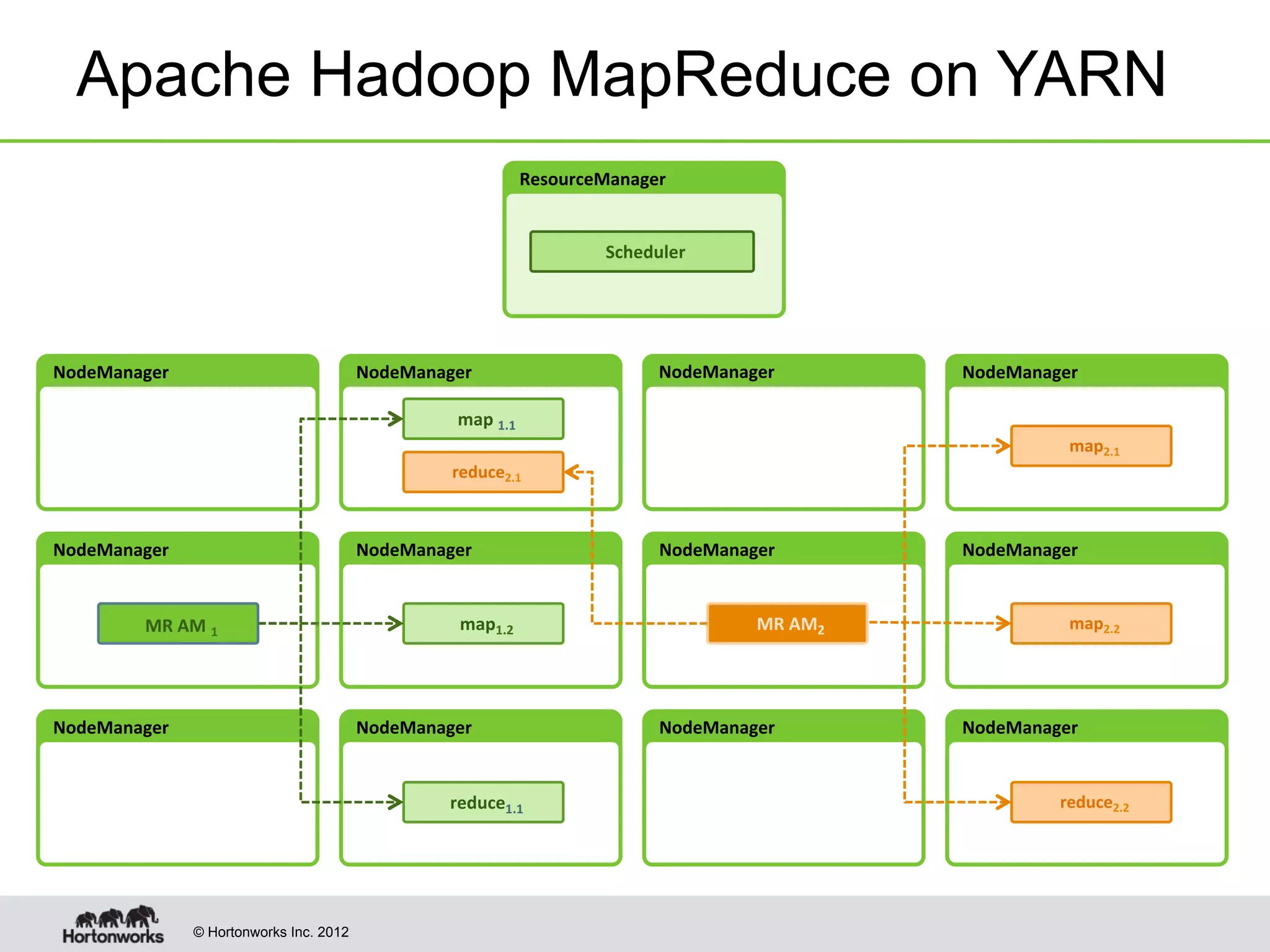
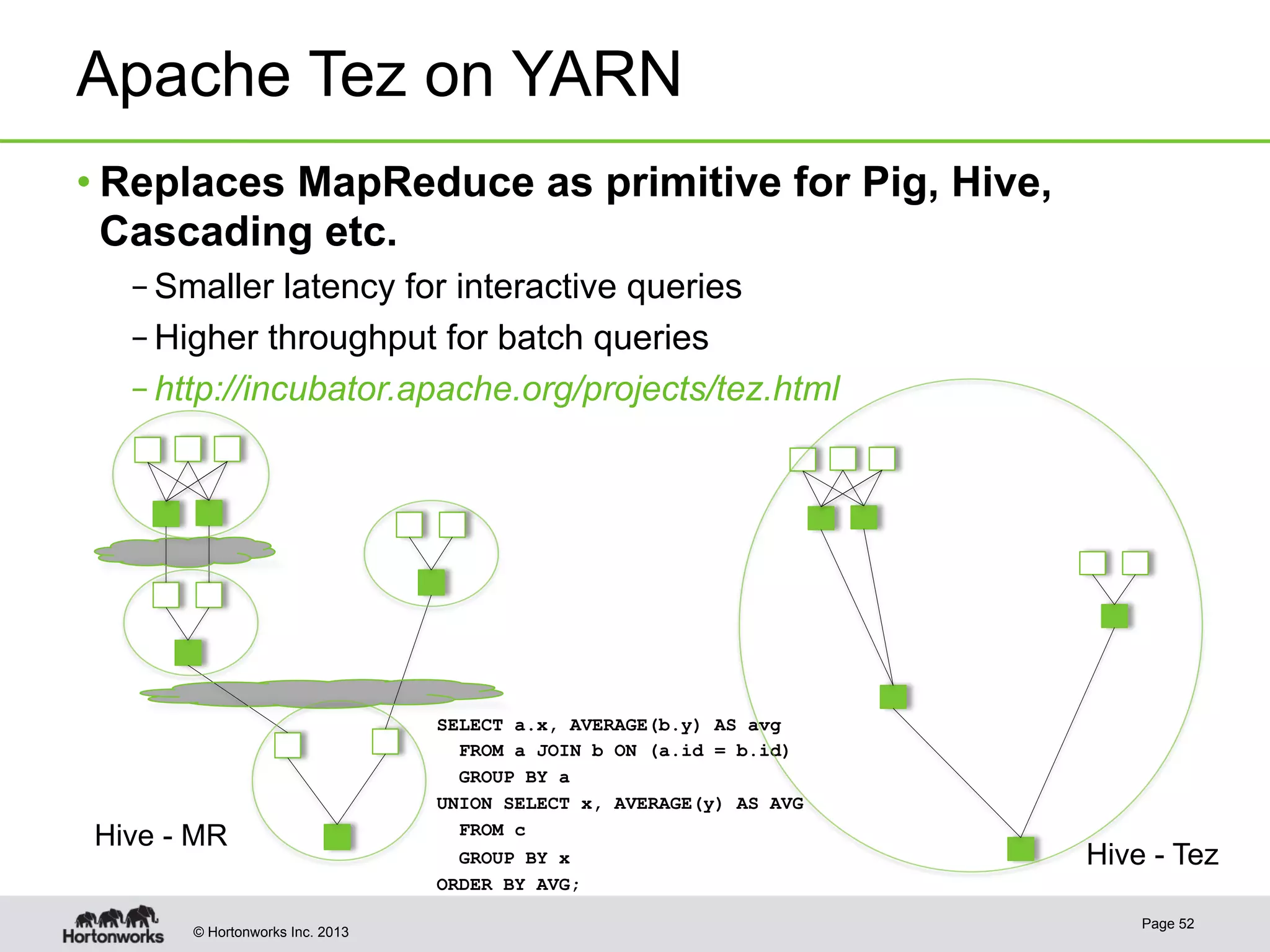
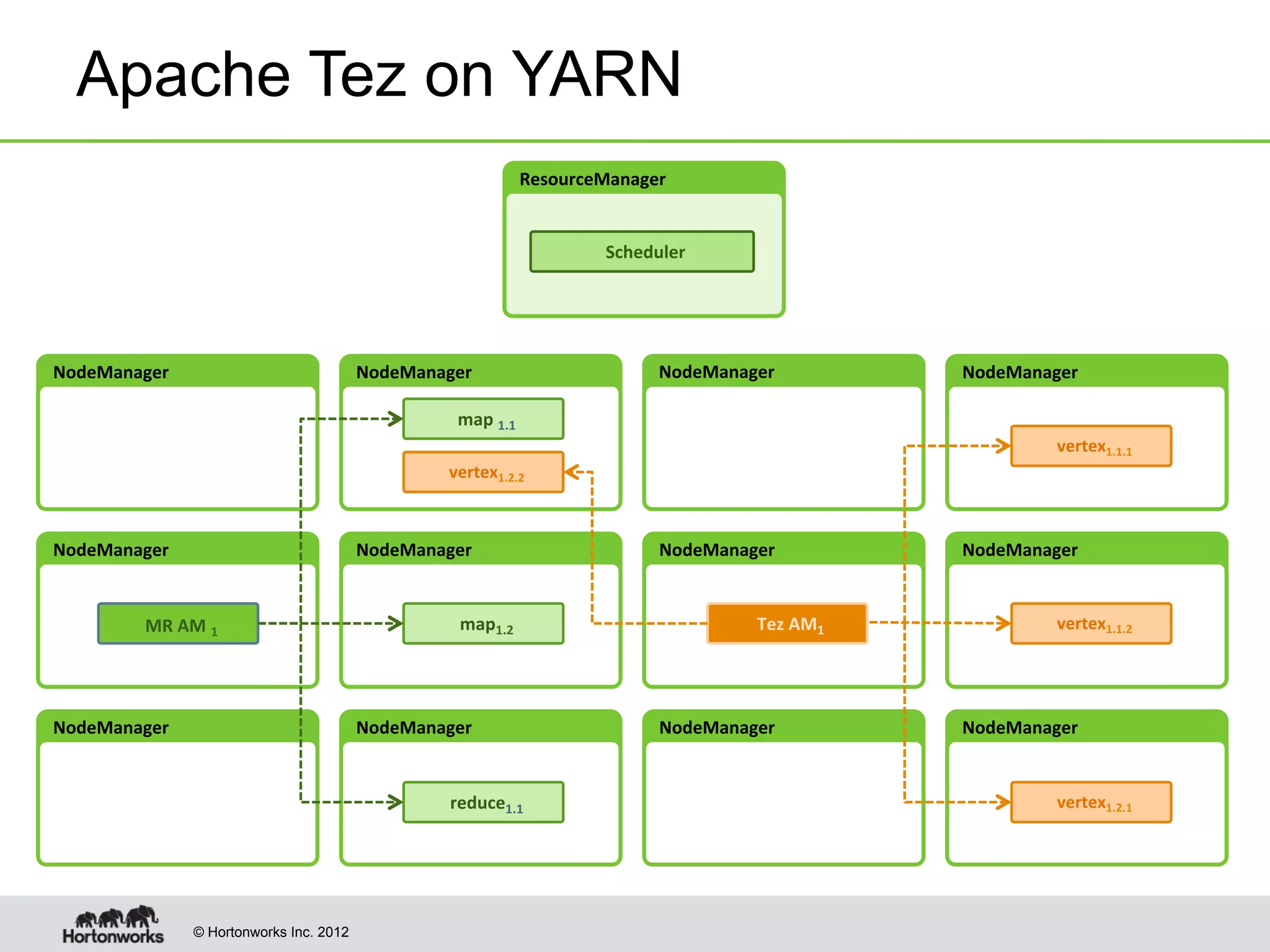
