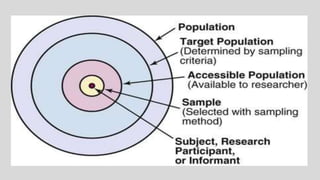
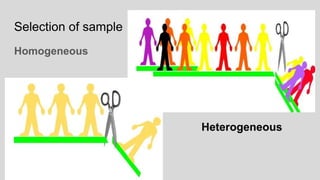
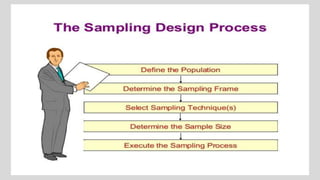
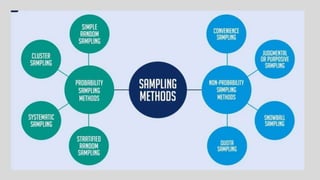
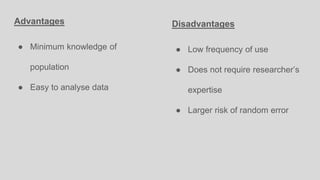
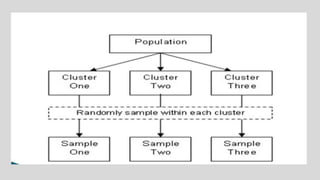
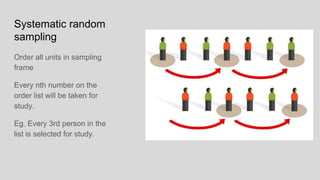
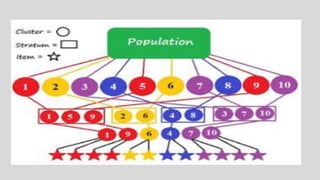
This document discusses different concepts related to sampling, including population, sample, sampling process, and probability sampling methods. It defines population as the total group being studied, while sample is a subset selected to represent the population. Probability sampling methods like simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, cluster sampling, and systematic random sampling are covered. These methods aim to select samples in a way that gives all population members an equal chance of being selected to avoid bias. The document provides details on how to implement each sampling technique.