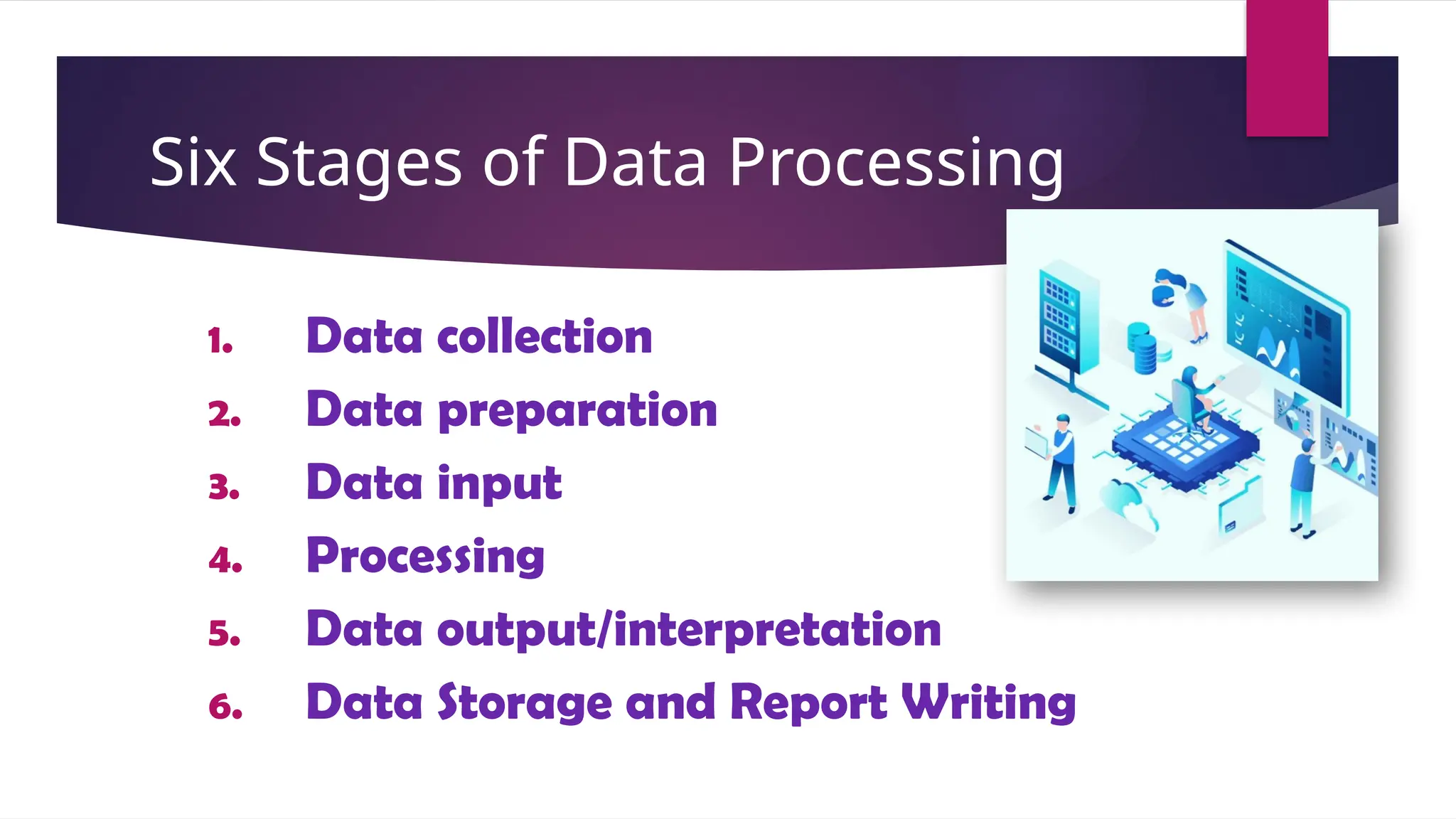
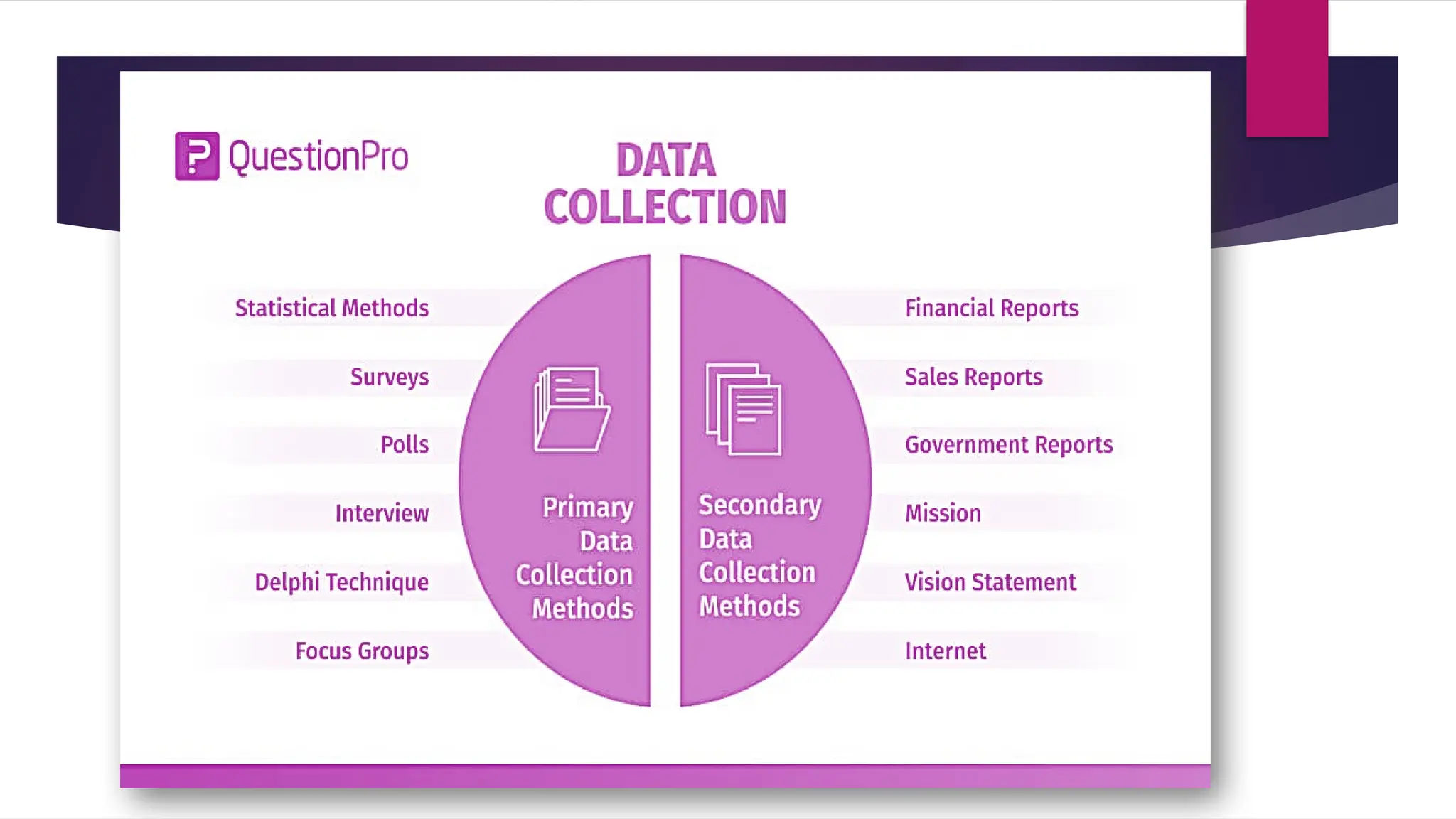
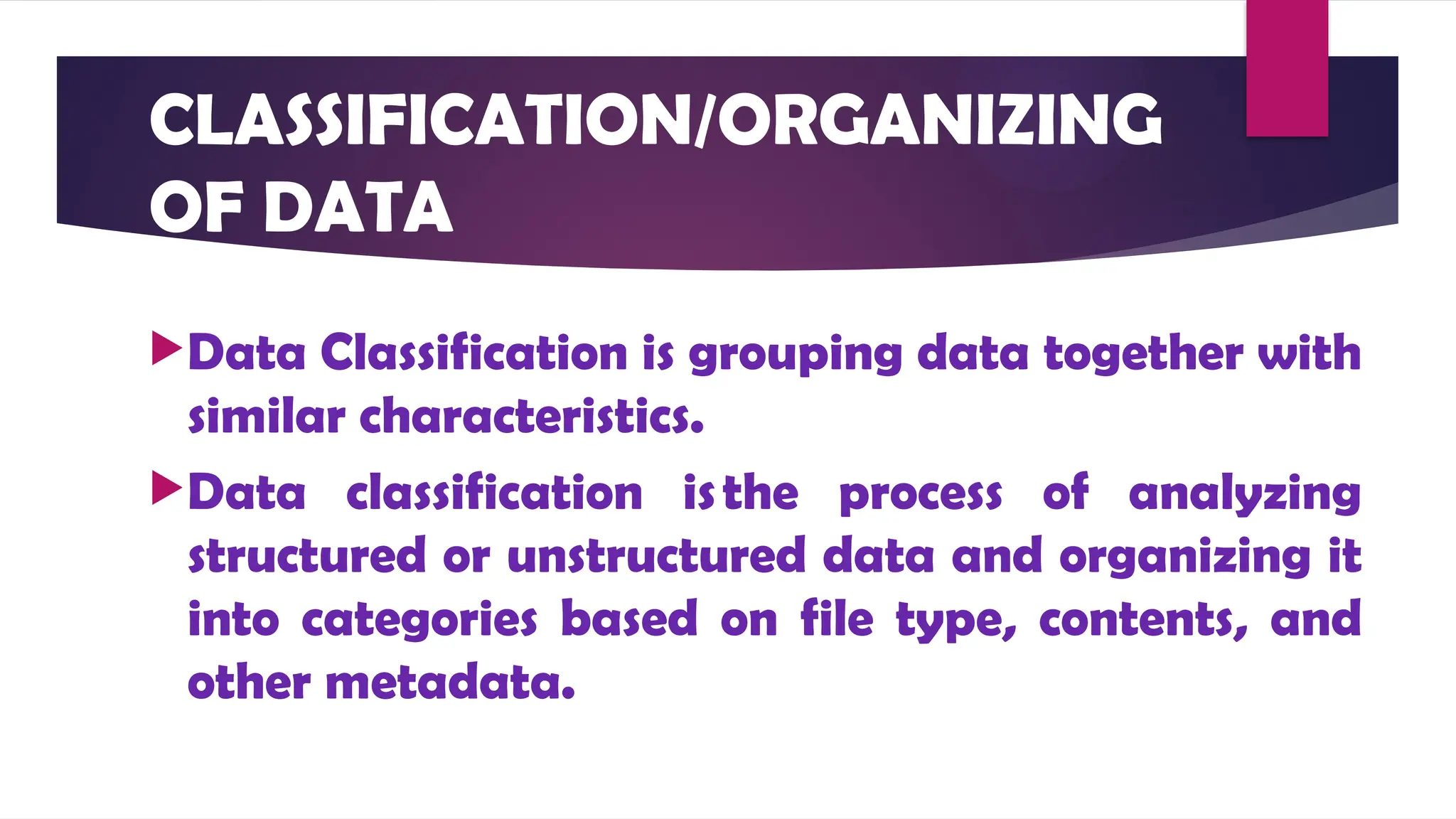