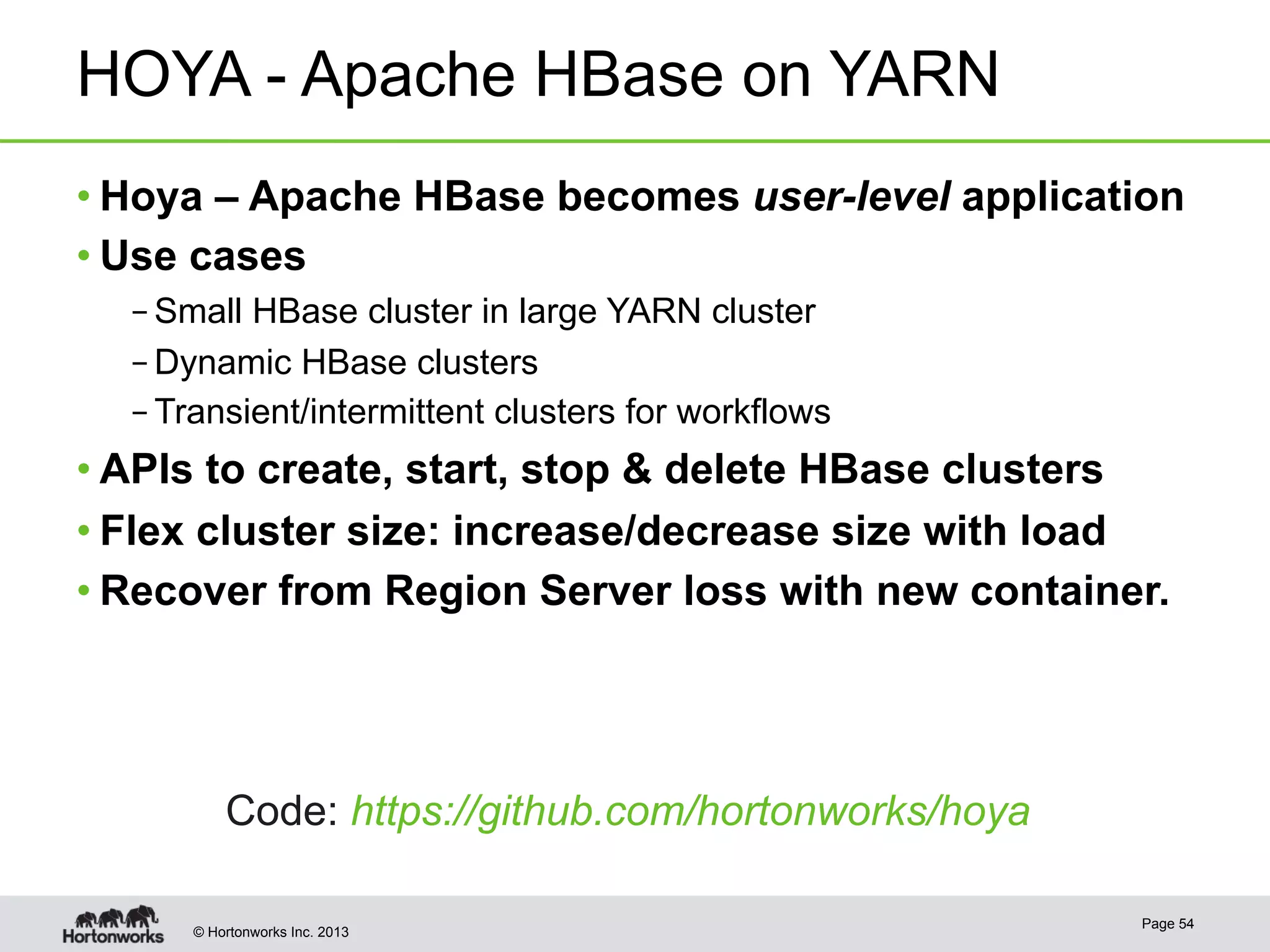
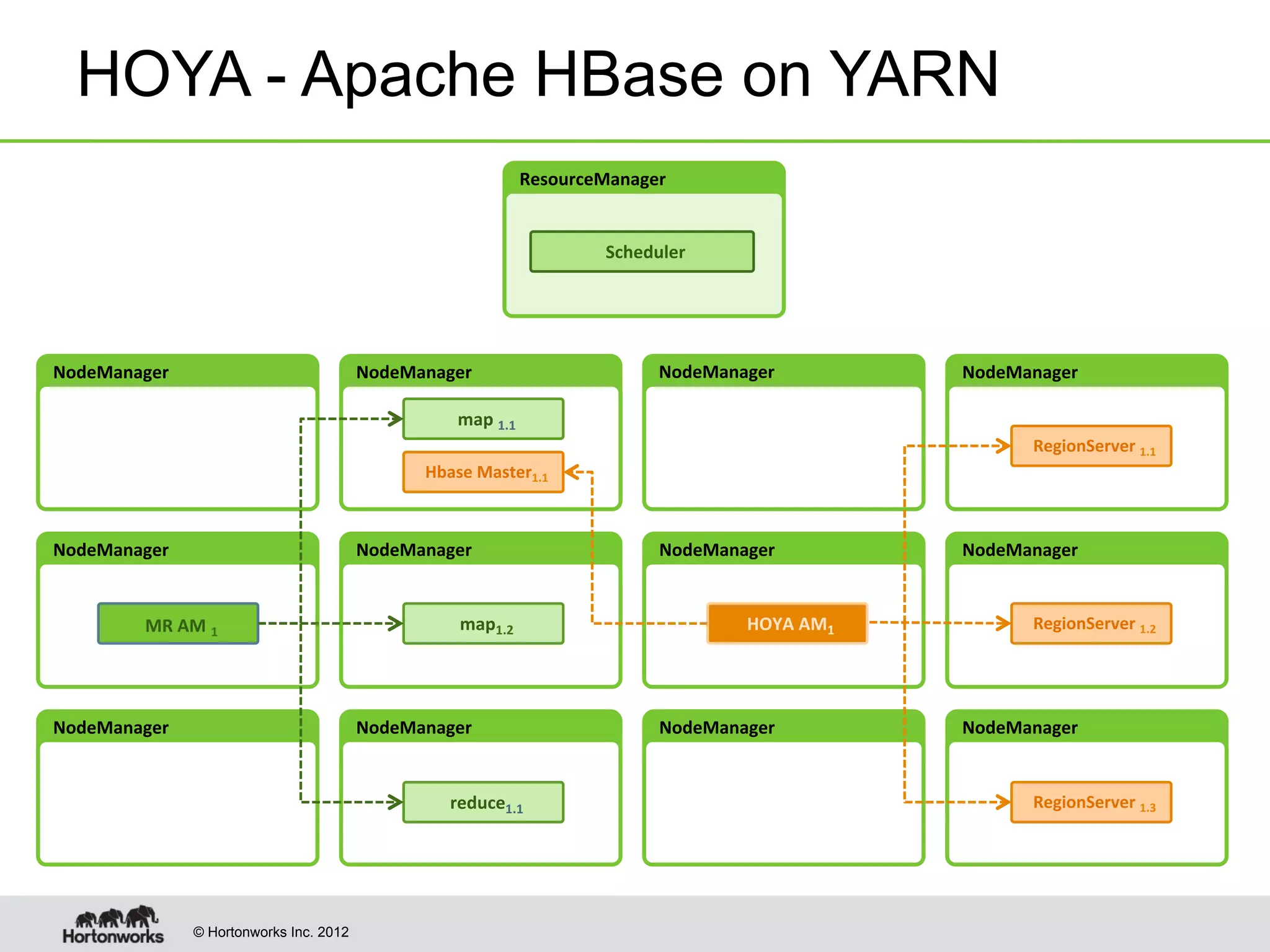
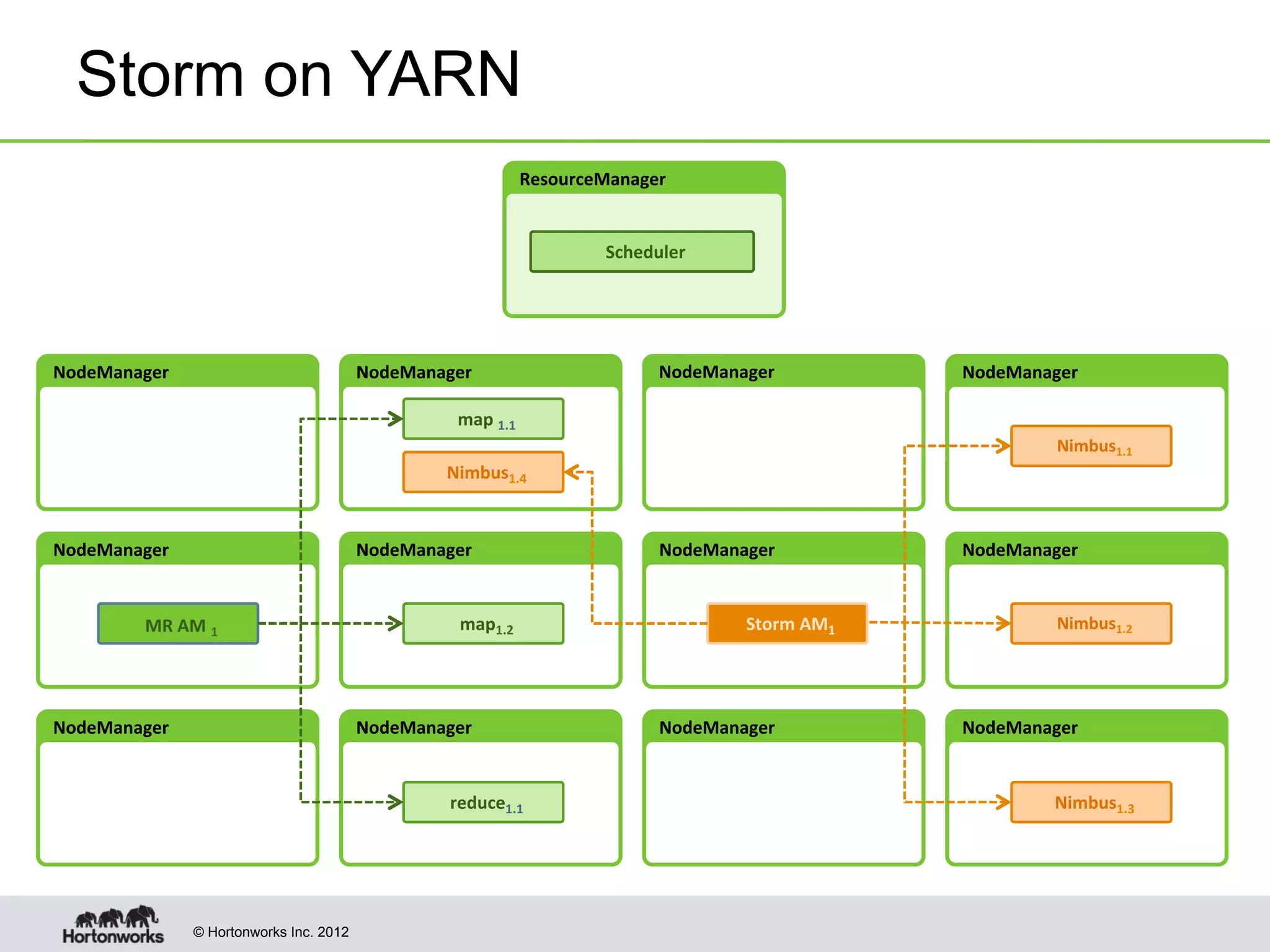
The document provides an overview of Apache Hadoop YARN, discussing its architecture and advantages over the original Hadoop 1.0 framework, which was limited to batch processing. YARN allows for more flexibility, scalability, and support for multiple application types, enabling better resource utilization and facilitating varied data processing paradigms. It covers key components, such as resource managers and application masters, and provides insights into building applications leveraging the YARN platform.