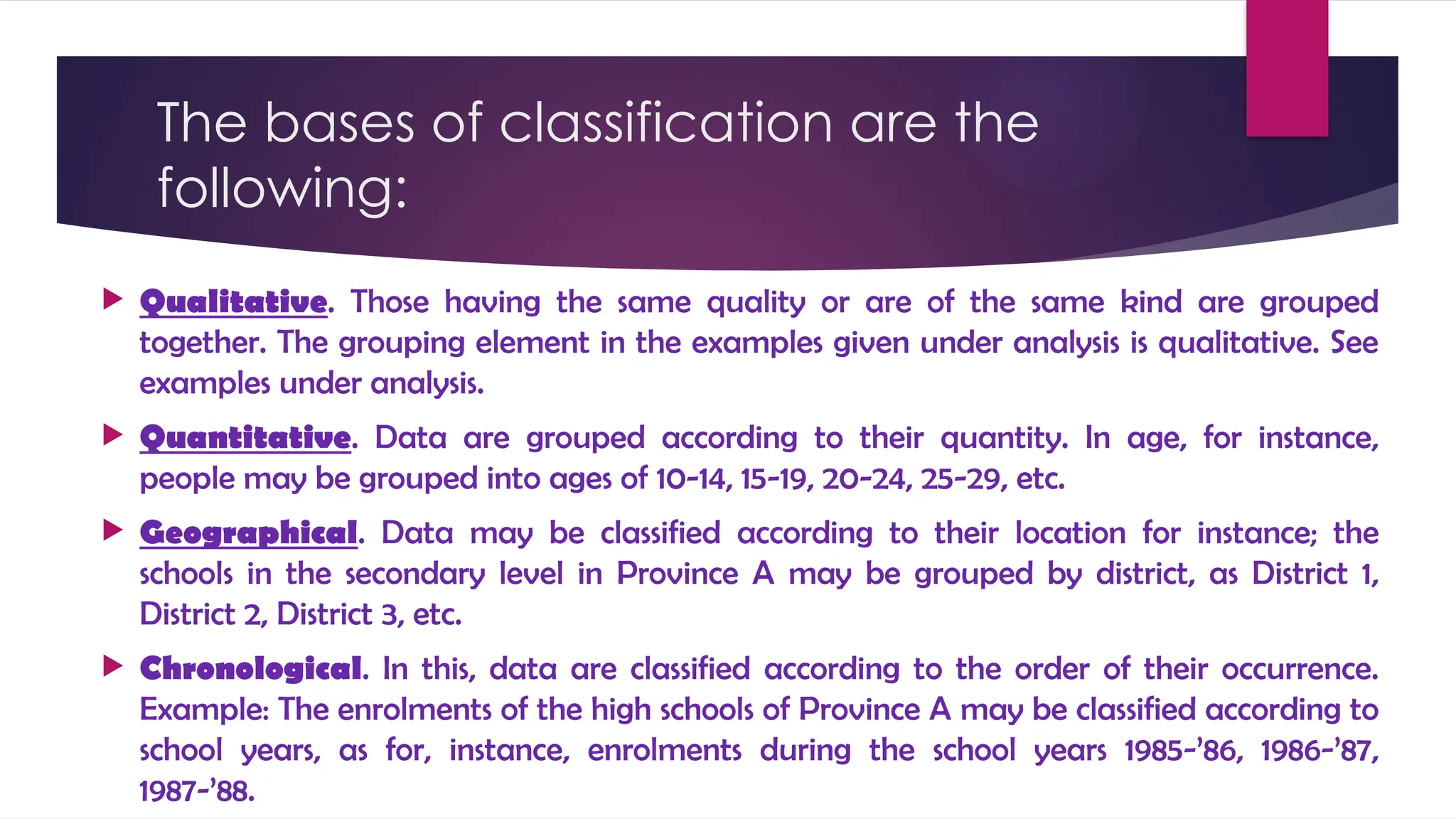
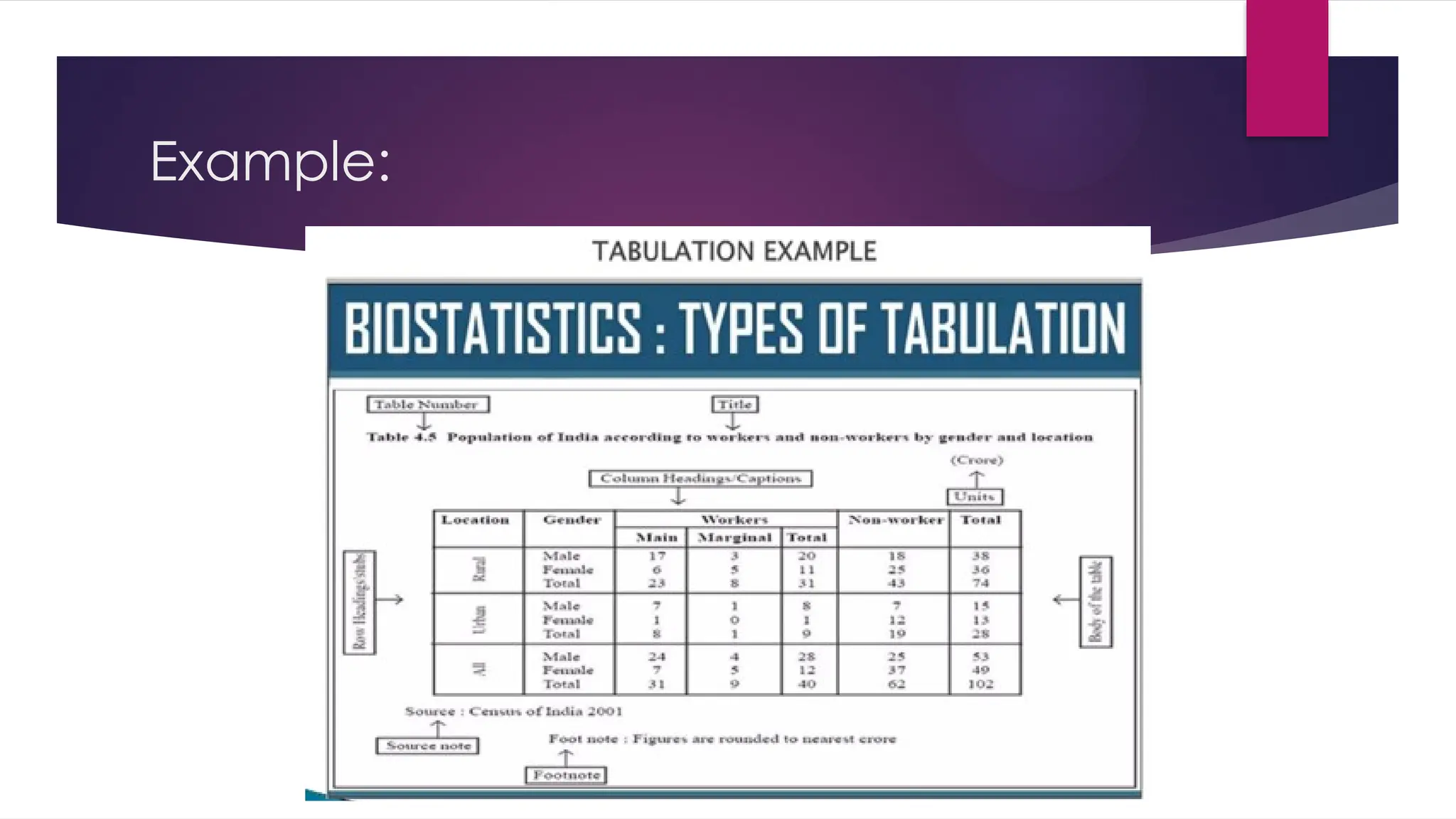
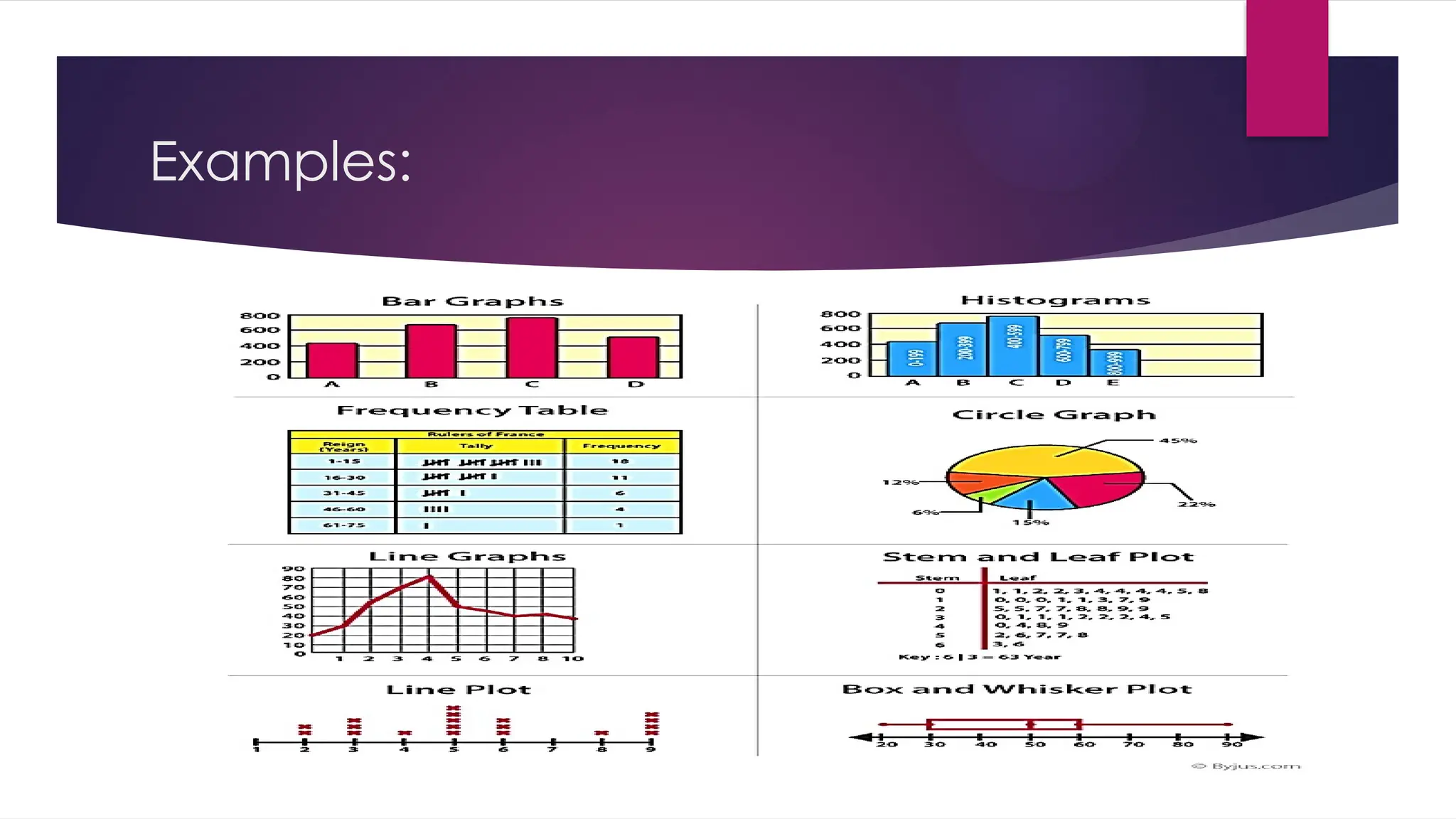
The document outlines the stages of data processing, which include data collection, preparation, input, processing, output, and storage. It details various methods of data collection, such as primary and secondary sources, and emphasizes the importance of editing, coding, classification, tabulation, and graphing in preparing data for analysis. Additionally, it highlights the necessity of organizing data to extract valuable insights for research purposes.